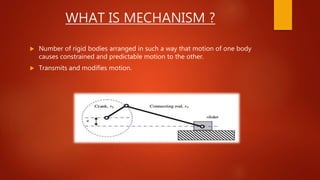
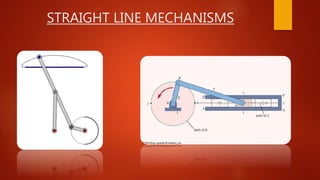
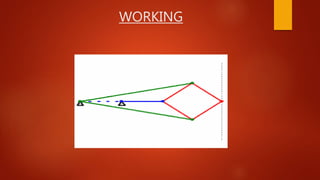
This document summarizes different mechanisms for straight line motion, including the Paucellier mechanism and Robert mechanism. The Paucellier mechanism uses six rigid bars of fixed lengths arranged to produce exact straight line motion from one point. The Robert mechanism is a four bar linkage that converts rotary motion into approximate straight line motion. Both mechanisms have applications in machinery for converting rotational motion into reciprocal or linear motion.