Embed presentation
Download to read offline


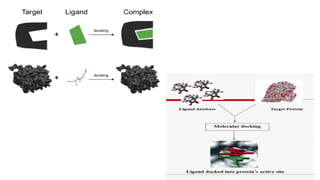



The document provides an overview of molecular docking, which simulates the interaction between a candidate ligand and a receptor to predict binding modes and affinities. It discusses various docking methods, including flexible and rigid docking, and highlights the physical forces that drive ligand-receptor binding. Additionally, it mentions different computational approaches used in docking, such as shape-based methods, Monte Carlo simulations, and genetic algorithms.





