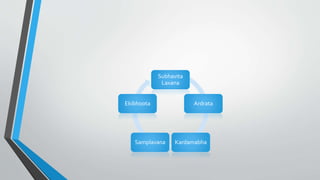
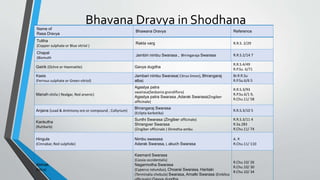
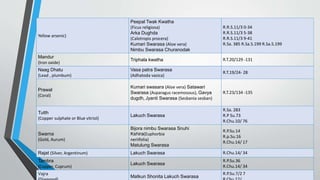
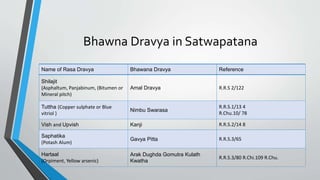
The seminar by Dr. Bankimchandra S discusses the concept of 'samskara' in Ayurveda, emphasizing 'bhavana' as a critical process for enhancing the potency of drugs through a method of wet grinding and mixing with specific liquids. Bhavana involves multiple steps that alter the physical and chemical properties of the drug, improving its absorption and therapeutic efficacy while removing impurities and reducing toxicity. The document outlines various preparations, their corresponding liquid media, and the significant role of bhavana in Ayurvedic medicine manufacturing.





![Quantity of media in Bhavana
• The quantity of Kasaya Dravya must be equal to the quantity of the is added
in the Kwatha prepration. Here the heat produced during grinding and the
atmospheric heat helps in drying the materials quickly. By applying
Bhawana the drugs are rendered fine and potentiated.[3]
• If Kwatha is employed for Bhawana process it should always be Astamamsa
- Asasesita Kashaya (reduced to 1/8th part)[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-190121070023/85/BHAVANA-SAMSKARA-6-320.jpg)