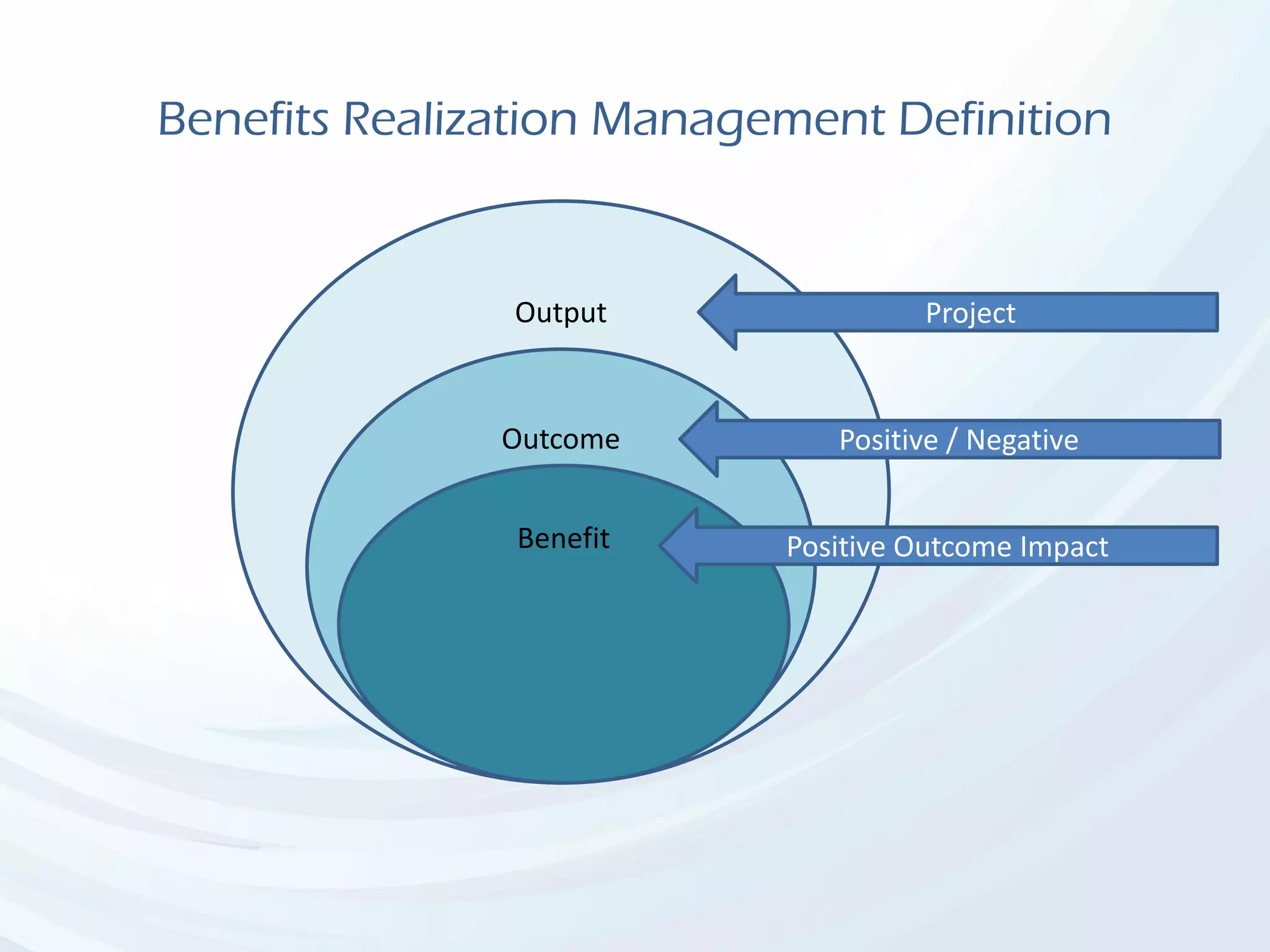
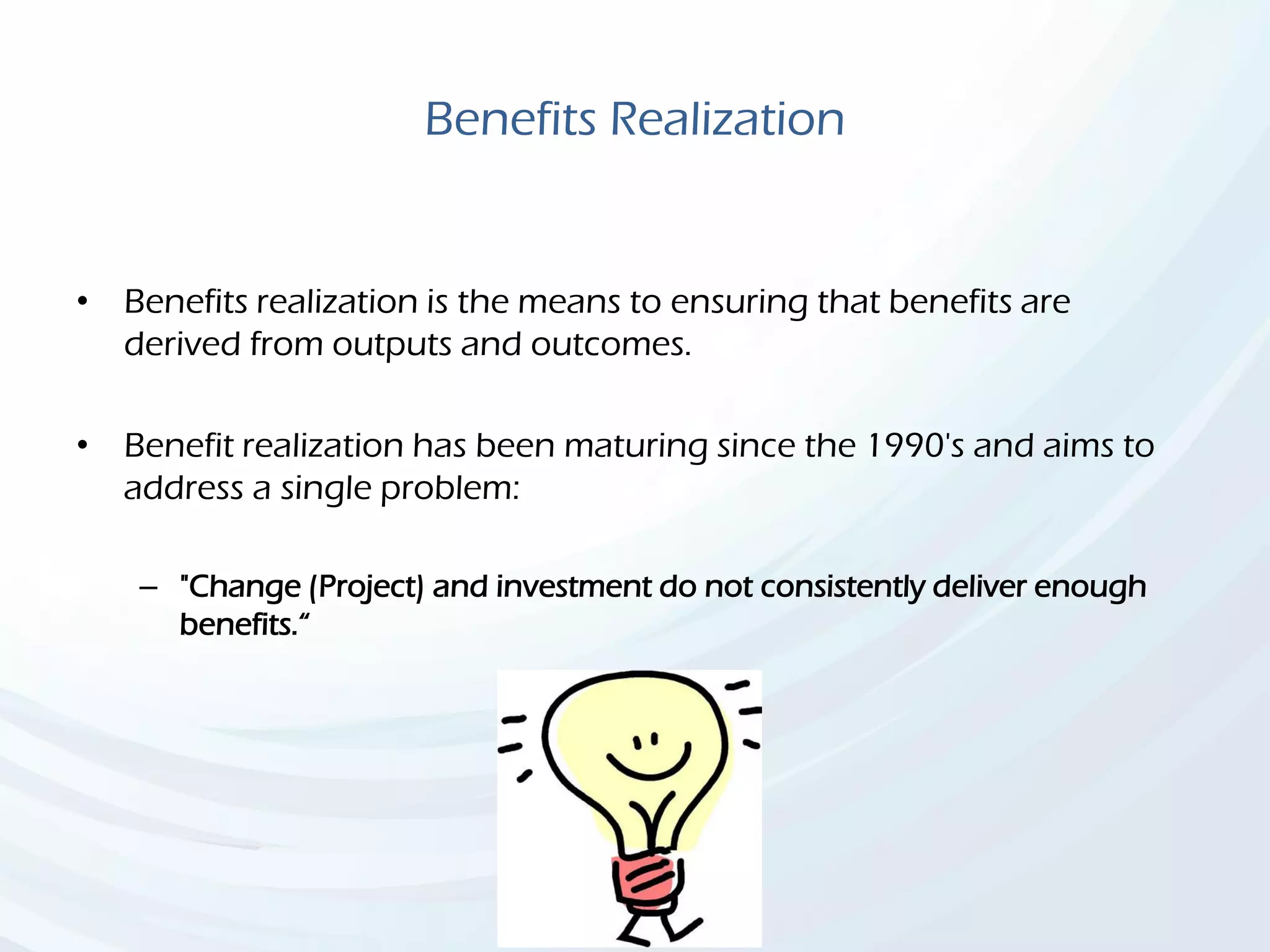
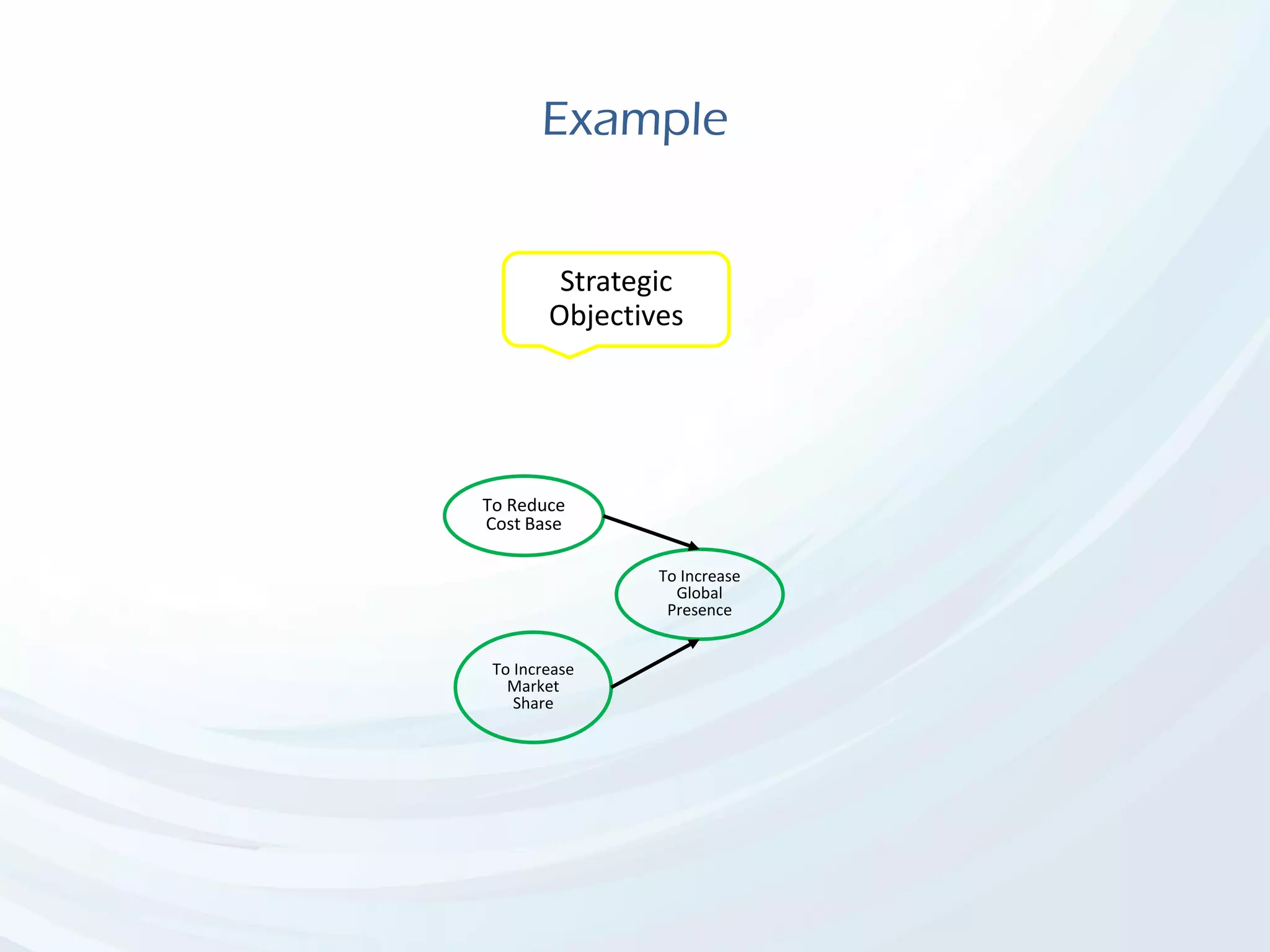
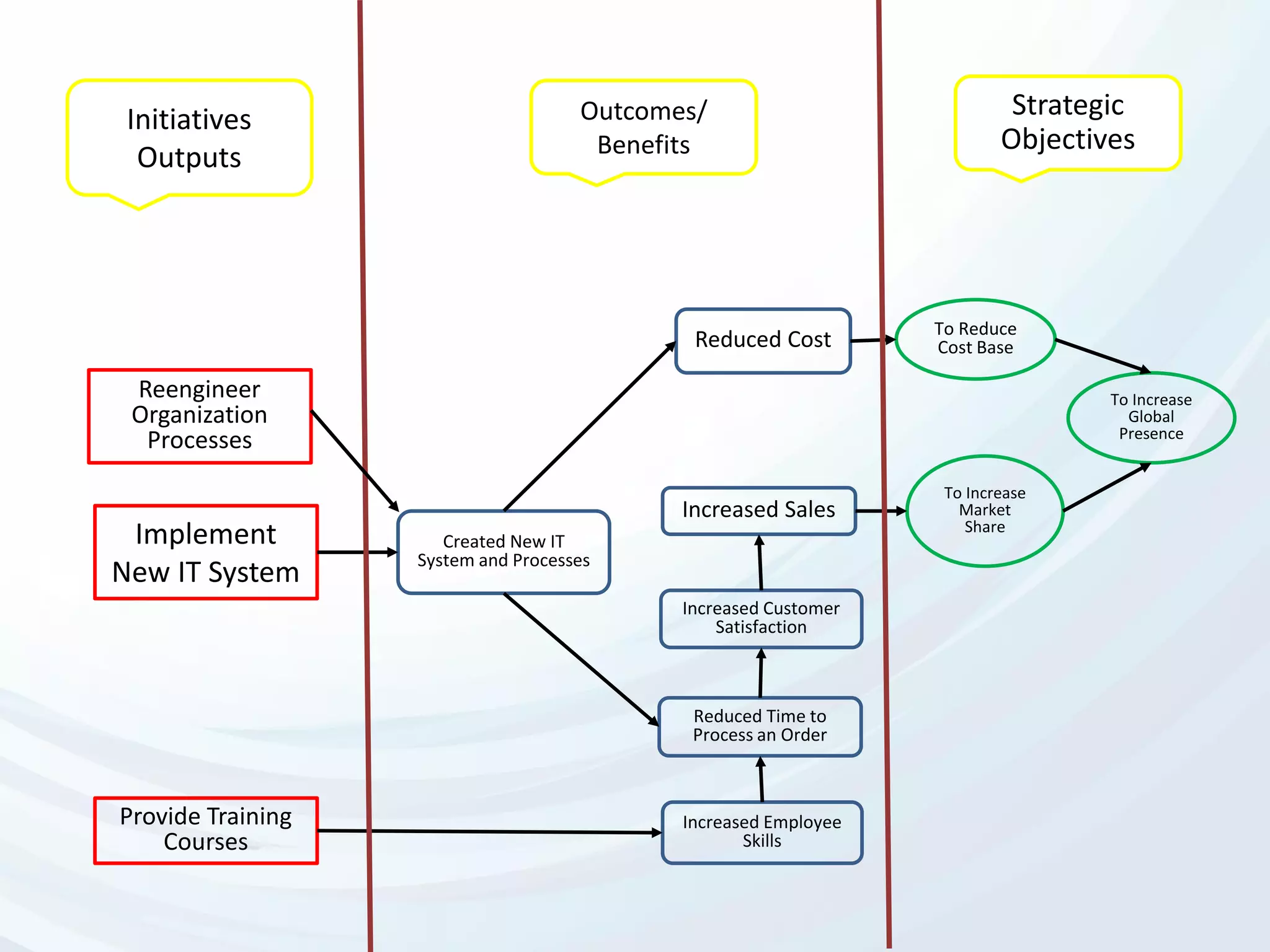
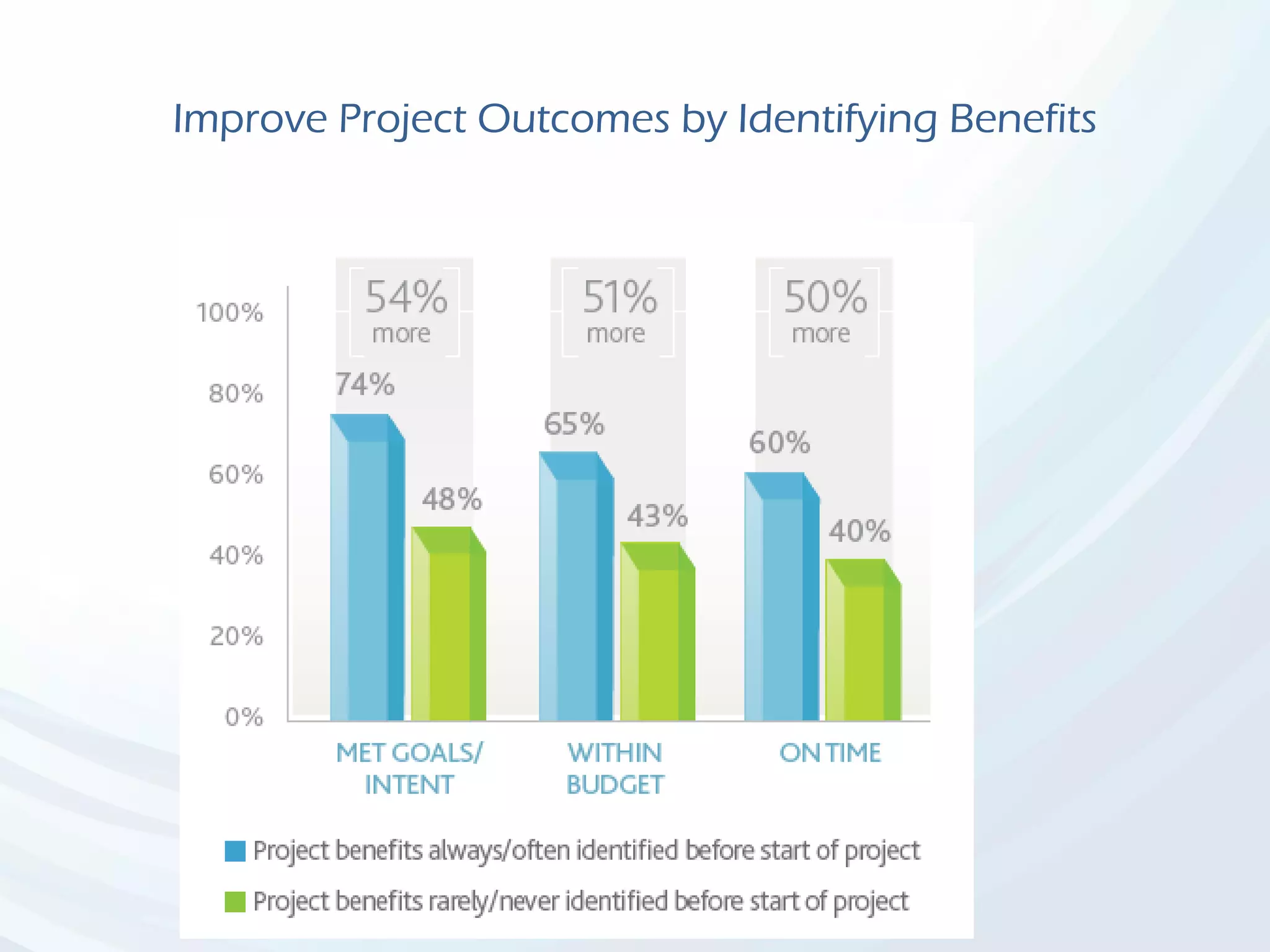
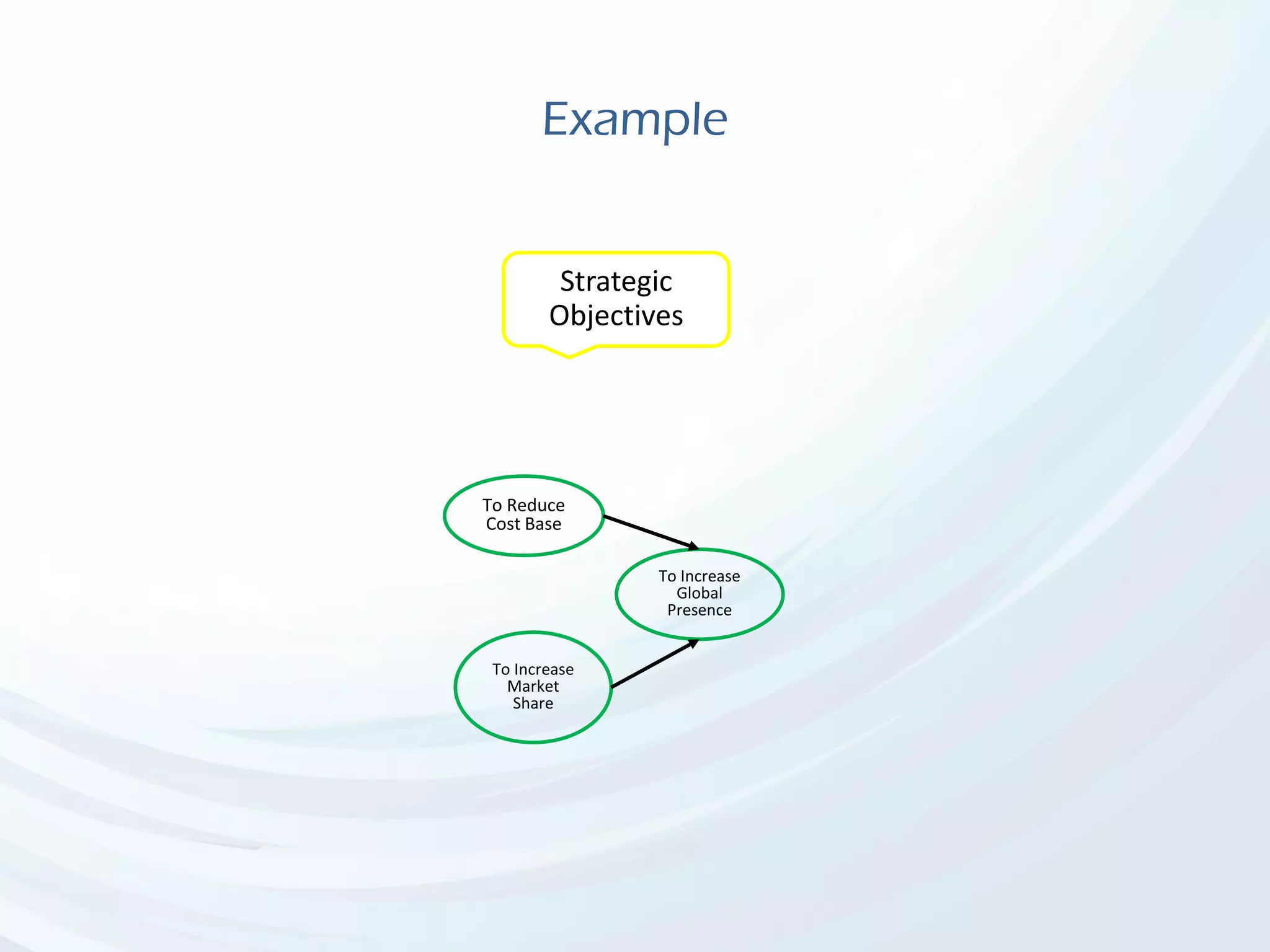
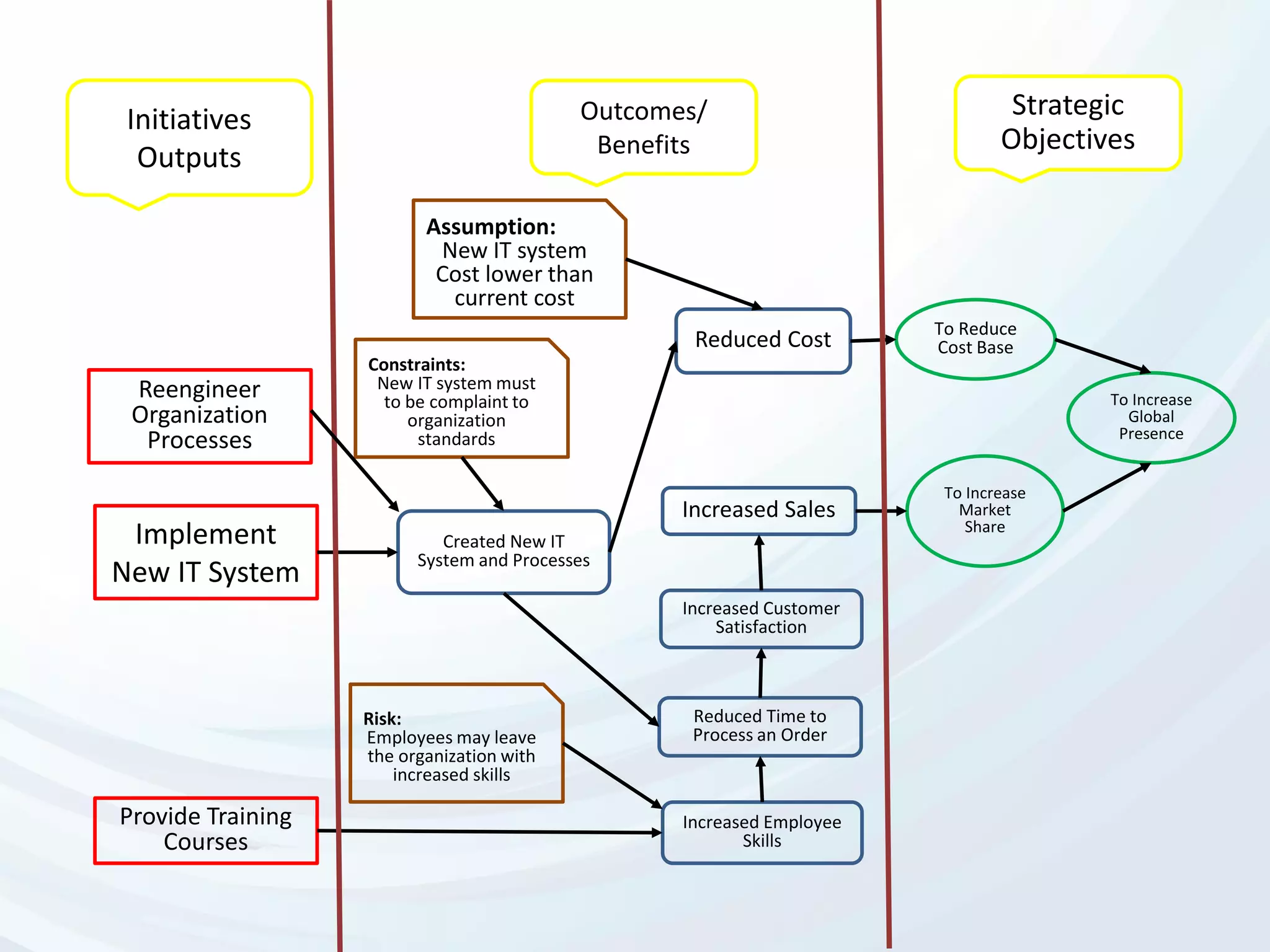
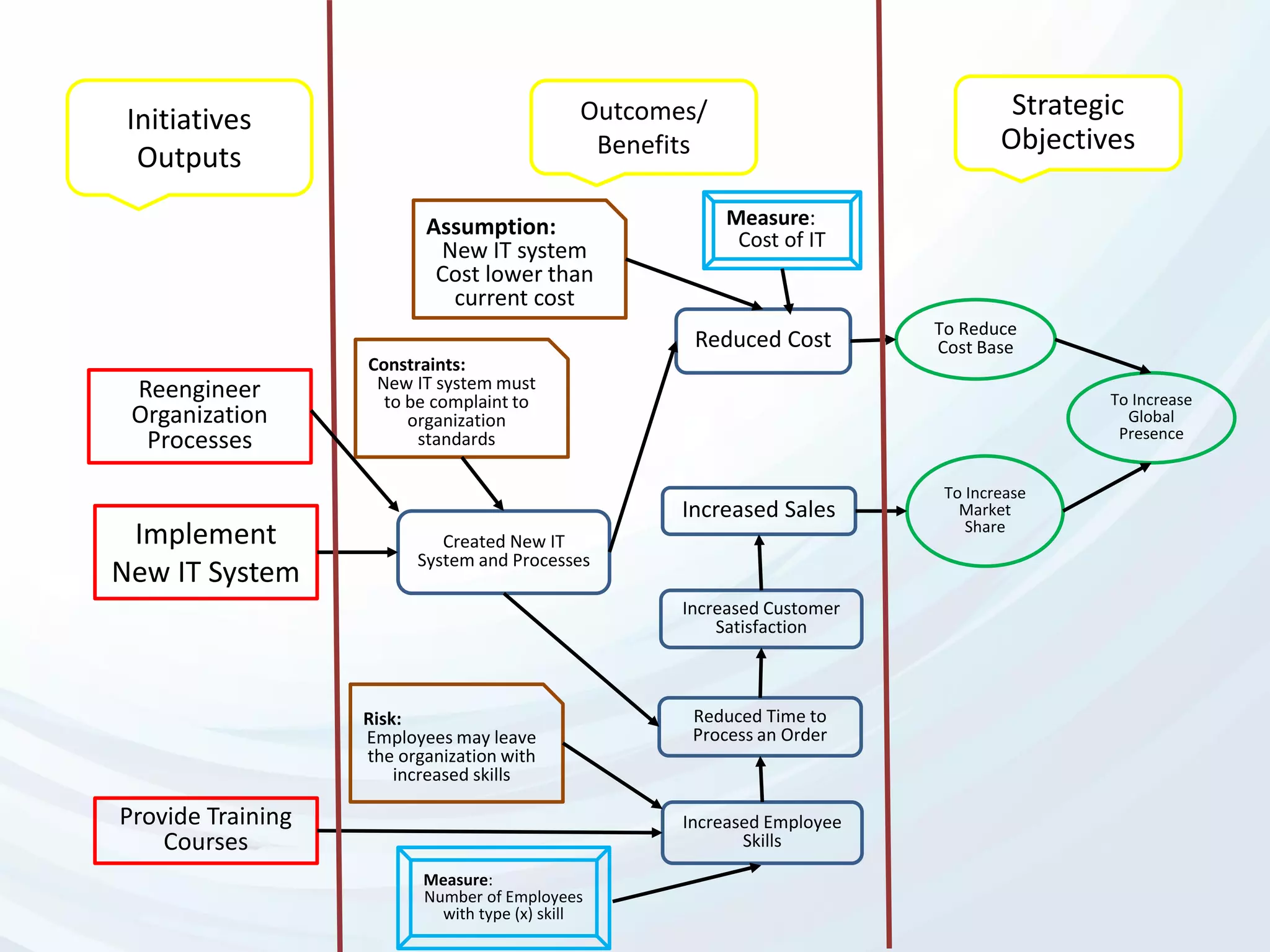
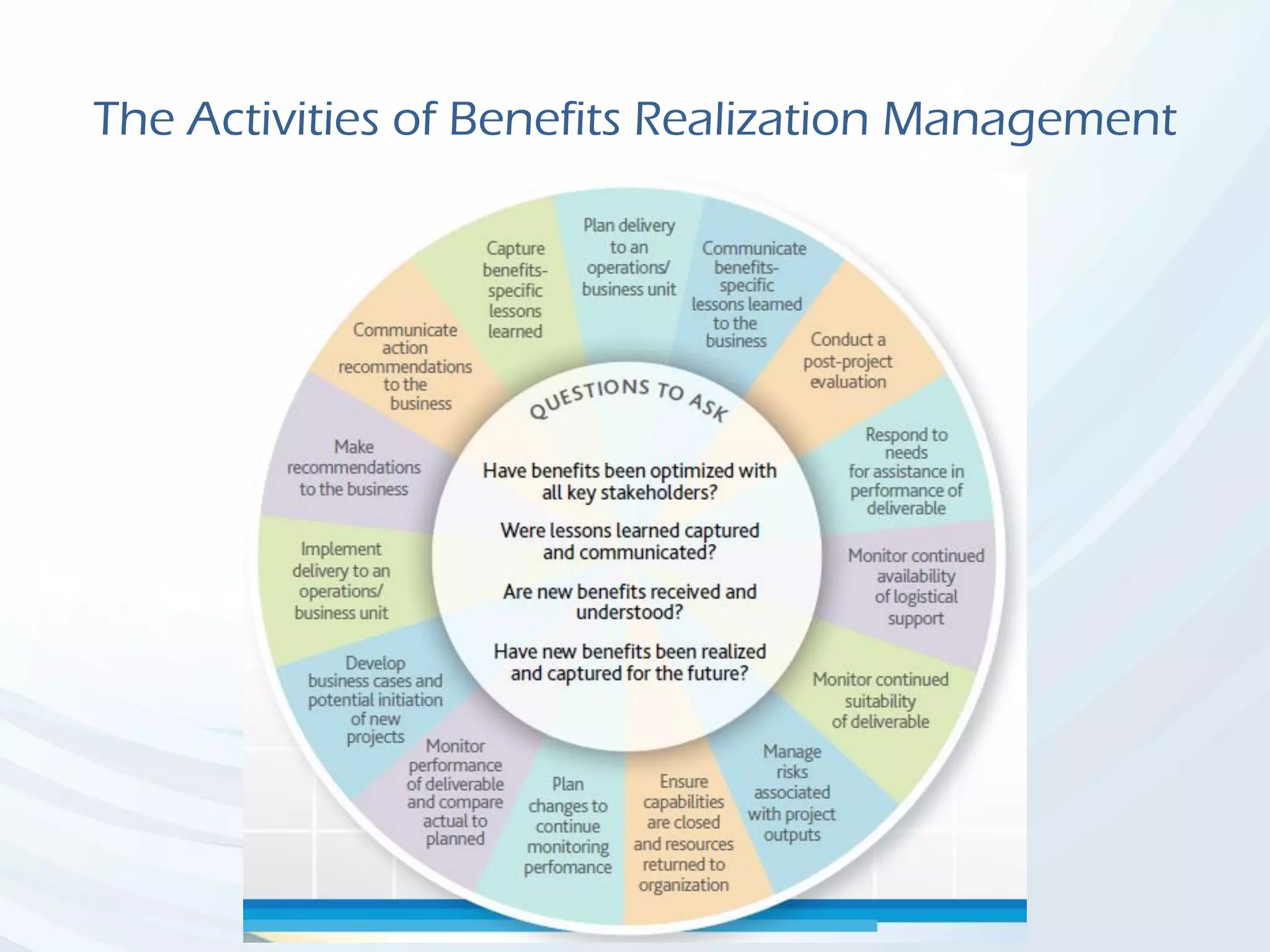
The document discusses Benefits Realization Management (BRM), detailing its definition, importance, and framework within organizations. It emphasizes the need for effective identification, execution, and sustainment of benefits from projects to ensure alignment with strategic goals and maximize return on investment. The document also highlights the critical role of executive PMOs in enhancing benefits realization maturity and improving project outcomes.