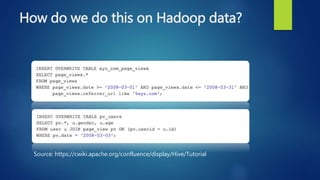
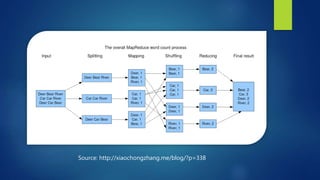
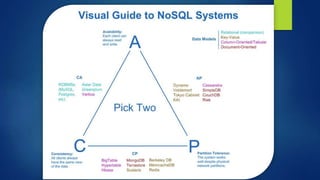
The document provides an overview of big data, including its definition, significance, and the role of technologies like Hadoop for batch processing of massive data sets. It discusses the challenges associated with traditional databases in handling size, speed, and scale, introducing NoSQL solutions and concepts such as the C.A.P. theorem. Additionally, it touches on real-time data processing frameworks like Apache Storm and Spark, highlighting their capabilities and use cases.