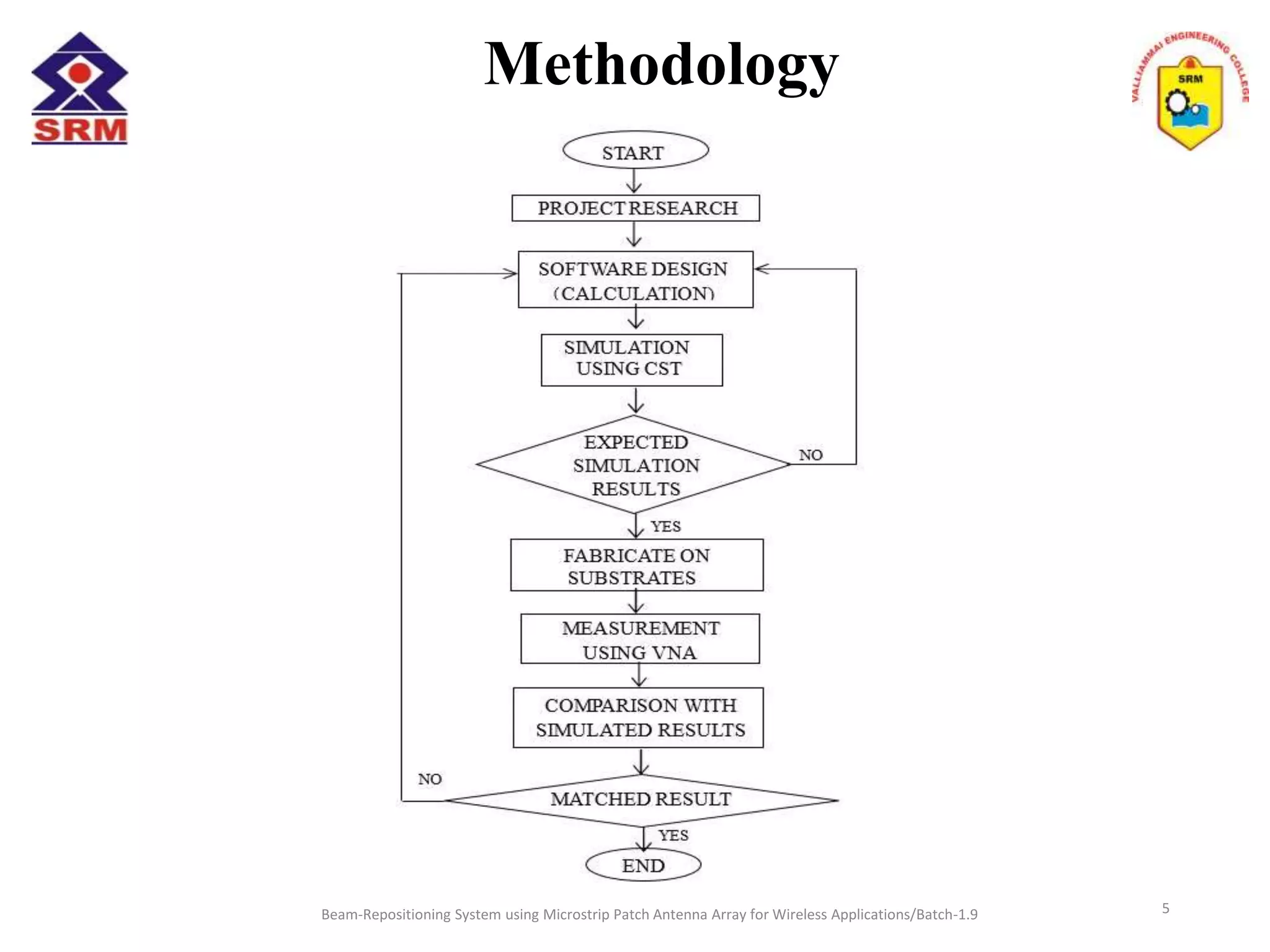
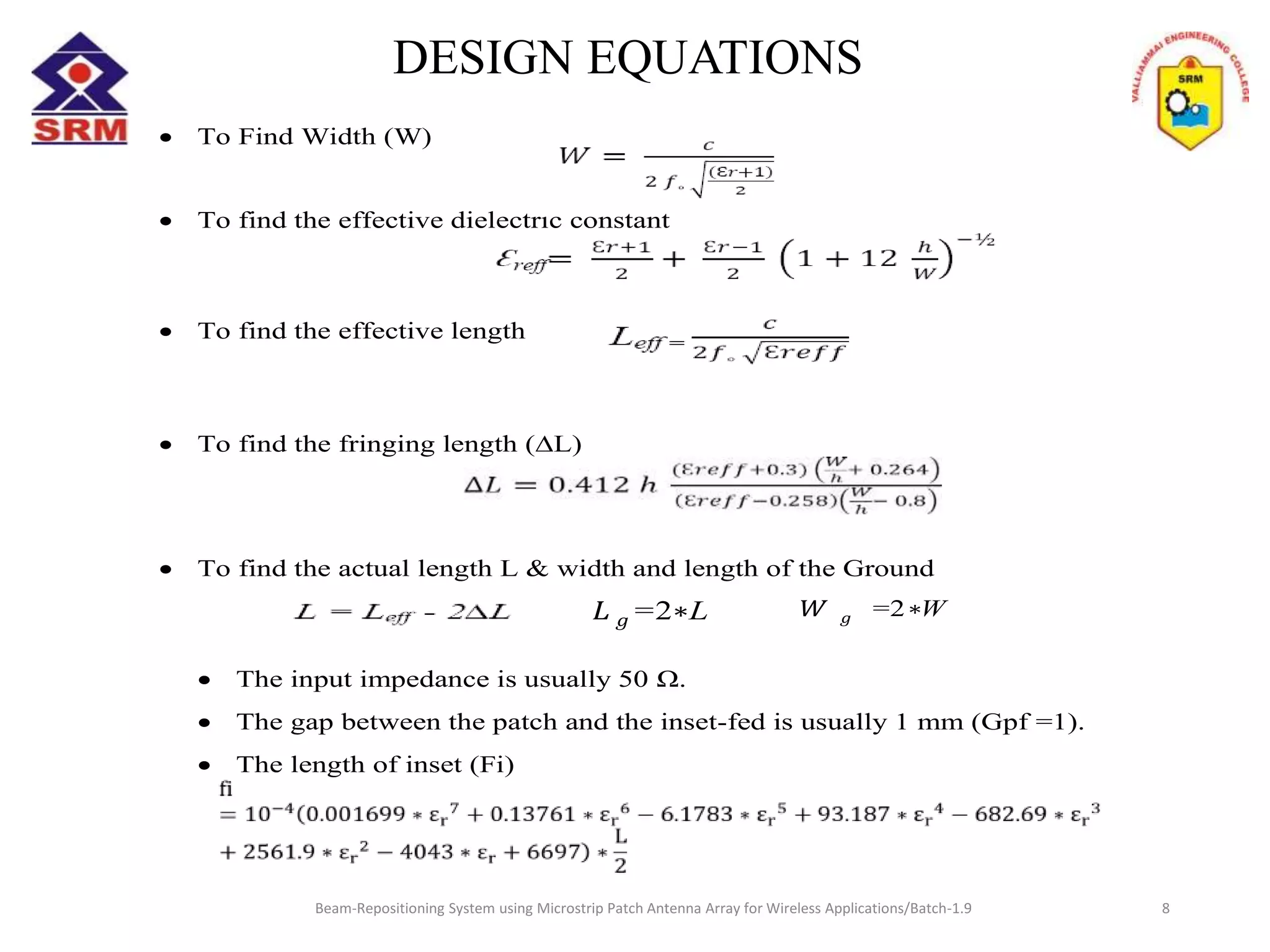
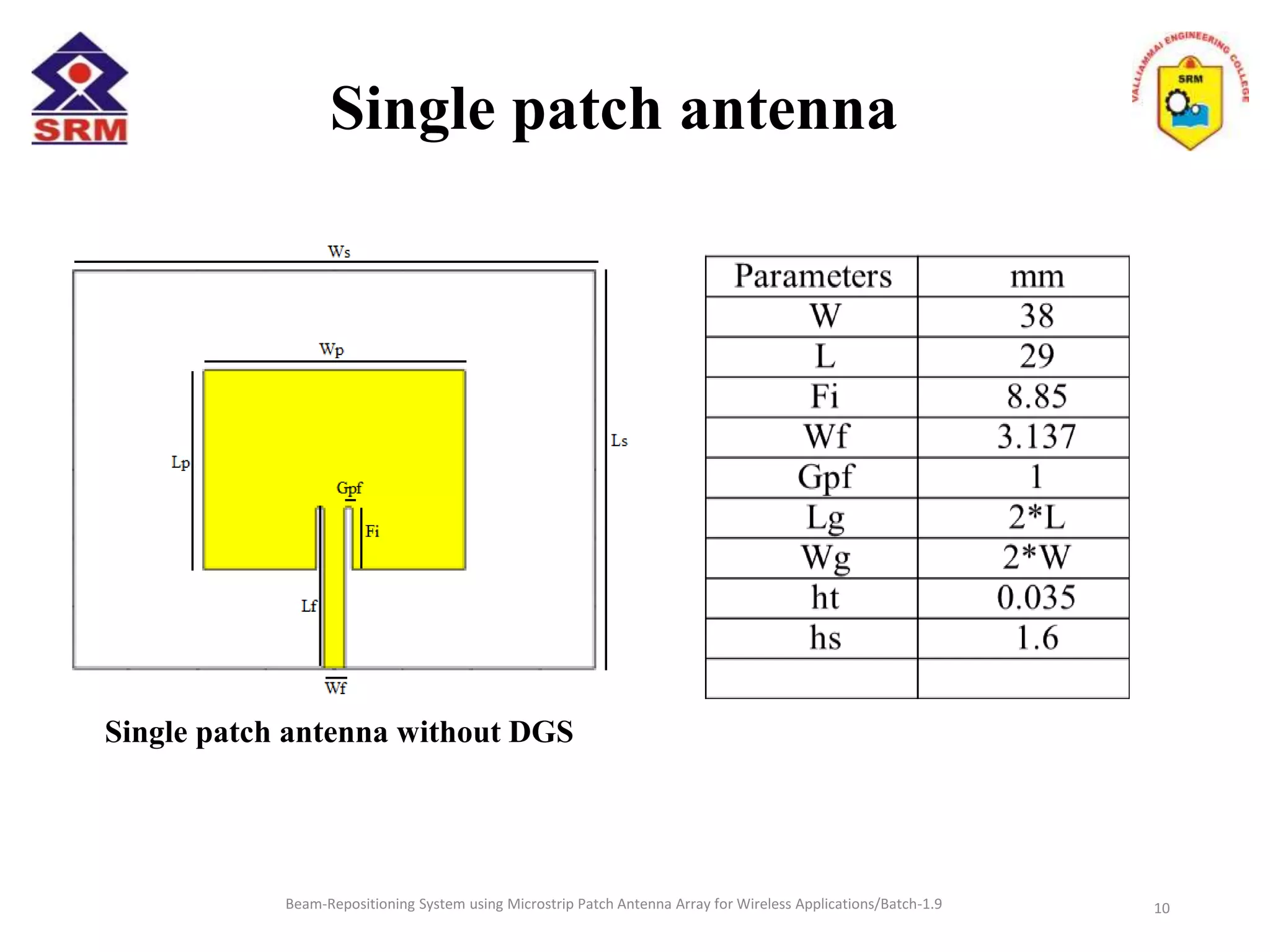
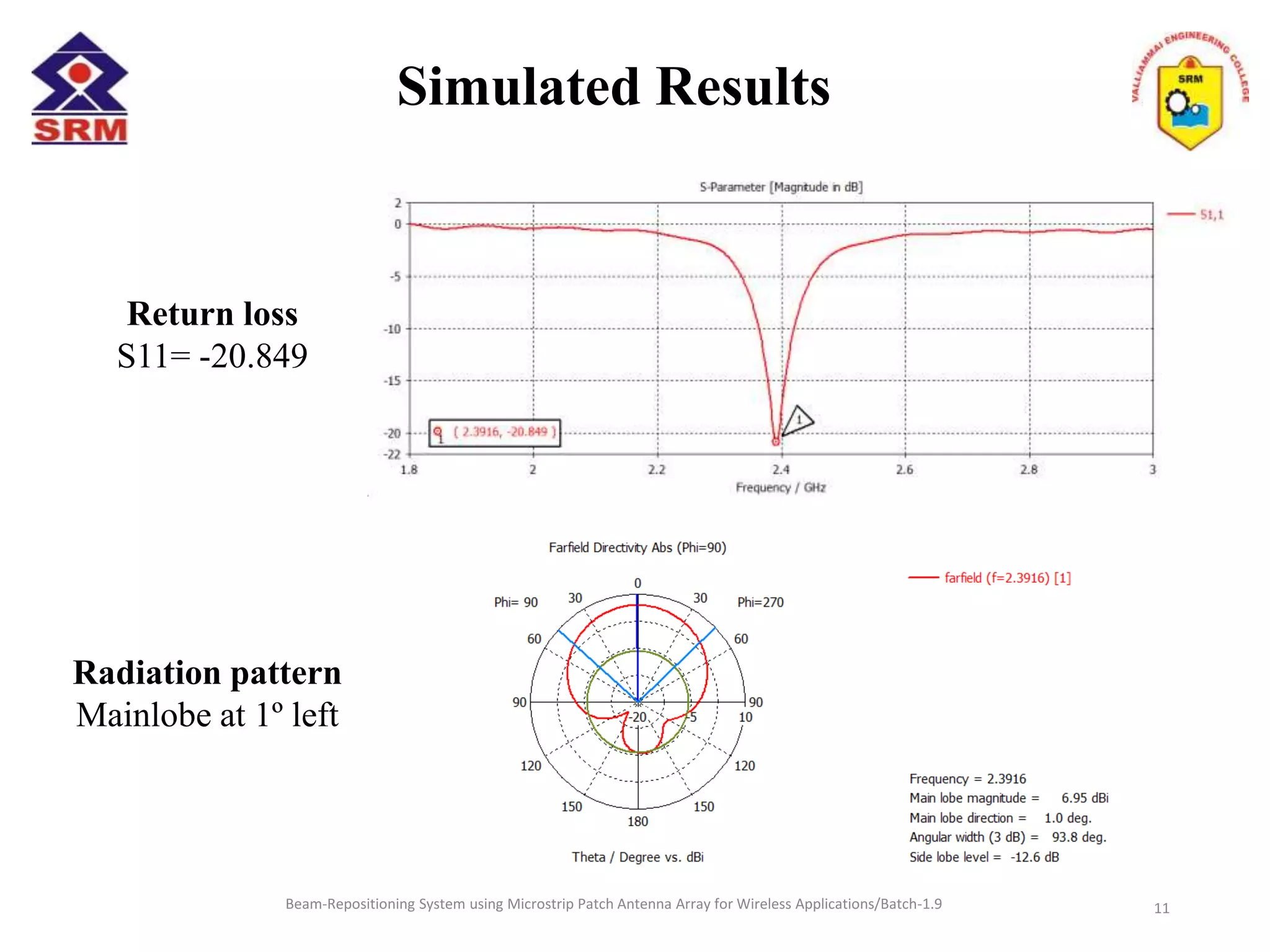
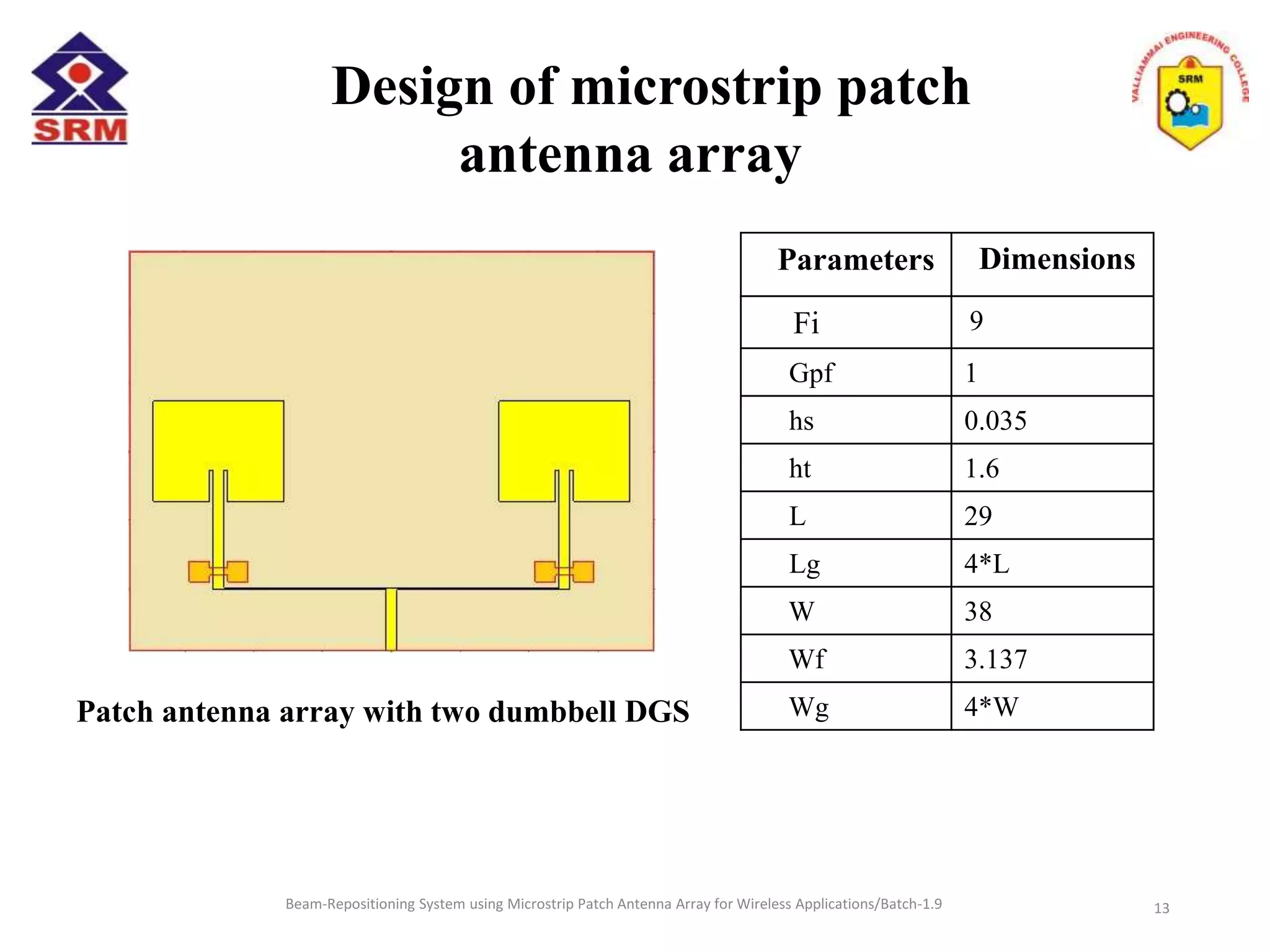
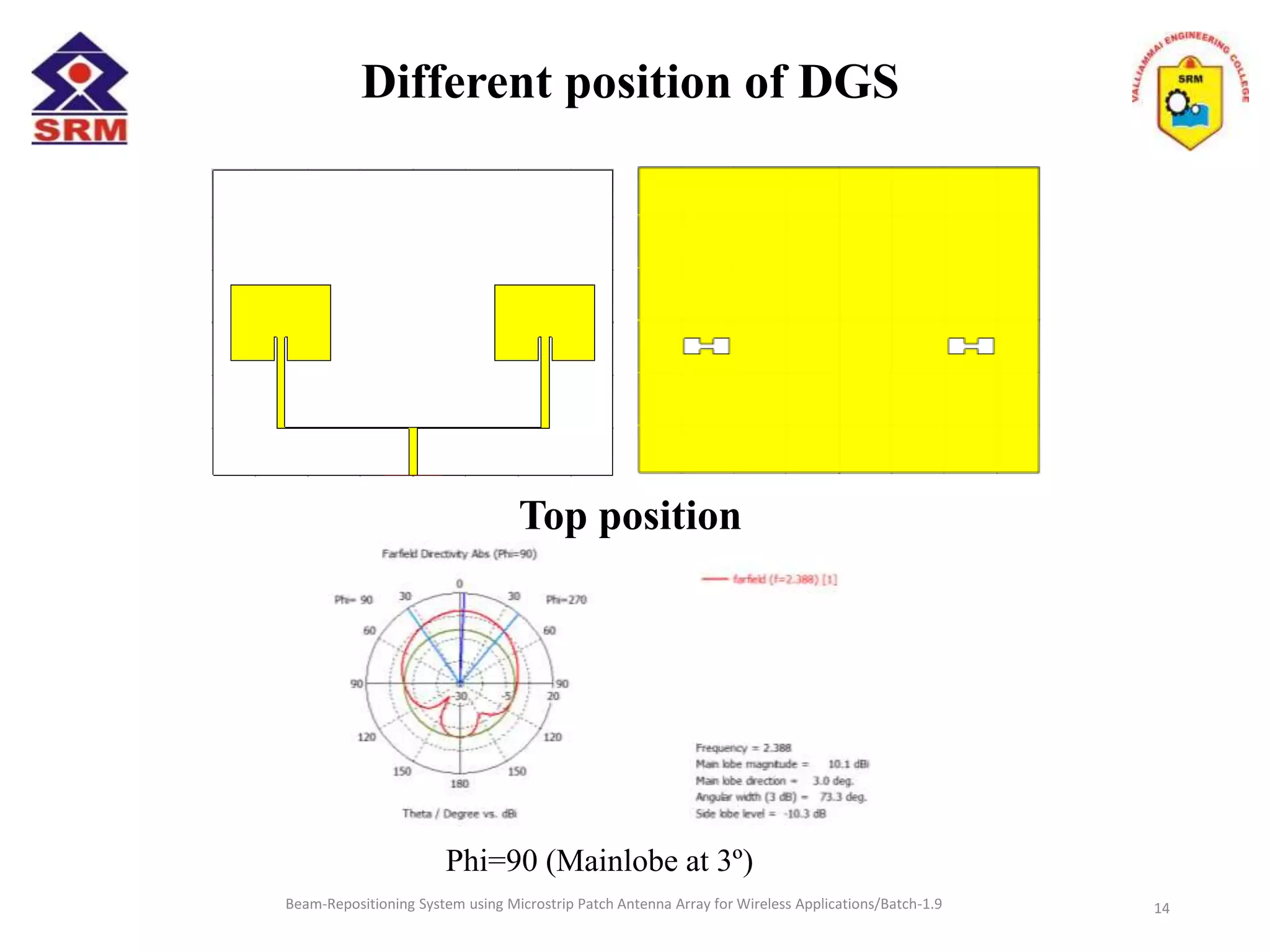
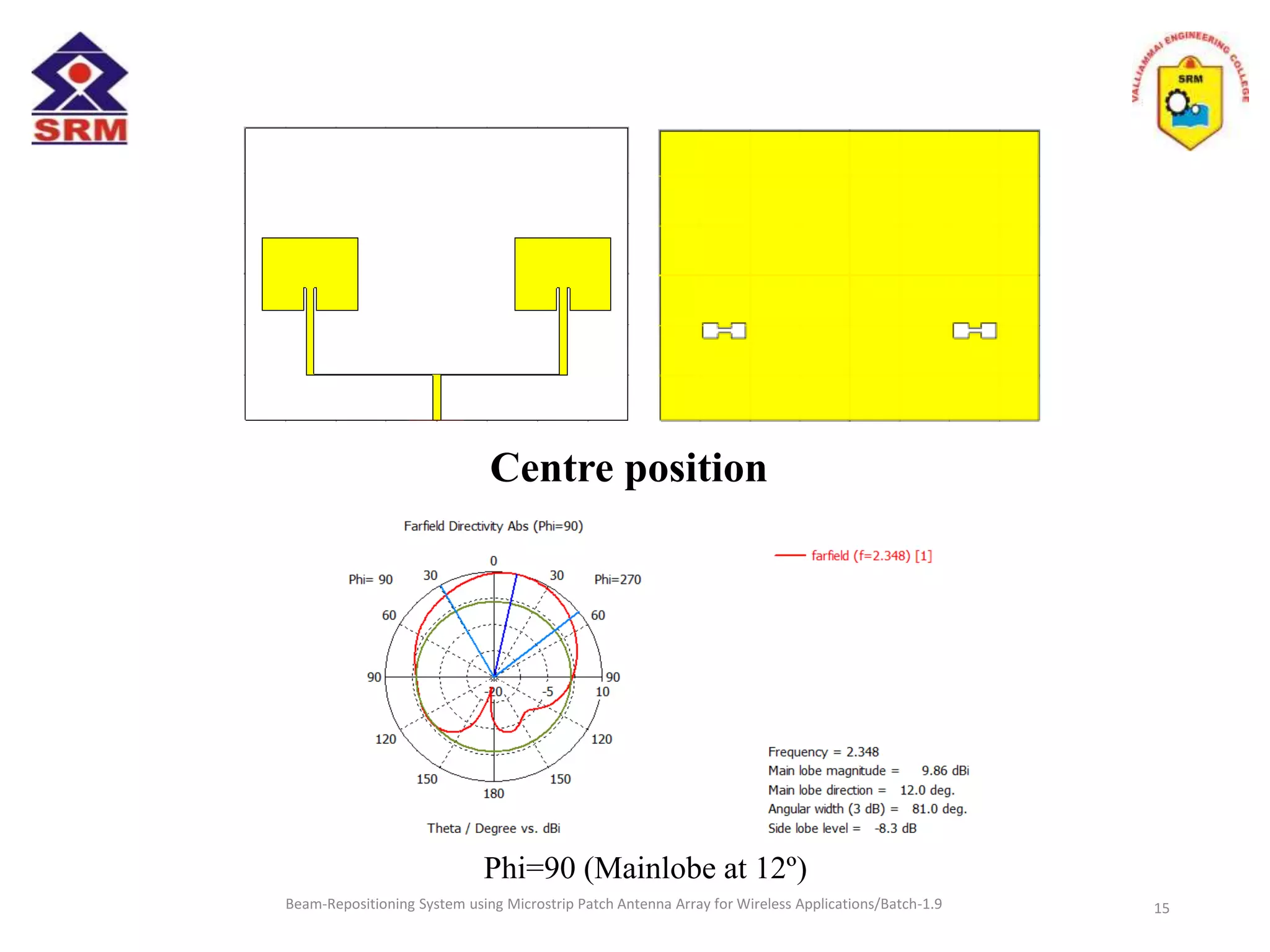
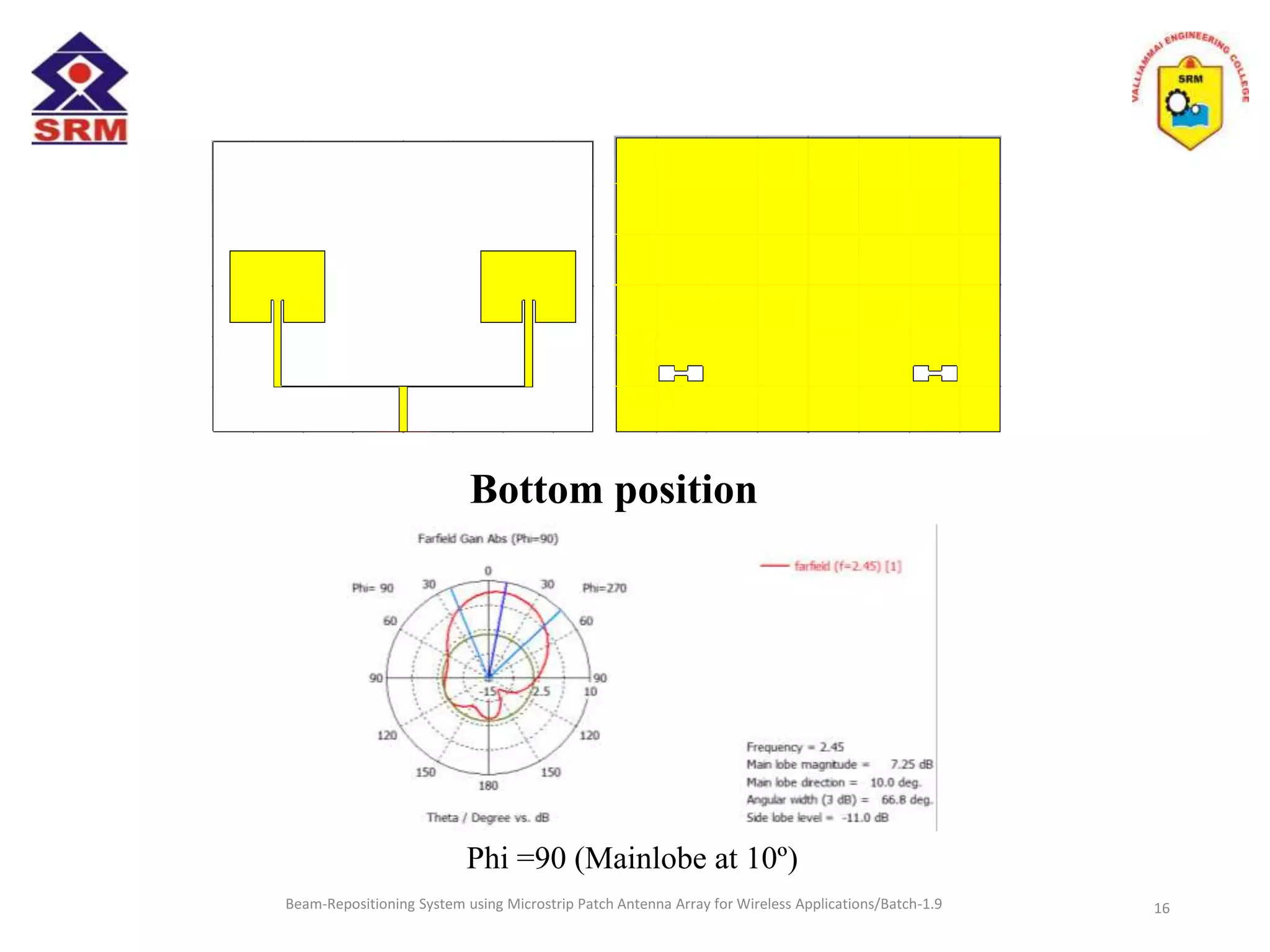
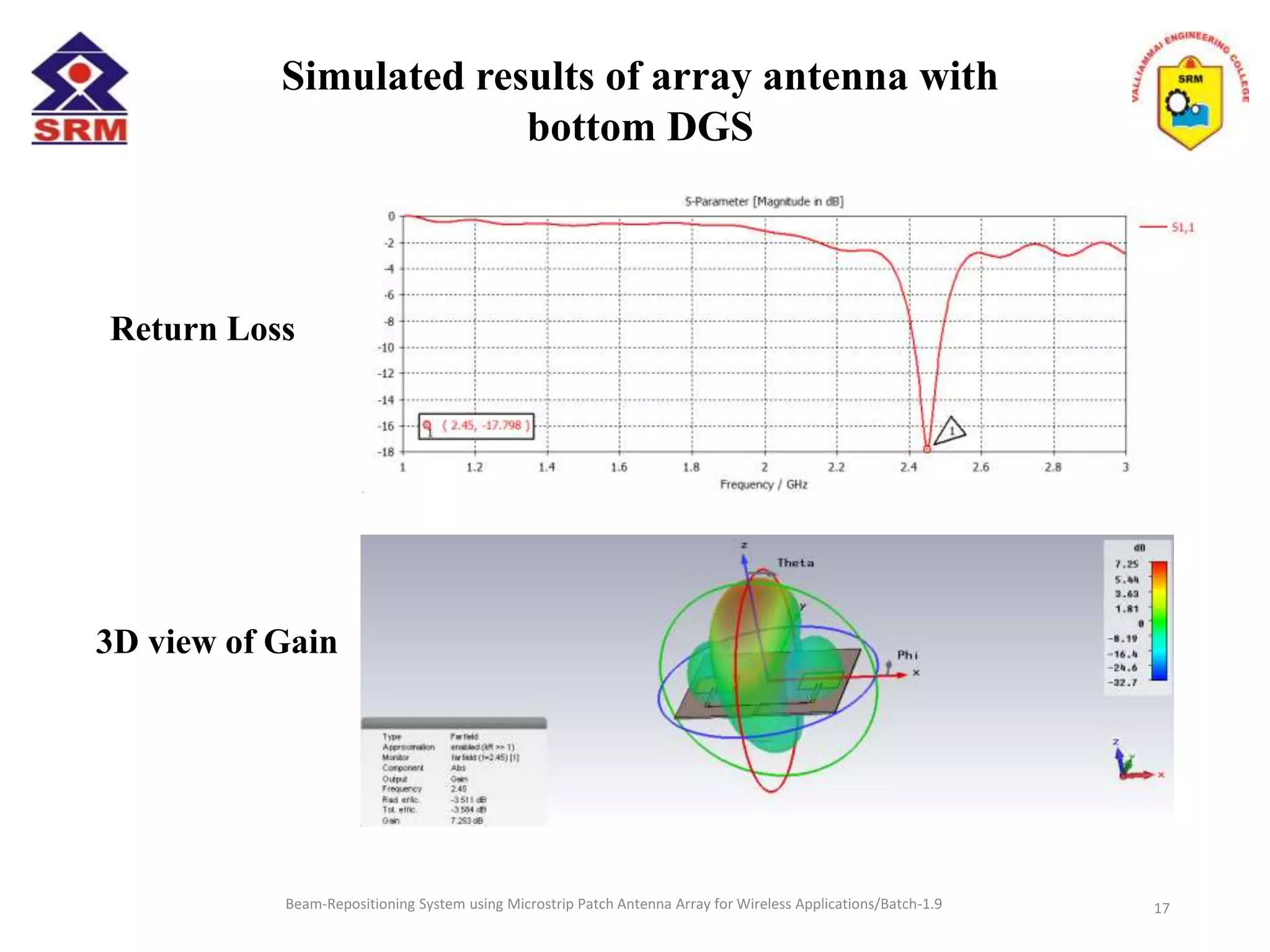
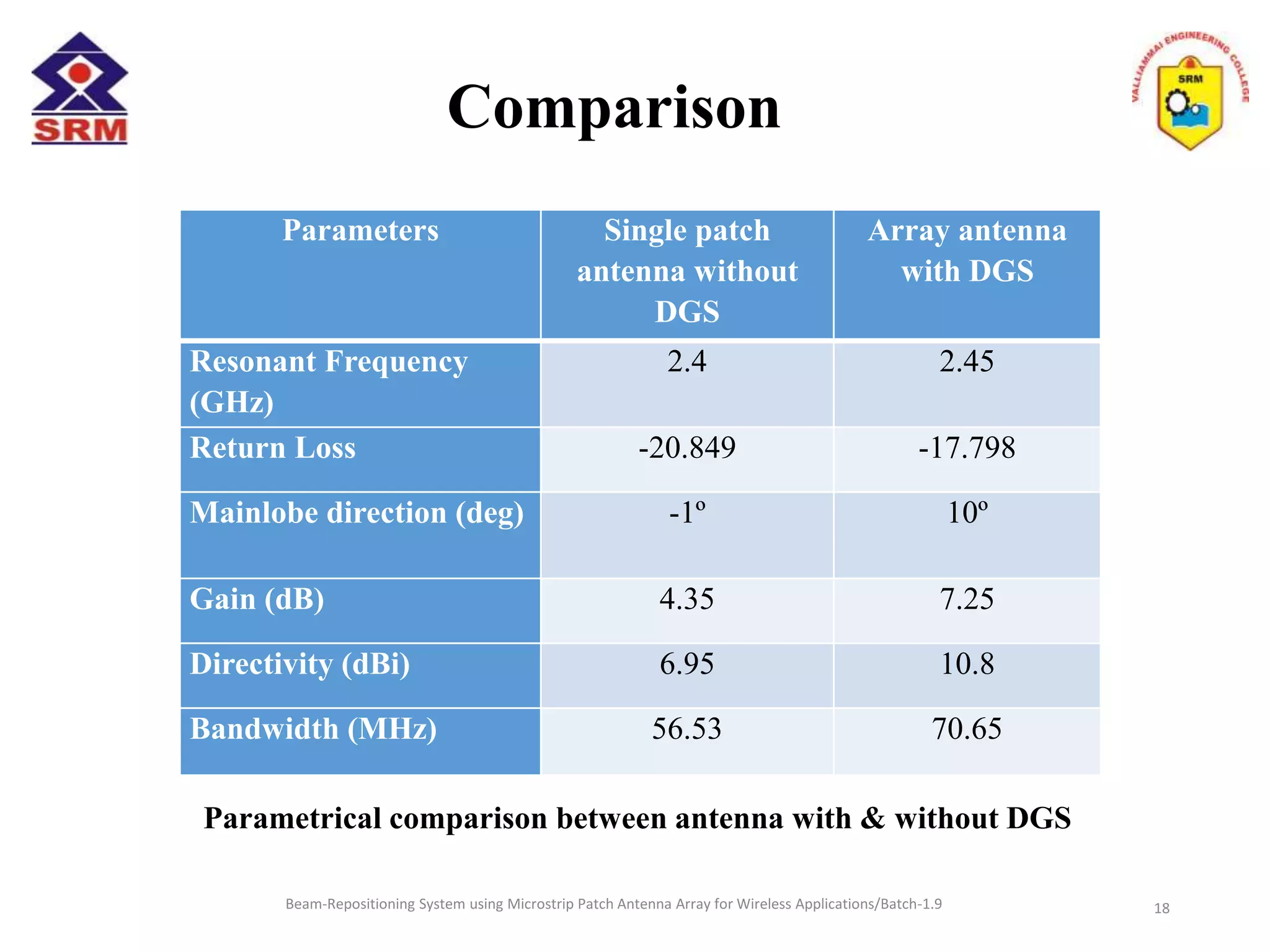
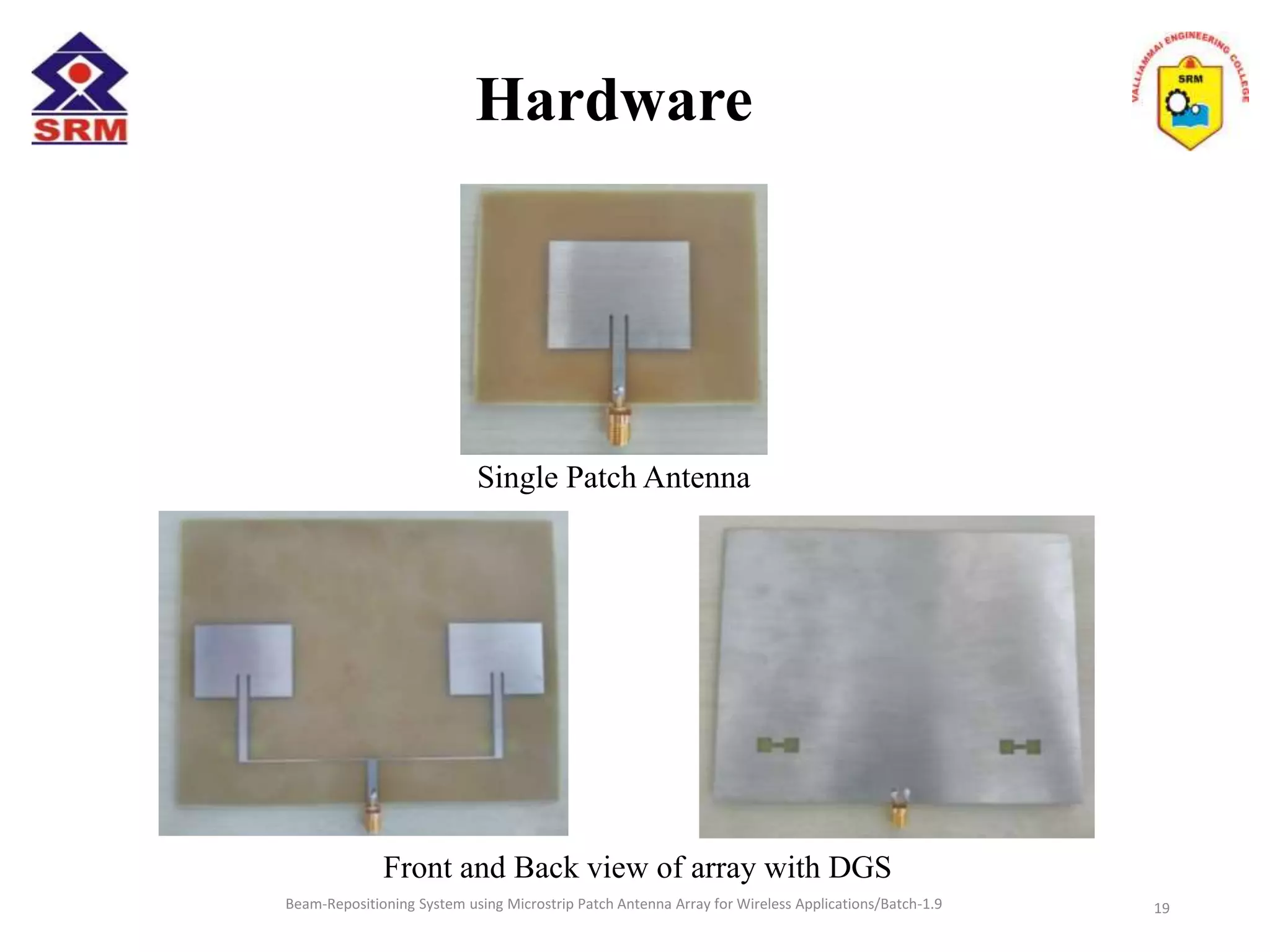
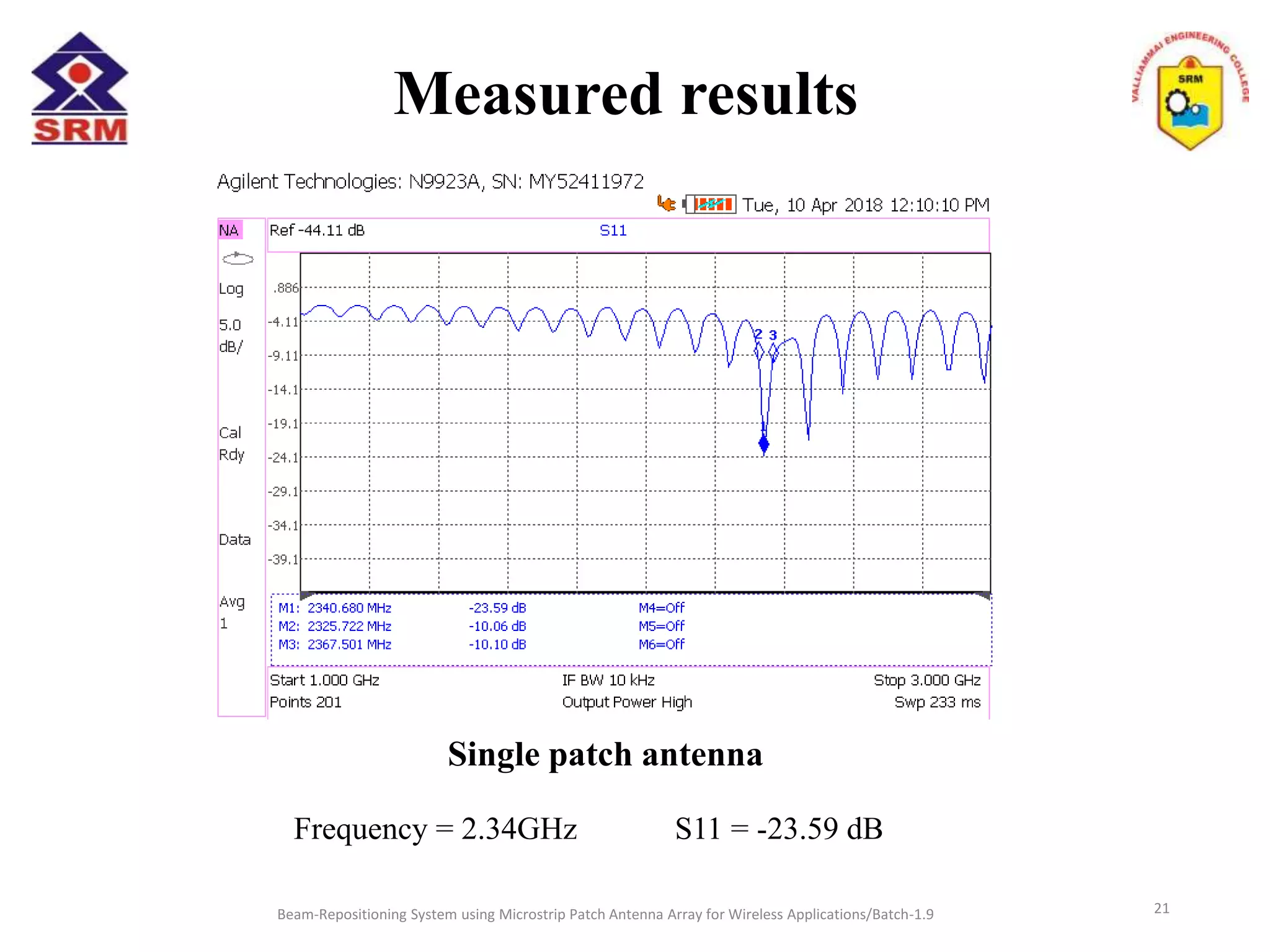
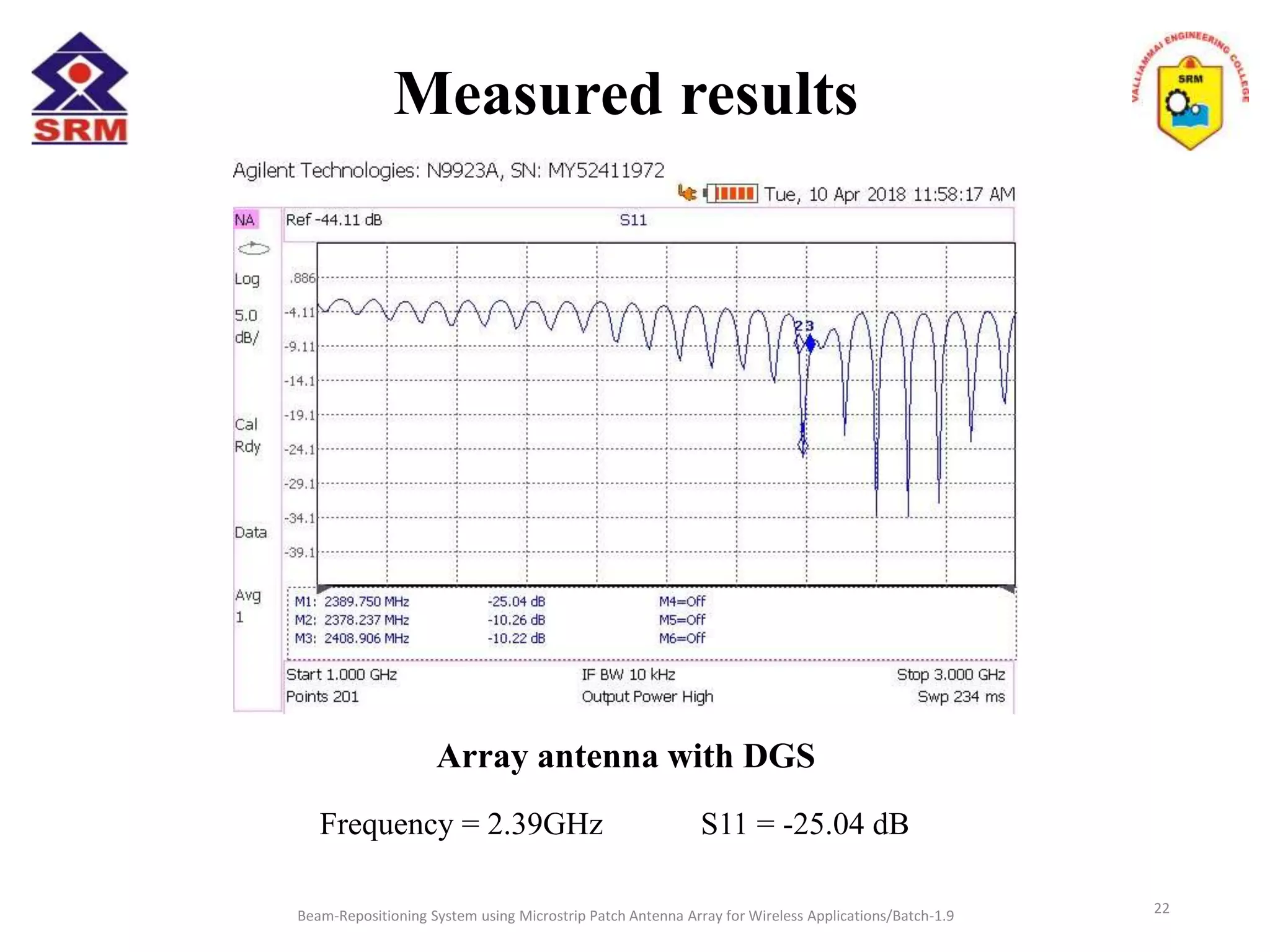
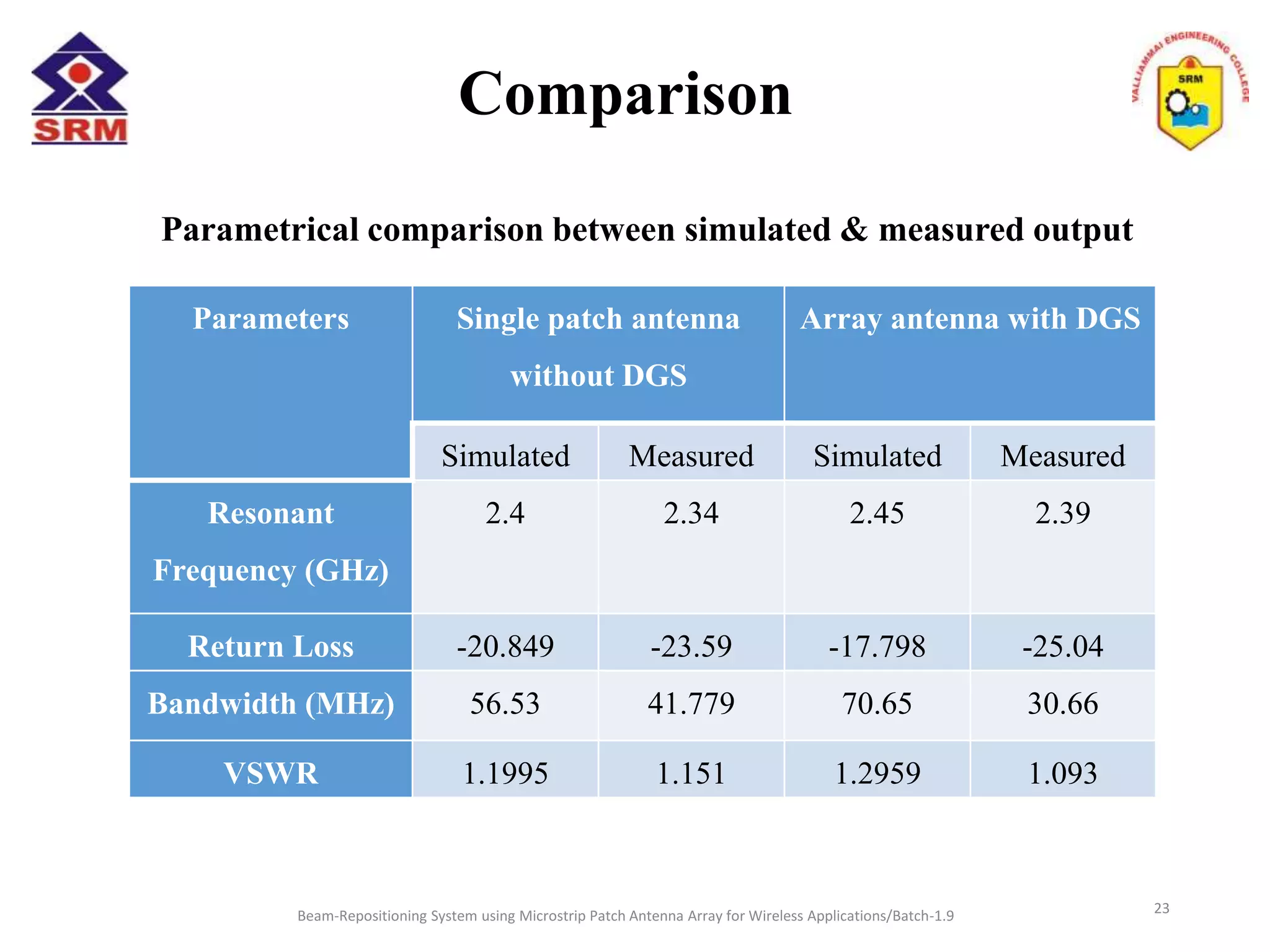
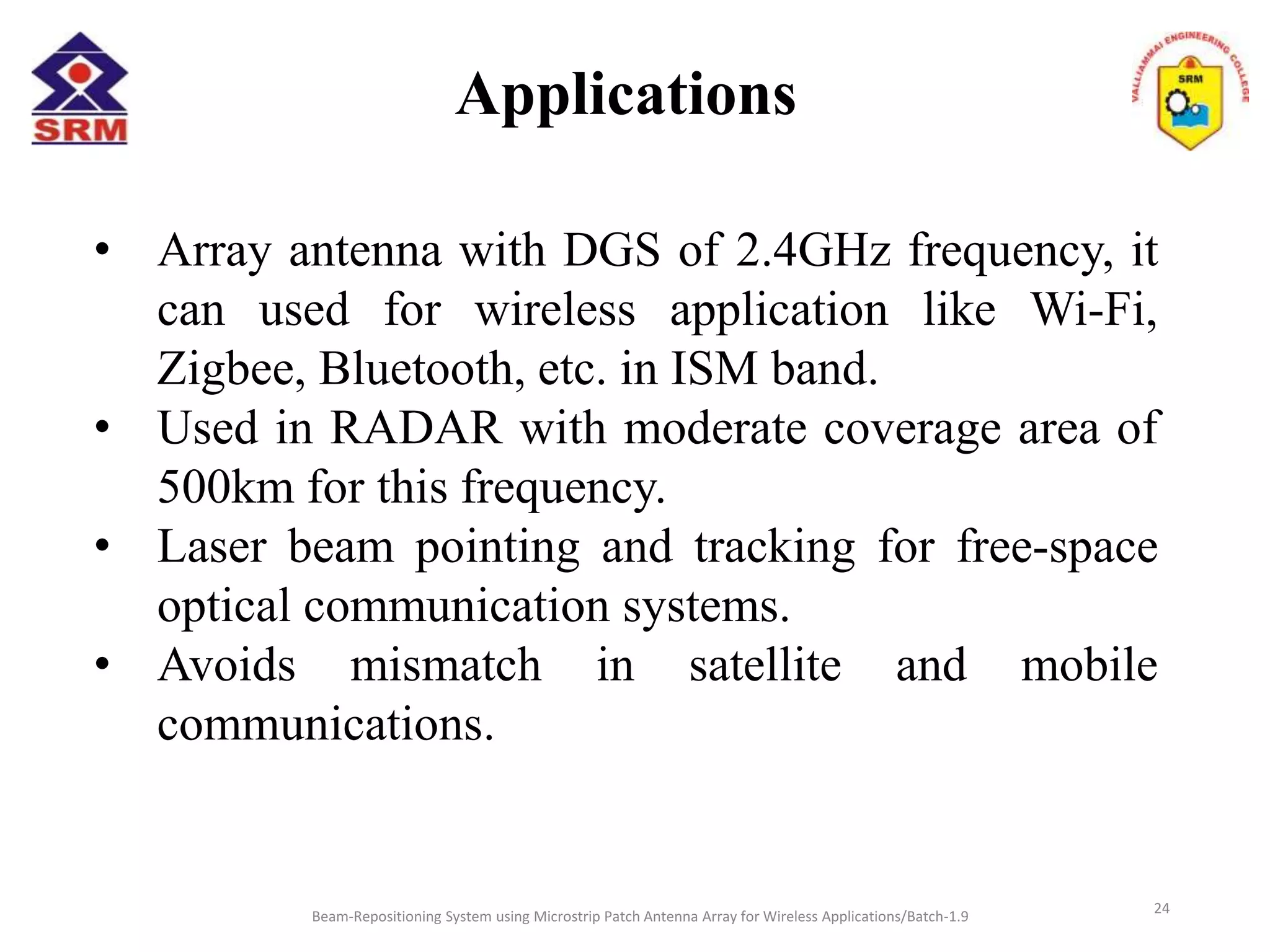
The document presents a beam-repositioning system using a microstrip patch antenna array optimized for wireless applications, specifically targeting WLAN frequencies at 2.4 GHz. It discusses the design, simulation, and testing of both single patch antennas and arrays with defected ground structures (DGS) to enhance performance metrics such as return loss, gain, and directivity. The findings indicate significant improvements in antenna characteristics with the DGS integration, alongside potential applications in wireless communications and radar systems.