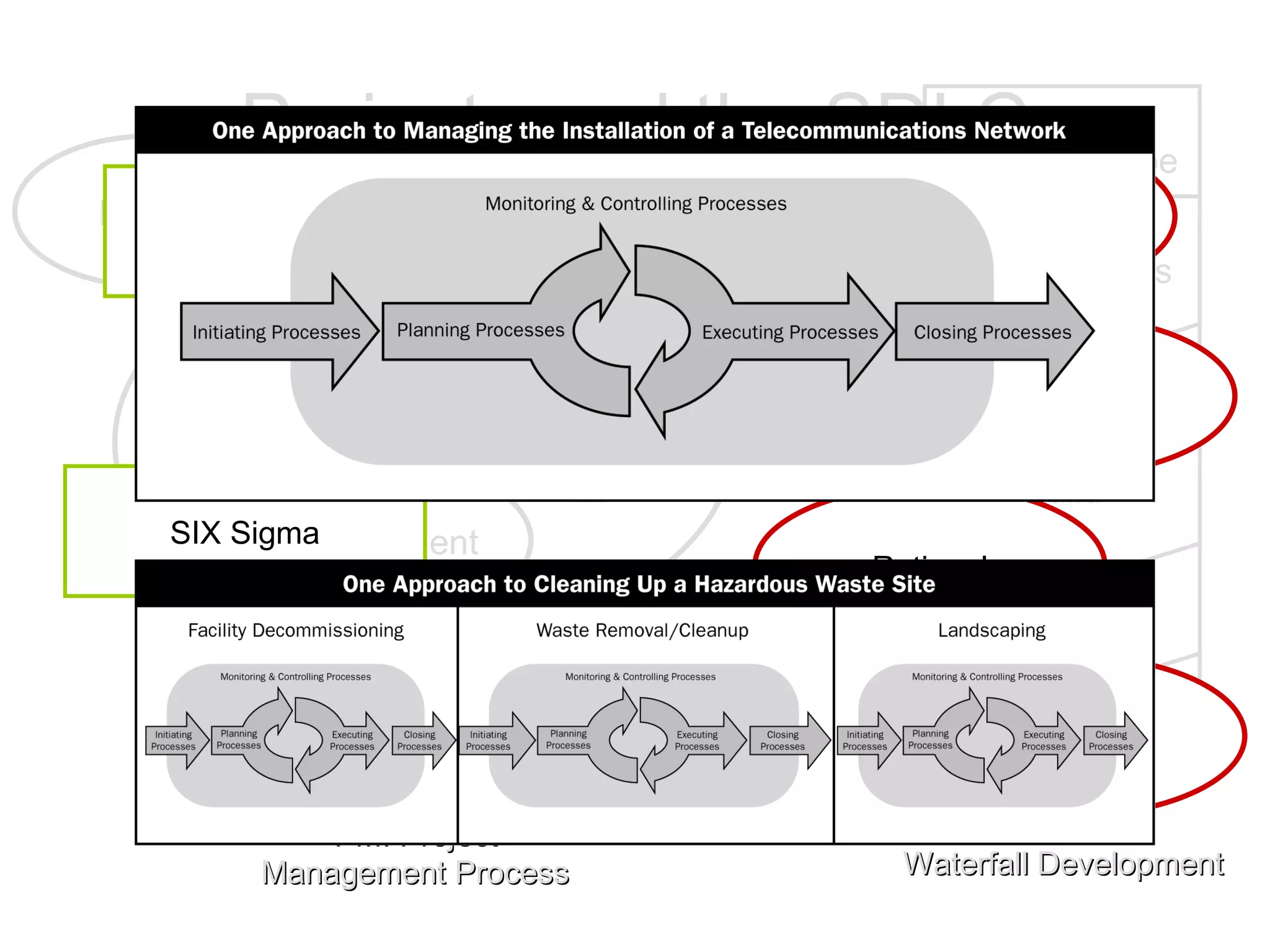
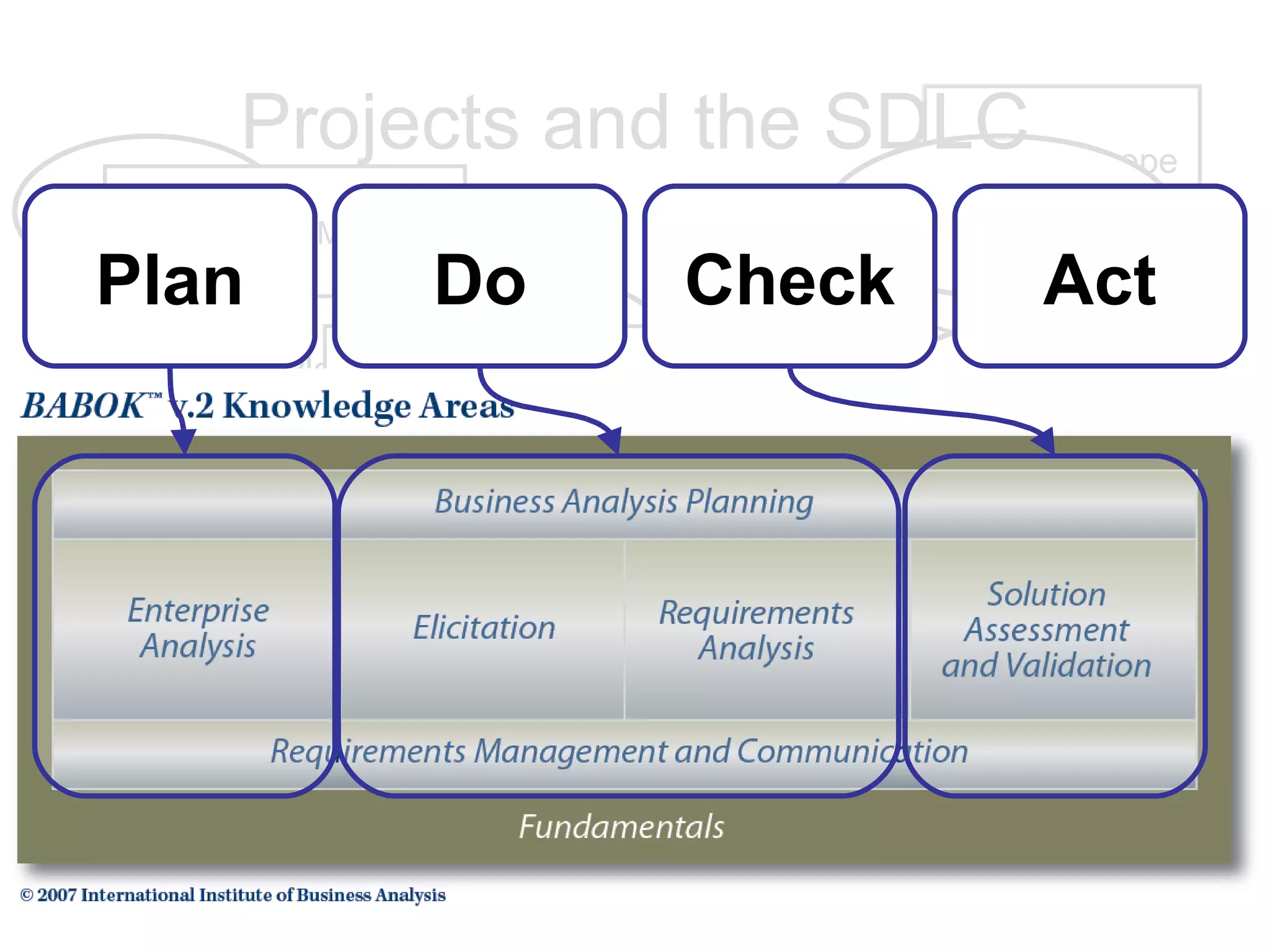
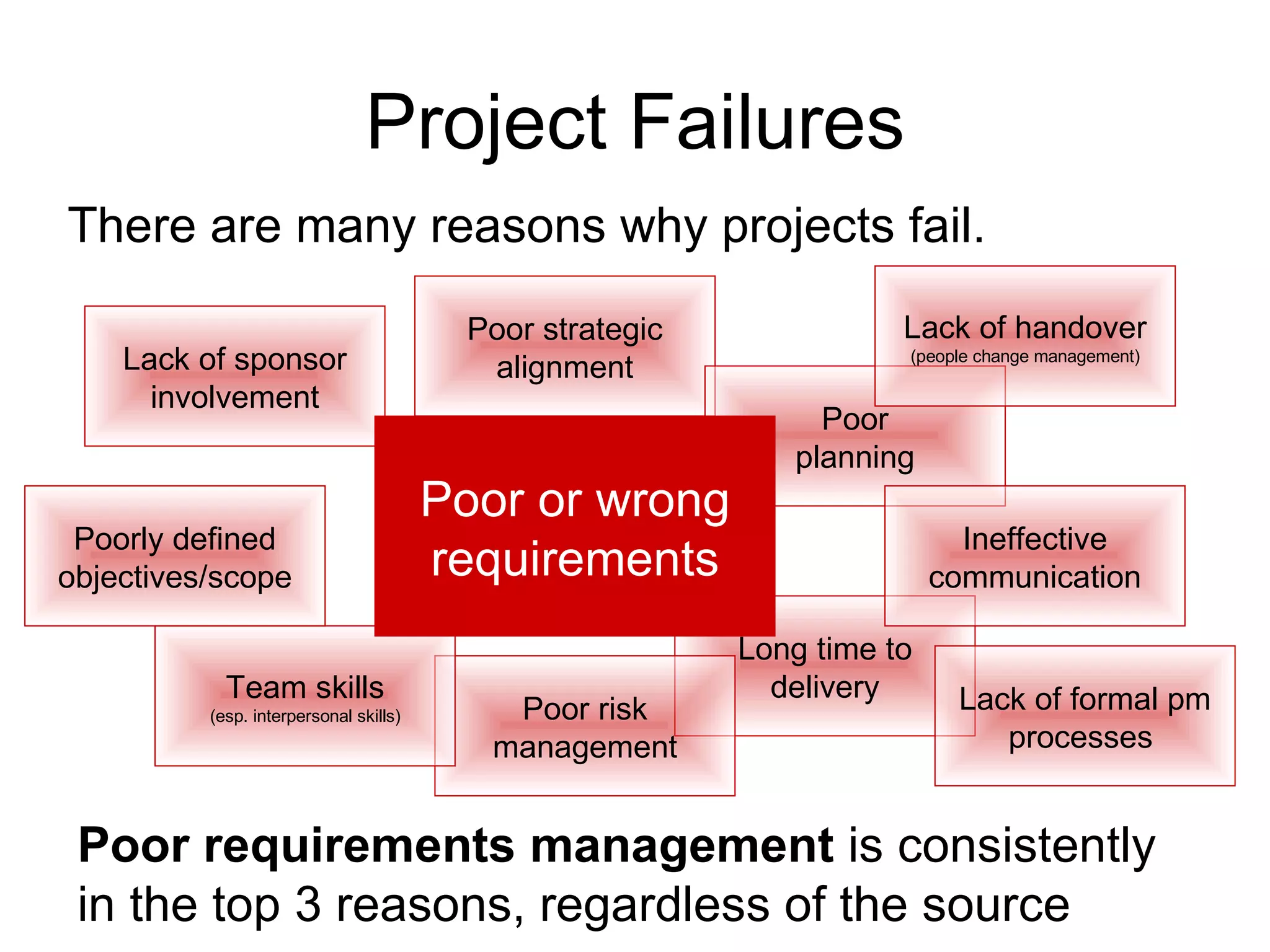
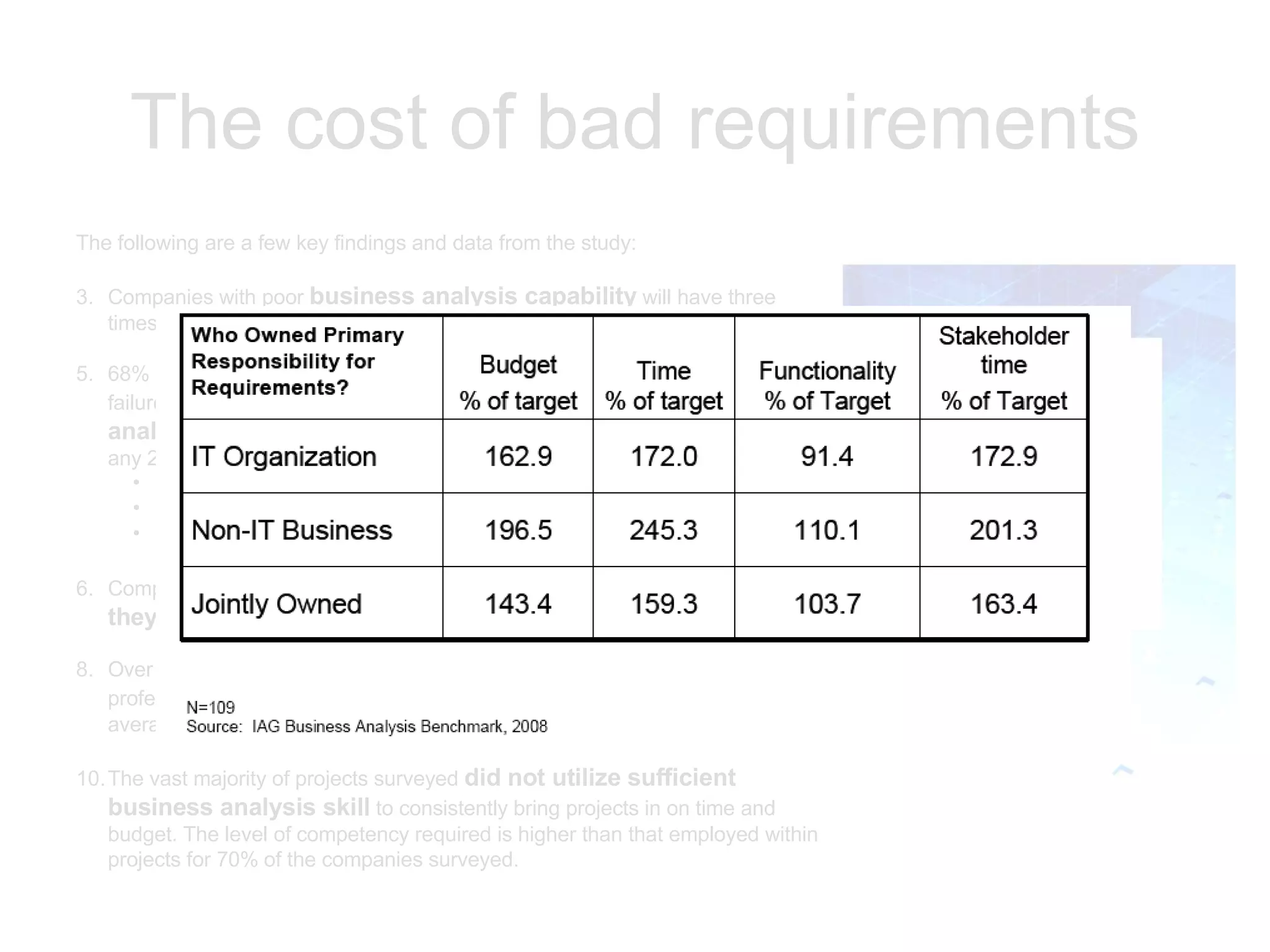
The document discusses the role of business analysts and requirements management. It covers topics like why projects fail, the cost of poor requirements, business analysis skills, requirements practices, and techniques like use cases and swim lanes. The goal is to explain the business analyst role and how to effectively manage requirements to improve project success.