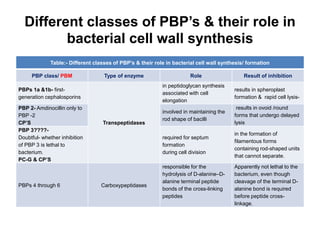
β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. There are several classes of β-lactam antibiotics including penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems. Penicillins are derived from Penicillium fungi and contain a thiazolidine ring fused to the β-lactam ring. Cephalosporins are derived from the fungus Cephalosporium and contain a dihydrothiazine ring fused to the β-lactam ring. Both penicillins and cephalosporins target bacterial transpeptidases to inhibit cell wall crosslinking. Structural modifications to these classes of β-lactams can












![Comparison of β- lactam antibiotics
4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptanes 5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene
6-carbonylaminopenicillanic acid
(6-APA)
7-acylaminocephalosporanic acid
(7-ACA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antibiotics31jan2021-220411044956/85/Beta-lactam-Antibiotics-ppt-14-320.jpg)

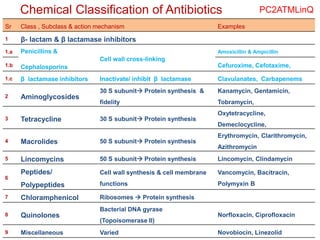
![•The Chemical Abstracts system initiates the numbering with the sulfur atom and
assigns the ring nitrogen the 4-position.
•Thus, penicillins are named as 4-thia-l-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptanes,
•The numbering system adopted by the USP is number 1 to the nitrogen atom and
number 4 to the sulfur atom.
•The penicillin molecule contains three chiral carbon atoms (C-3, C-5, and C-6).
•The carbon atom bearing the acylamino group (C-6) has the L configuration,
whereas the carbon to which the carboxyl group is attached has the D configuration.
Thus, the acylamino and carboxyl groups are trans to each other,
•The absolute stereochemistry of the penicillins is designated as 3S:5R:6R,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antibiotics31jan2021-220411044956/85/Beta-lactam-Antibiotics-ppt-16-320.jpg)