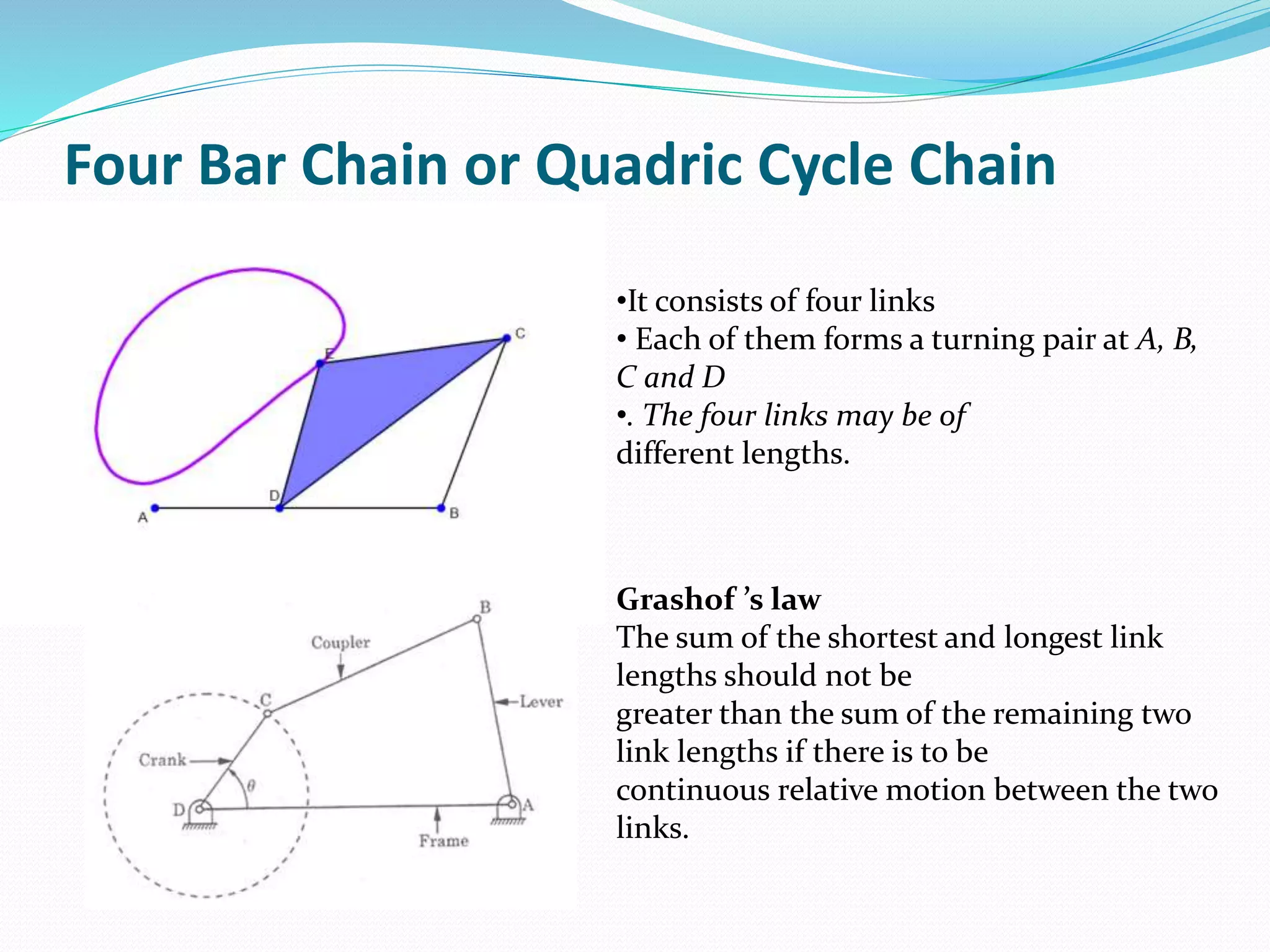
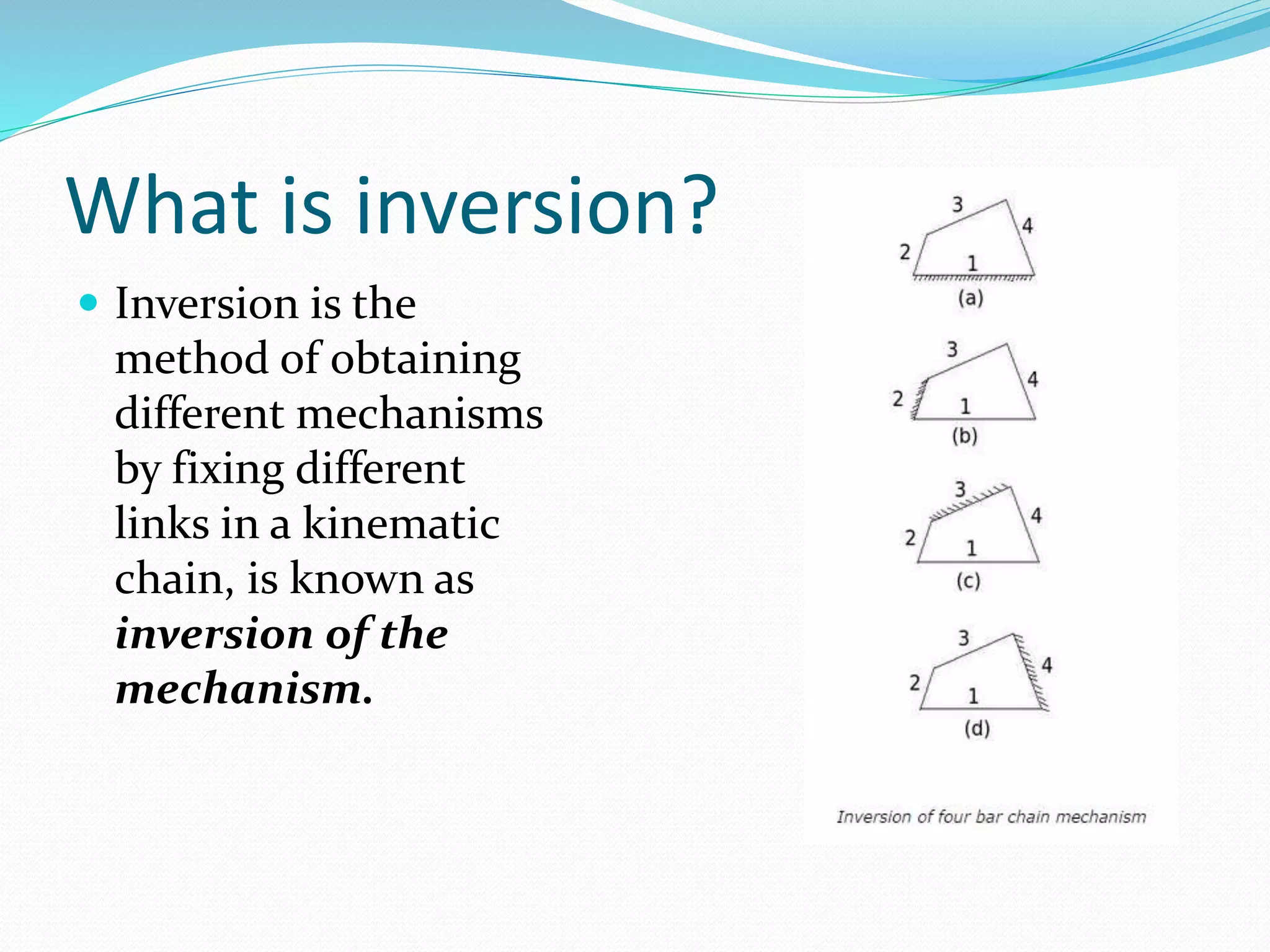
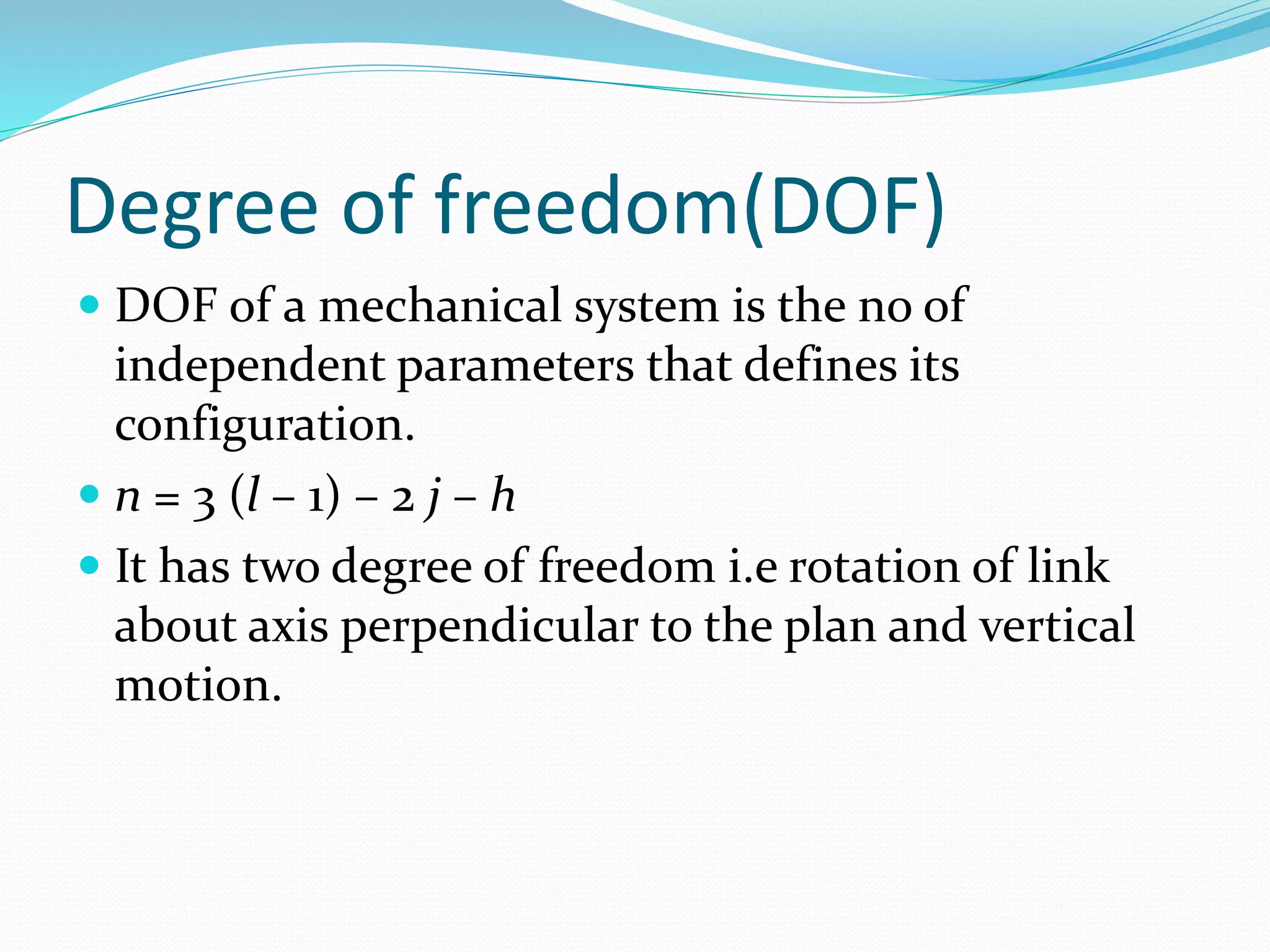
This document defines key terms related to mechanisms and describes the beam engine mechanism. It consists of four links with one end of lever CDE connected to a piston rod. The crank rotates about a fixed center A, causing the lever to oscillate about a fixed center D. This converts the rotary motion of the crank into the reciprocating motion of the piston. Beam engines were widely used in steam engines historically to pump water from mines or into canals.