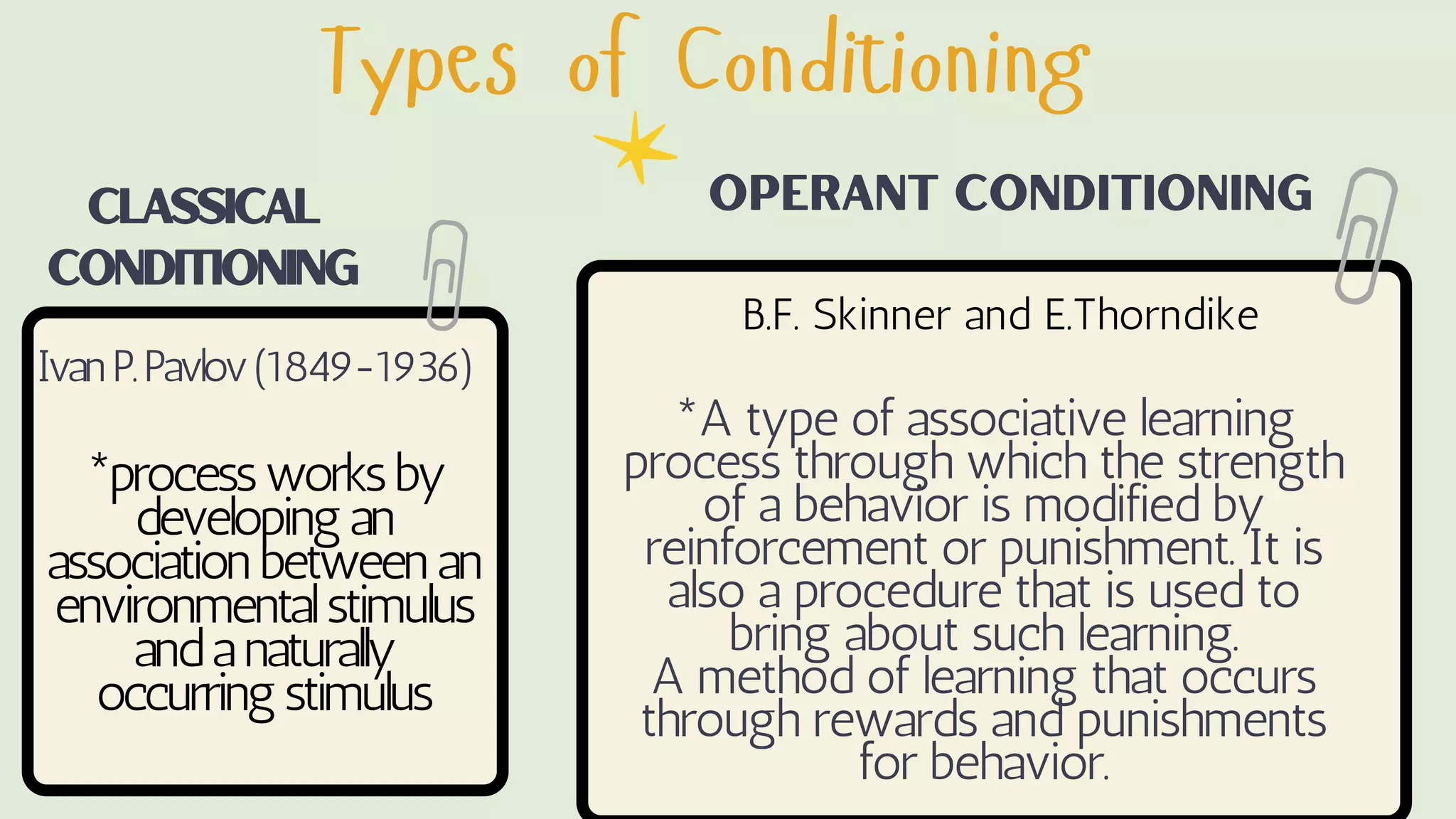
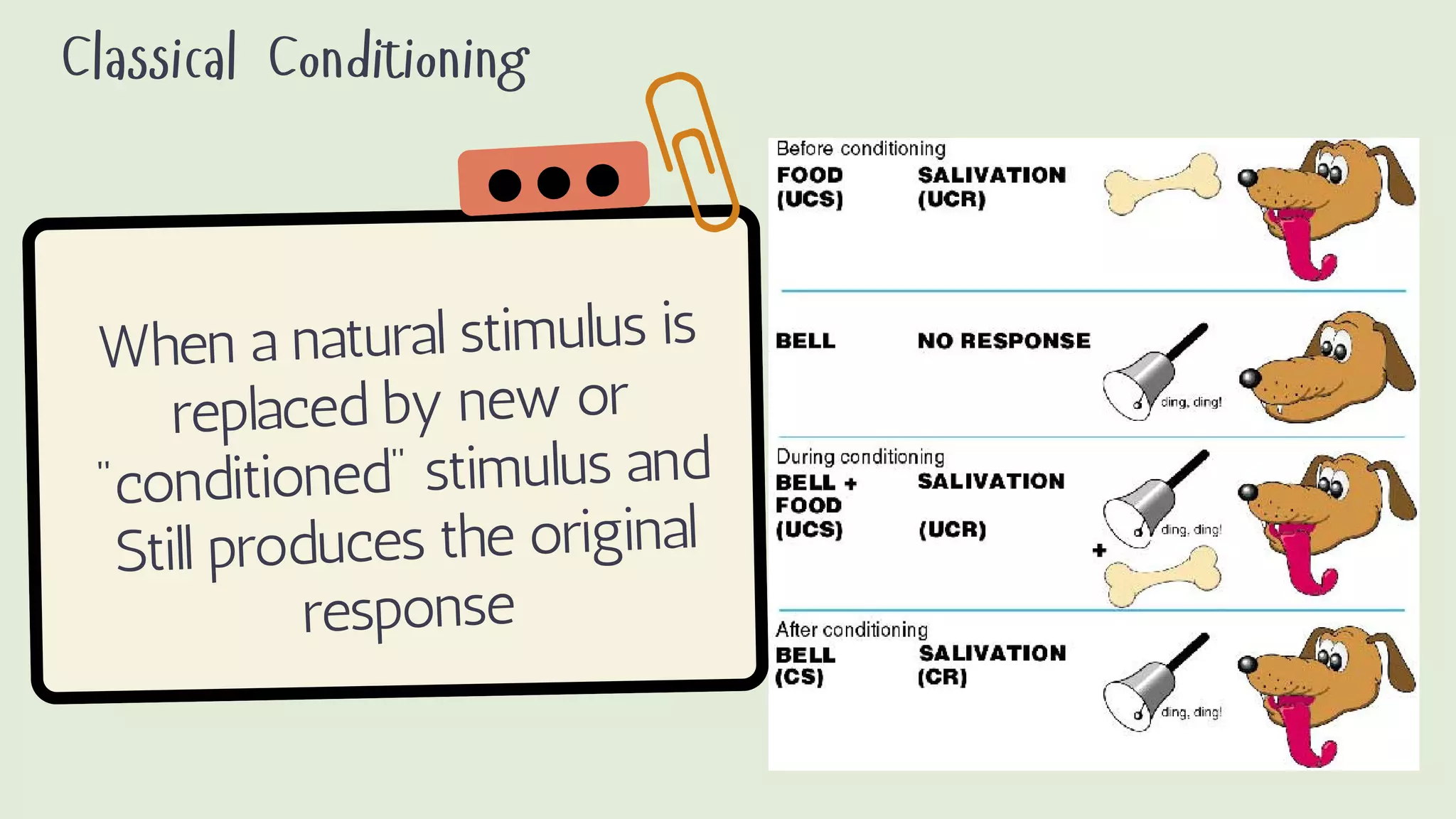
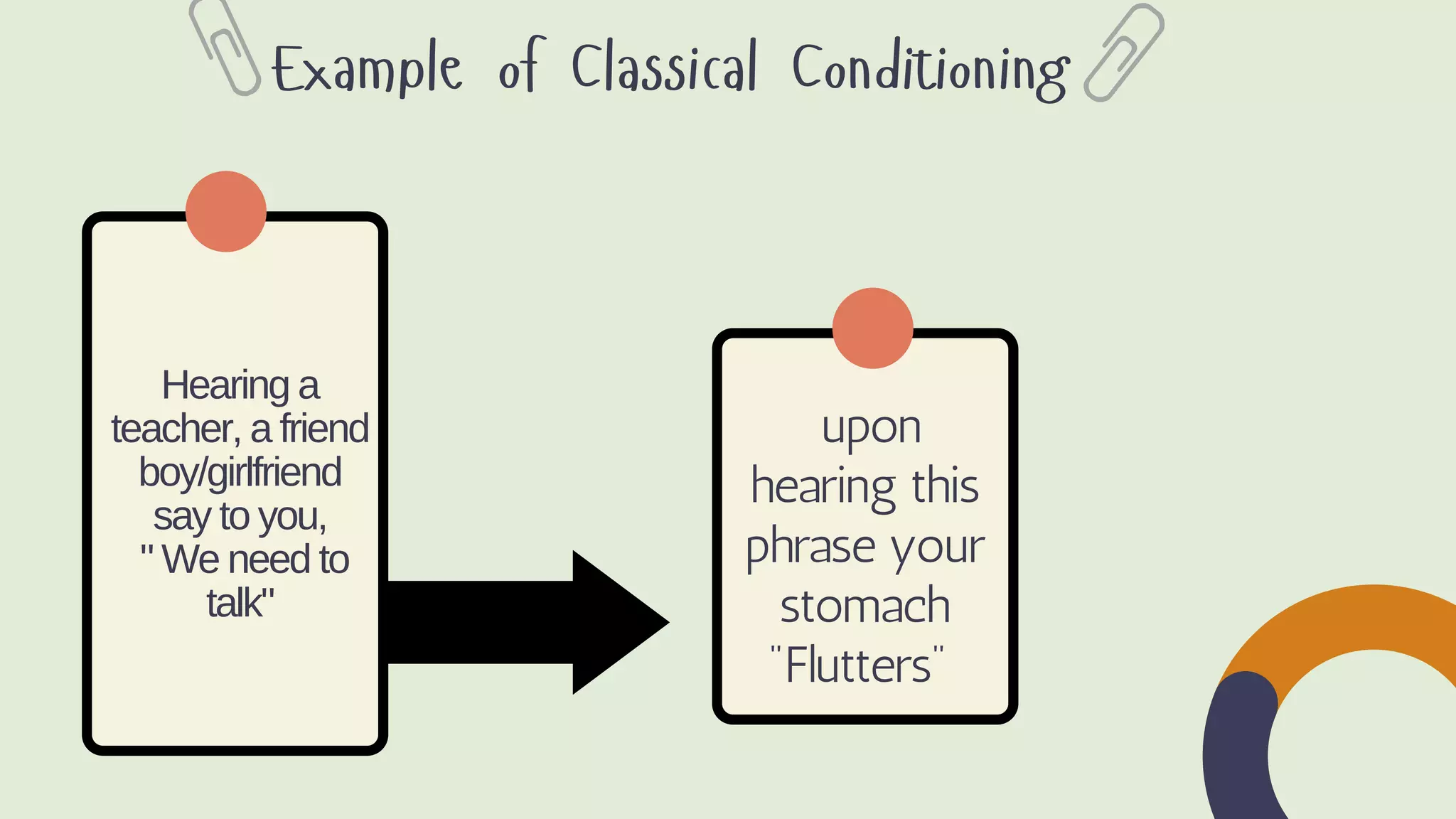
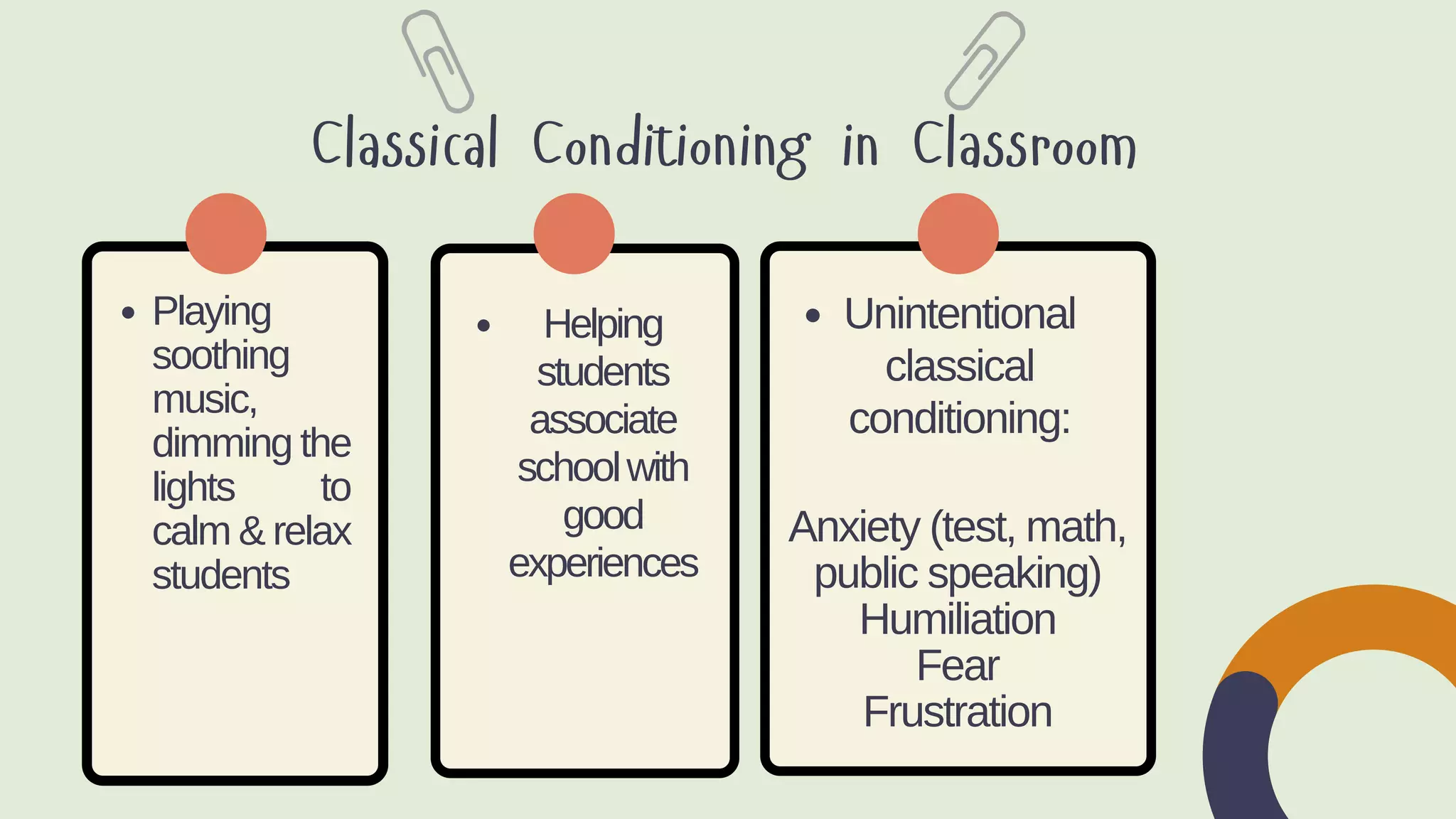
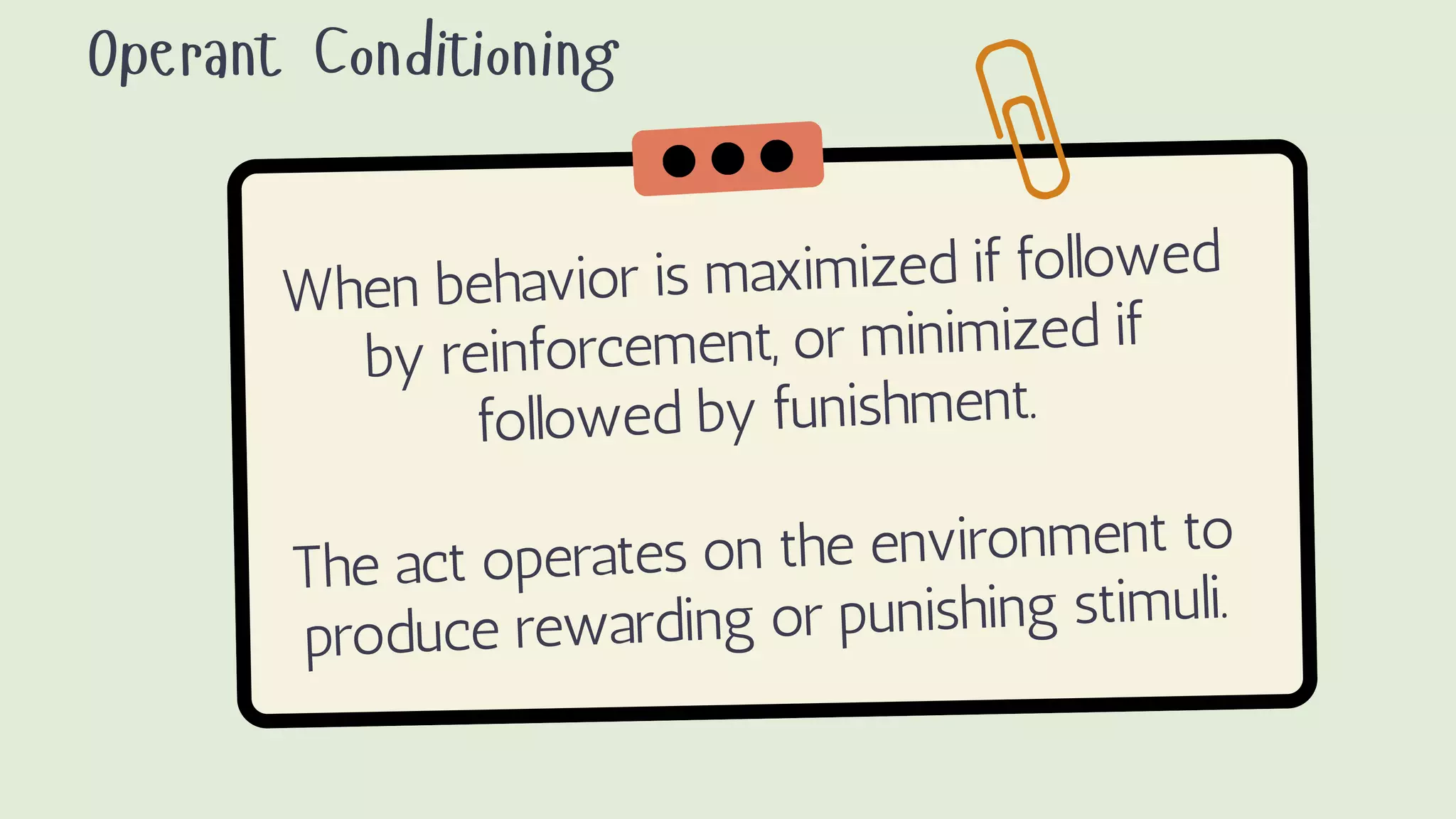
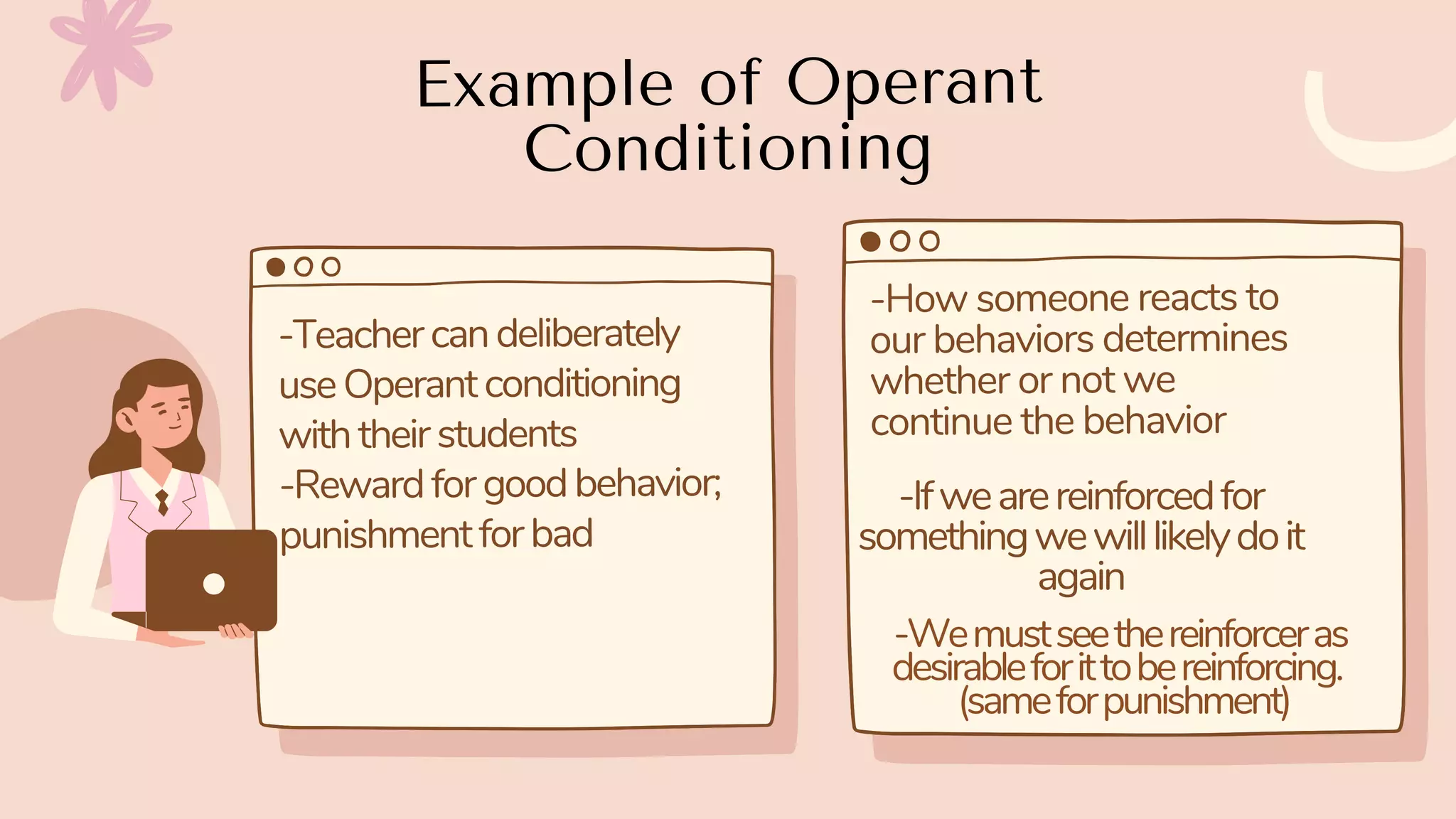
Behaviorism is a learning theory that focuses on observable behaviors and how they are shaped through interaction with the environment. It emphasizes that all behaviors are learned through conditioning, whether classical conditioning involving involuntary responses or operant conditioning involving voluntary behaviors and consequences like reinforcement and punishment. Key proponents discussed include John Watson, Ivan Pavlov, and B.F. Skinner. Behaviorism aims to predict and control behavior. In education, it focuses on manipulating the environment to change behaviors through techniques like positive reinforcement, drills, and practice. However, it is criticized for treating humans like machines without free will and for seeking to control behavior.