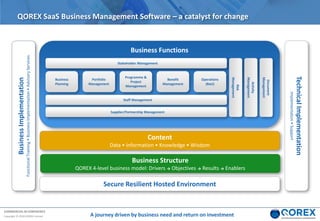
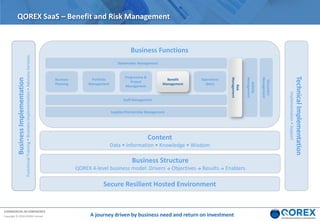
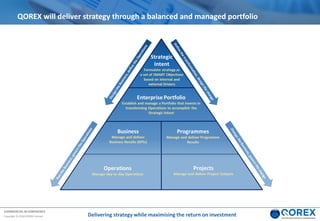
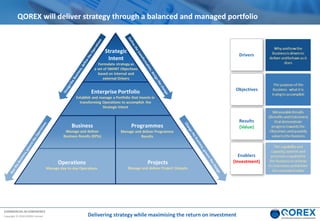
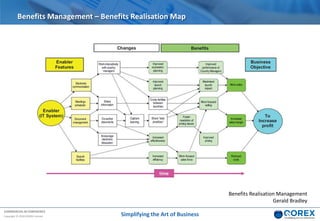
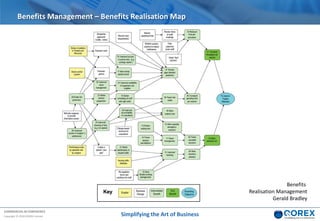
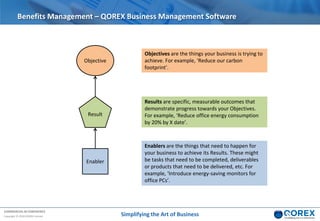
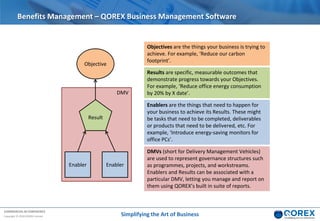
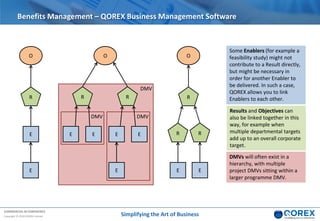
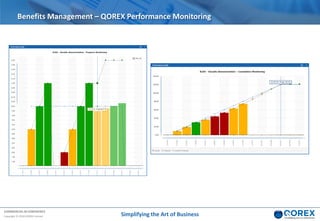
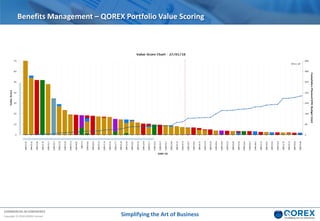
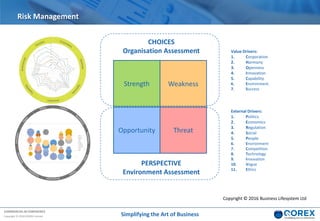
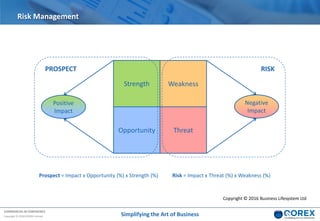
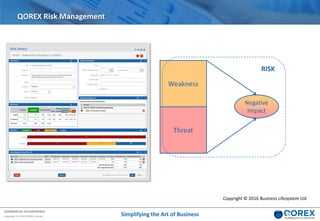
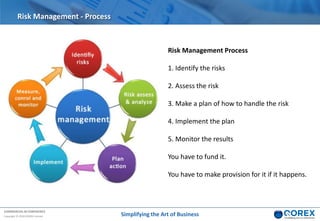
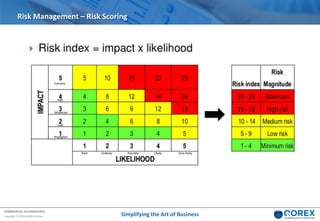
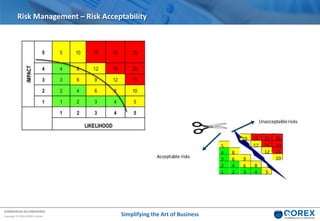
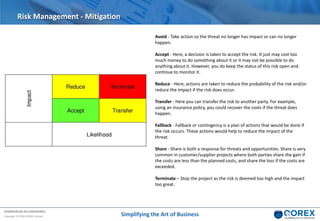
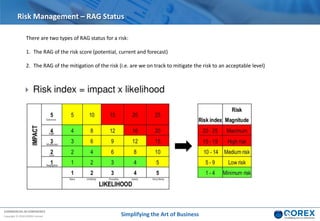
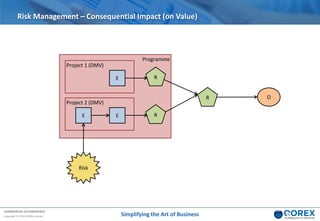
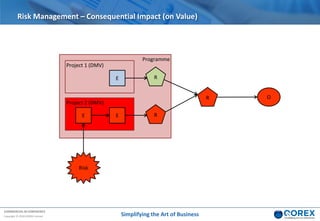
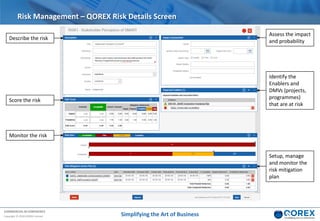
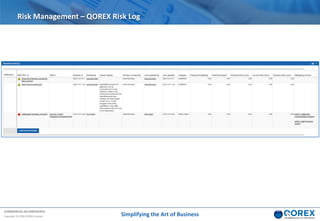
The document outlines Qorex's business management software focusing on benefits and risk management to enhance control, collaboration, and strategic delivery. It defines key concepts such as benefits management, risk management, and provides frameworks for identifying, executing, and sustaining benefits and risks within business projects. It emphasizes the importance of aligning benefits with organizational objectives and offers guidance on effective risk management processes.