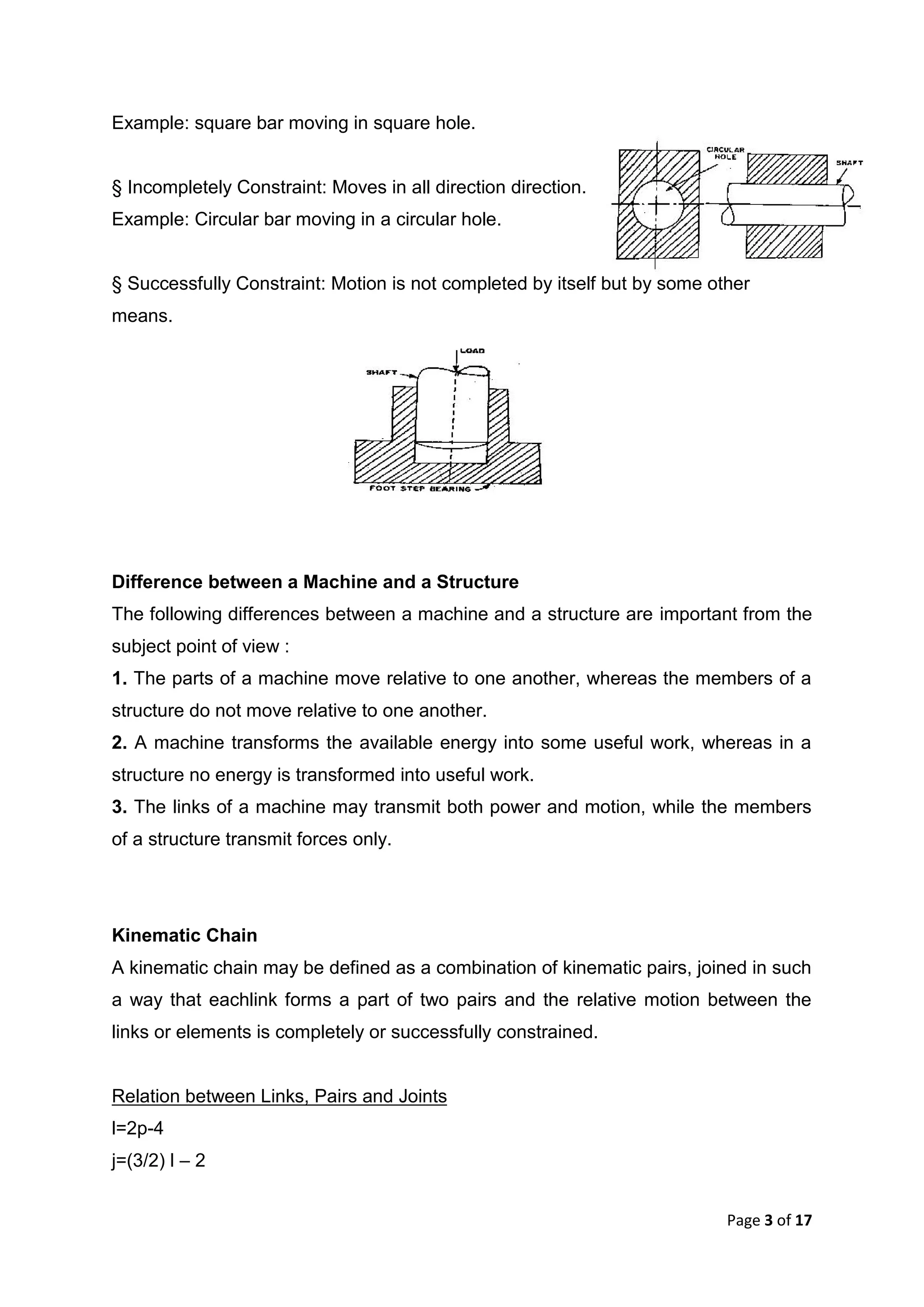
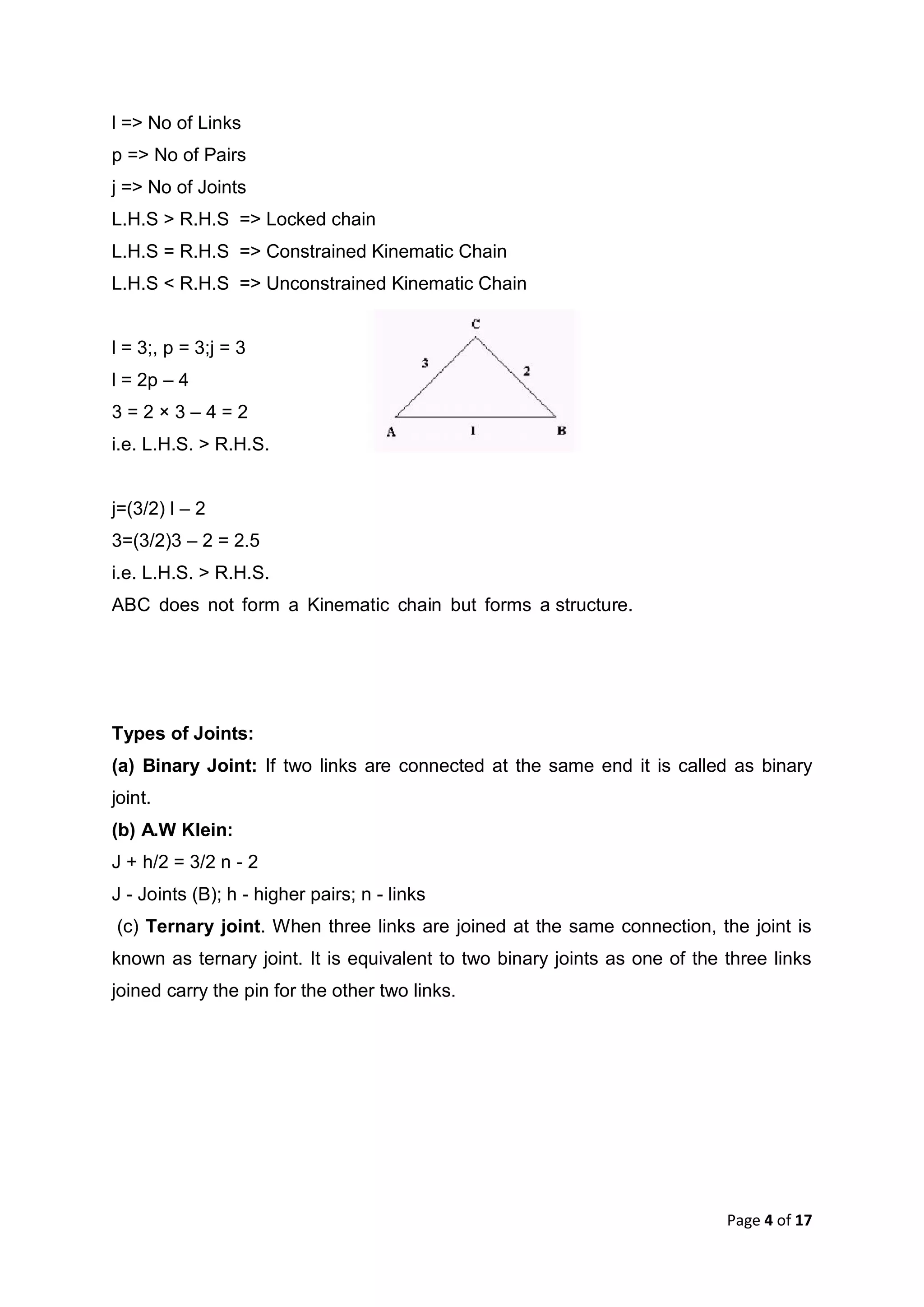
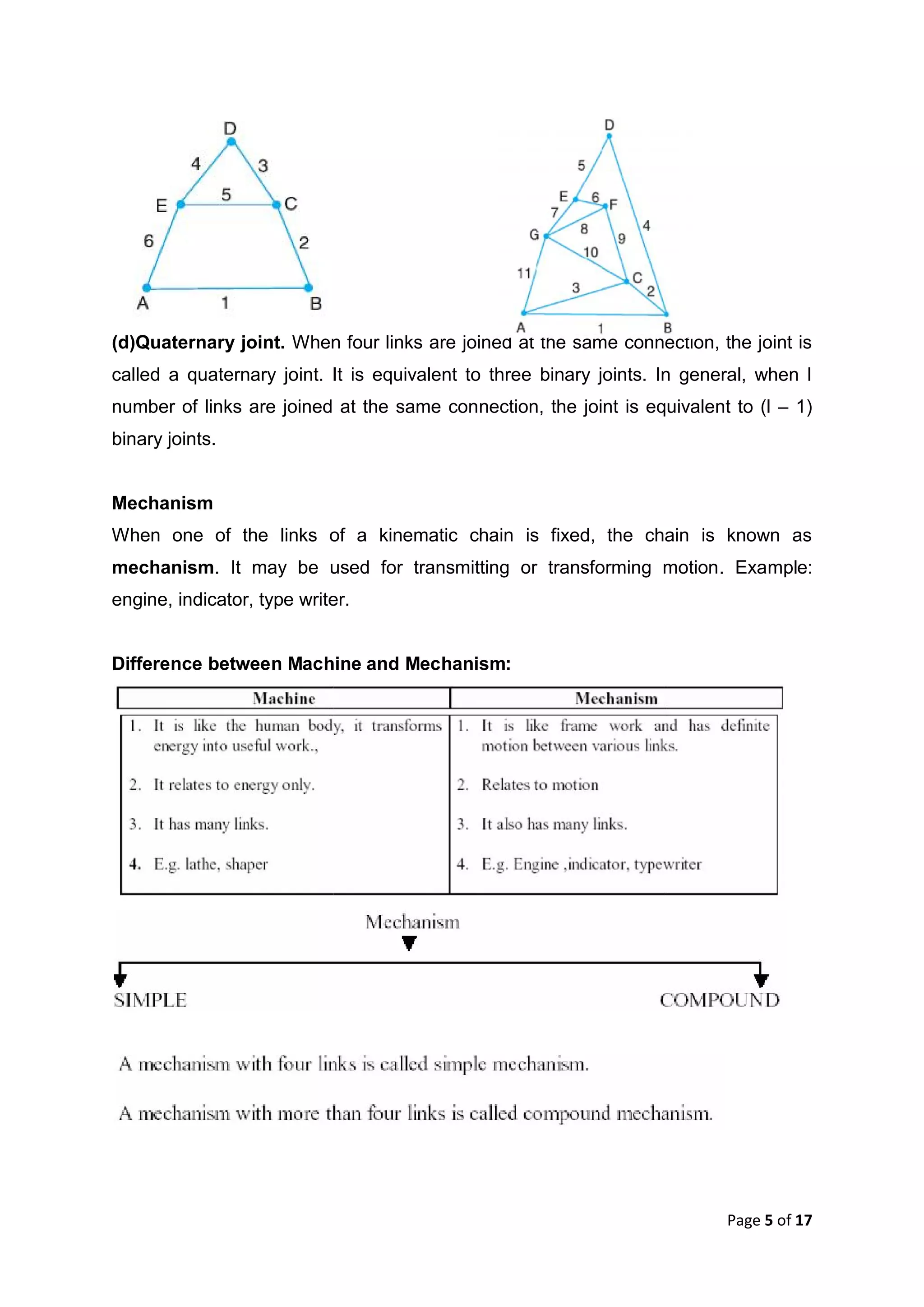
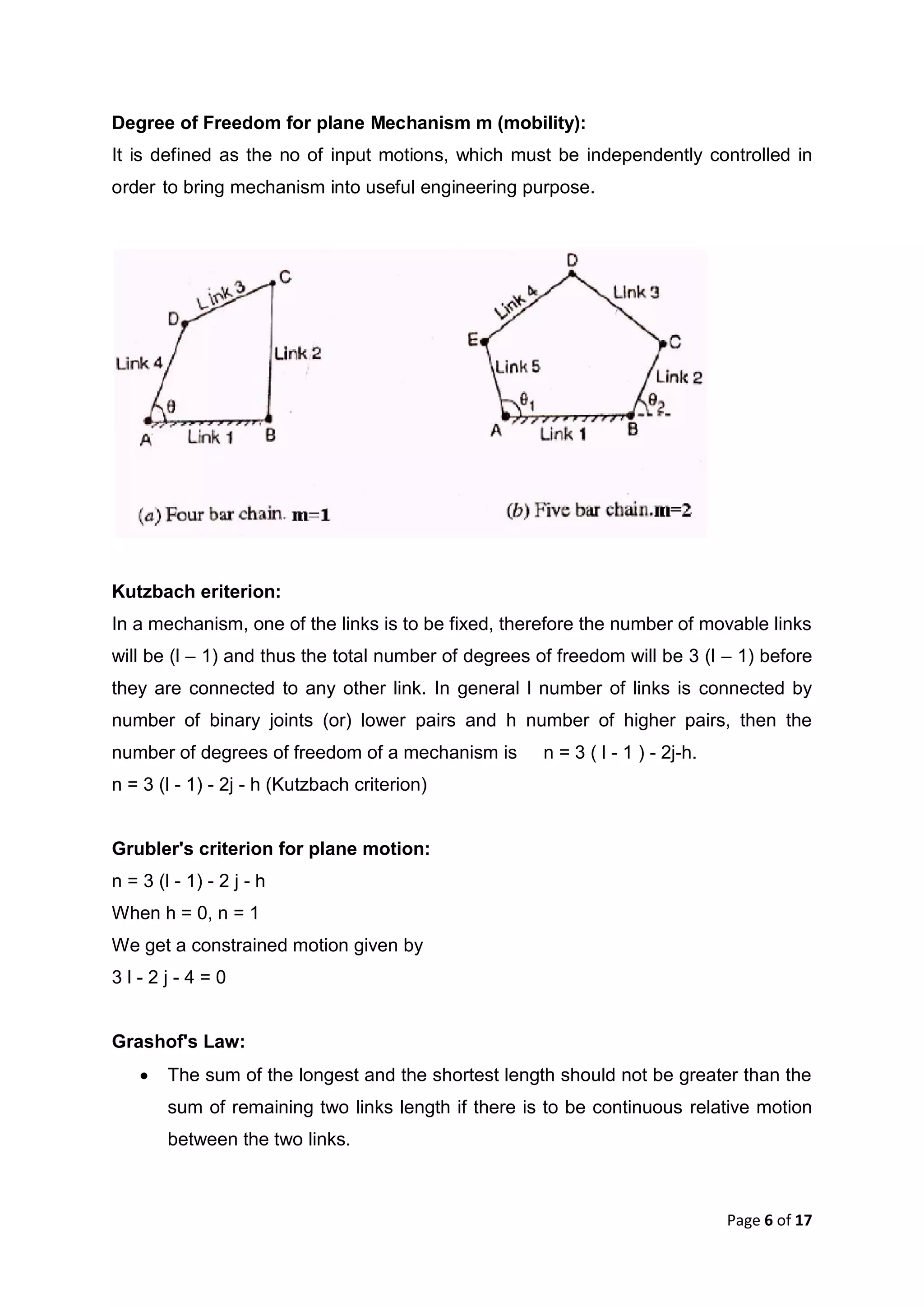
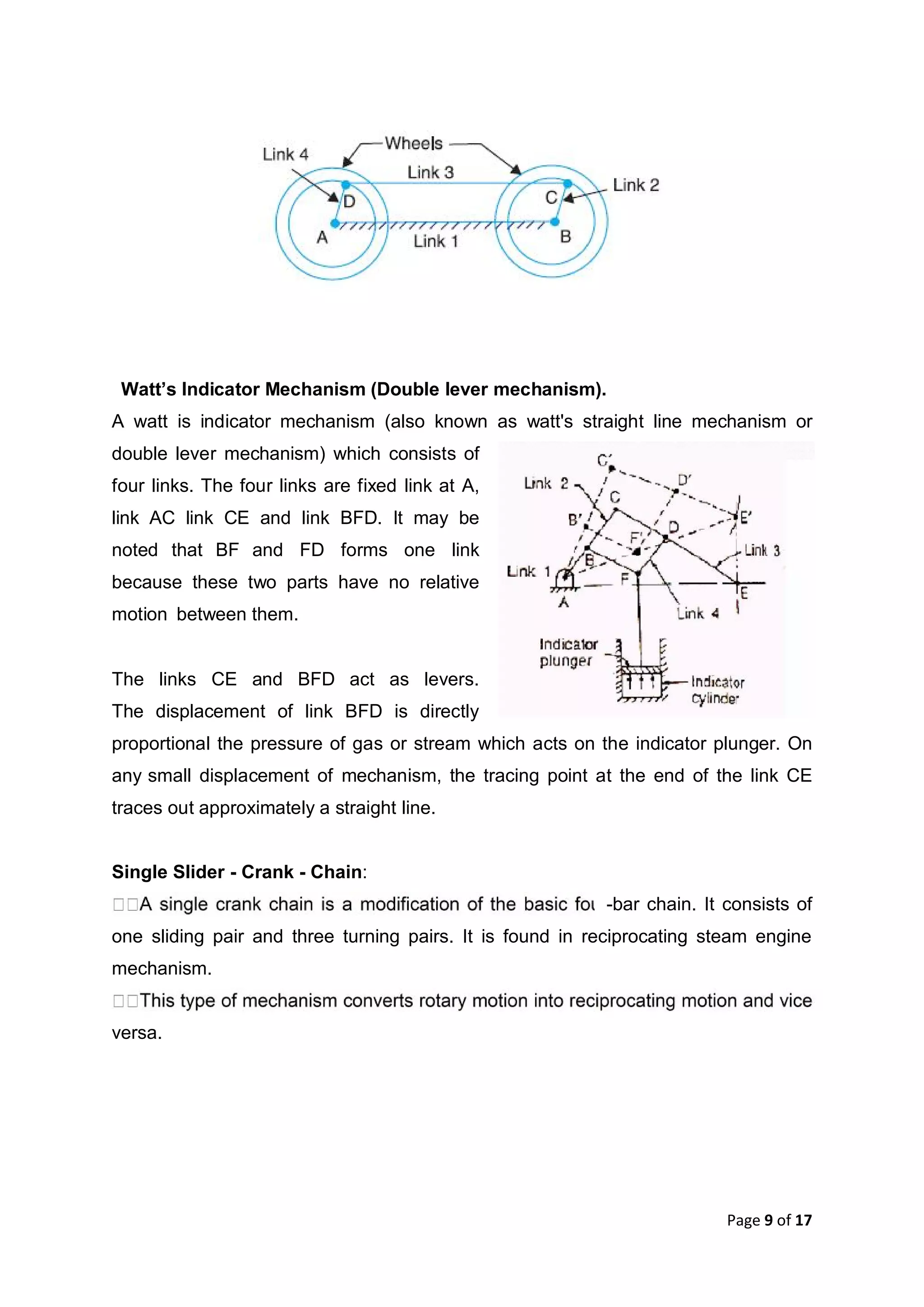
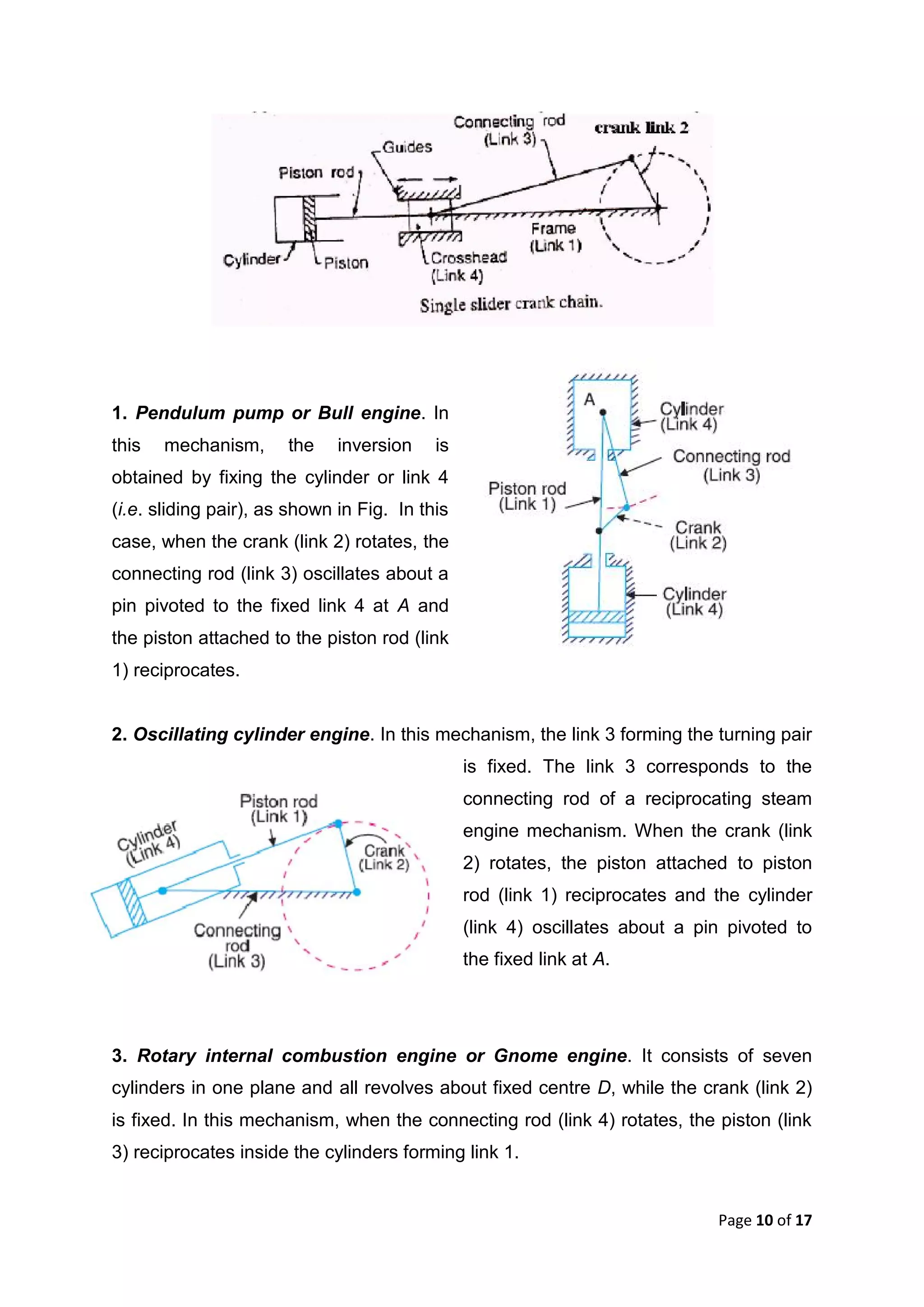
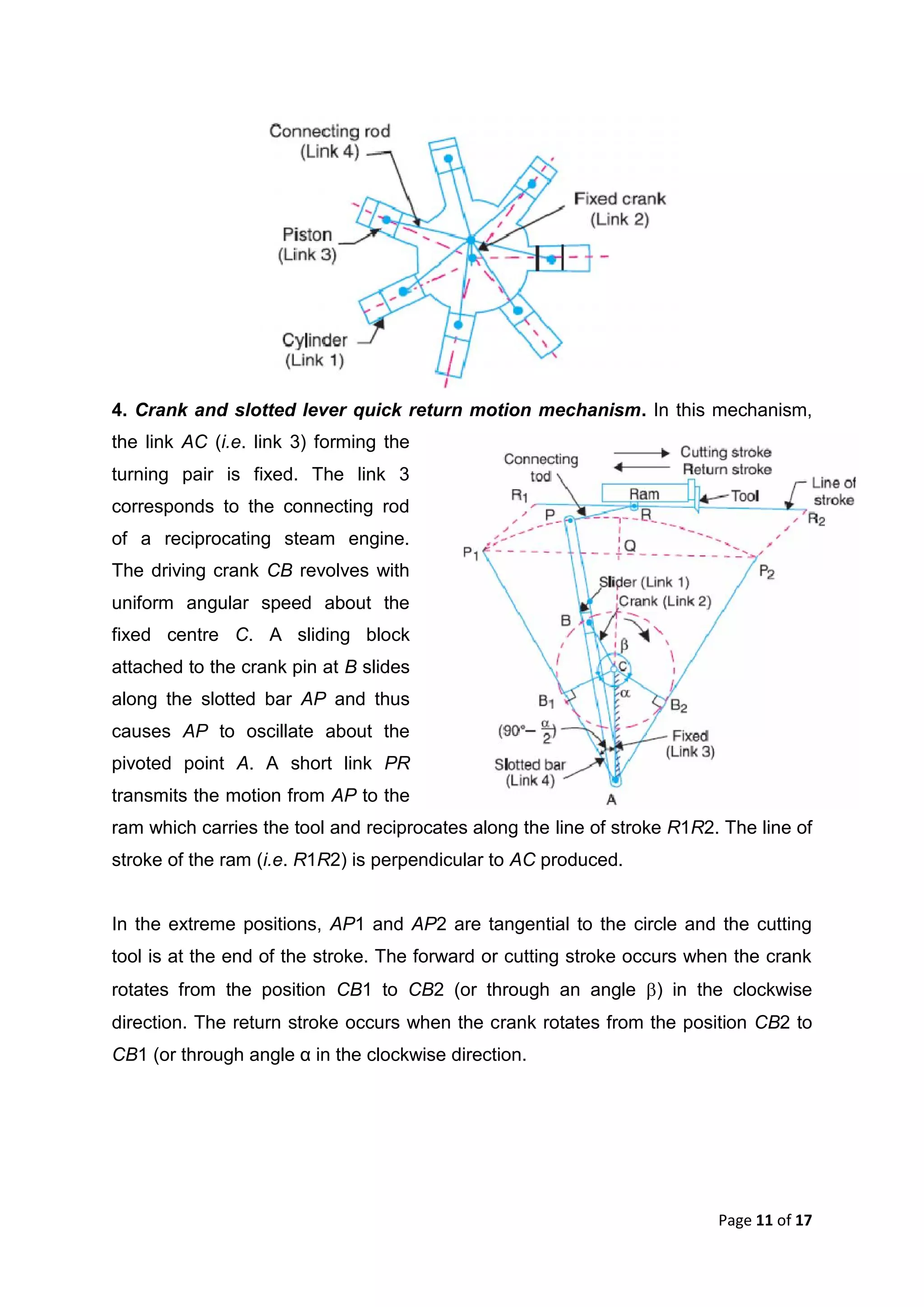
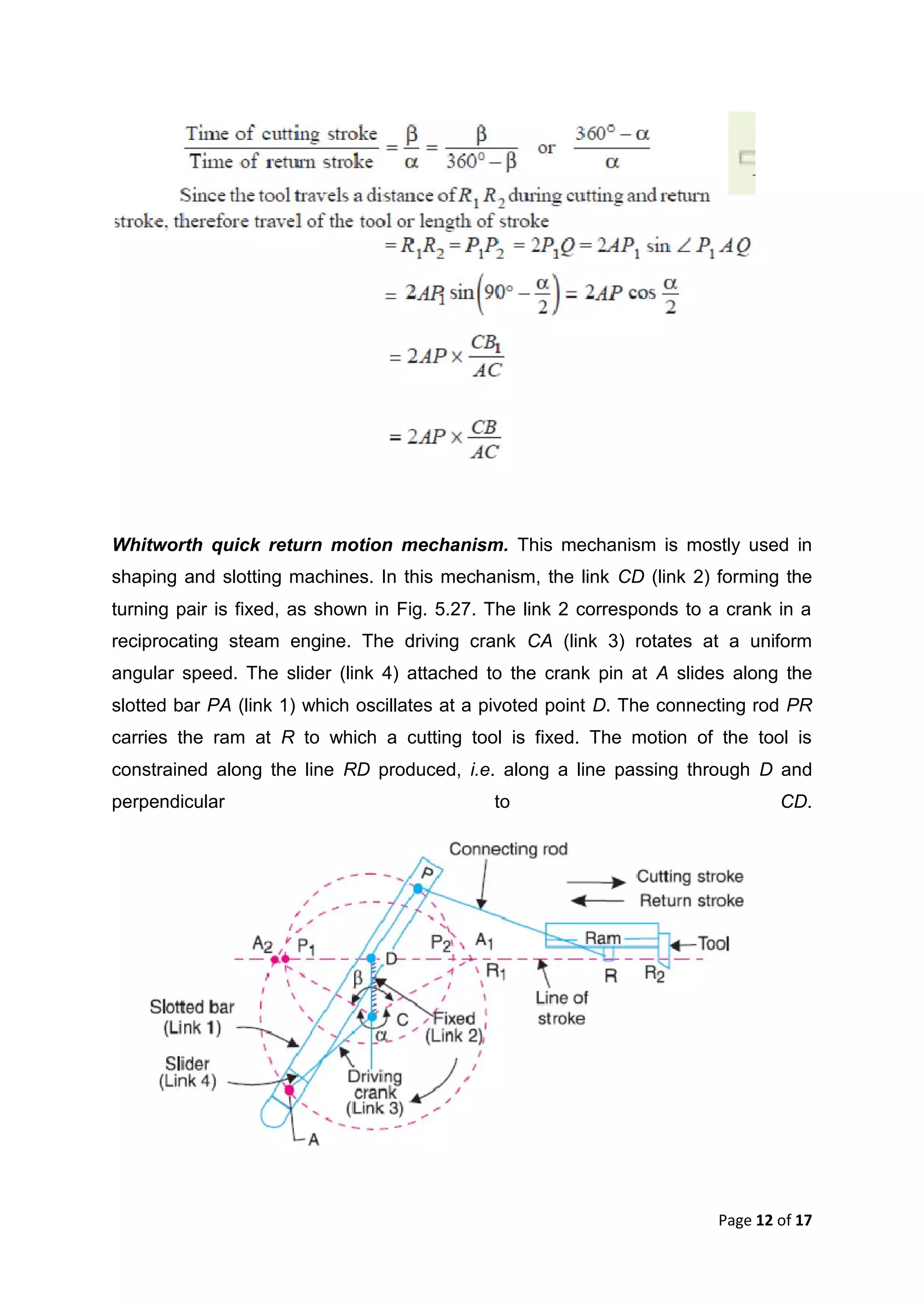
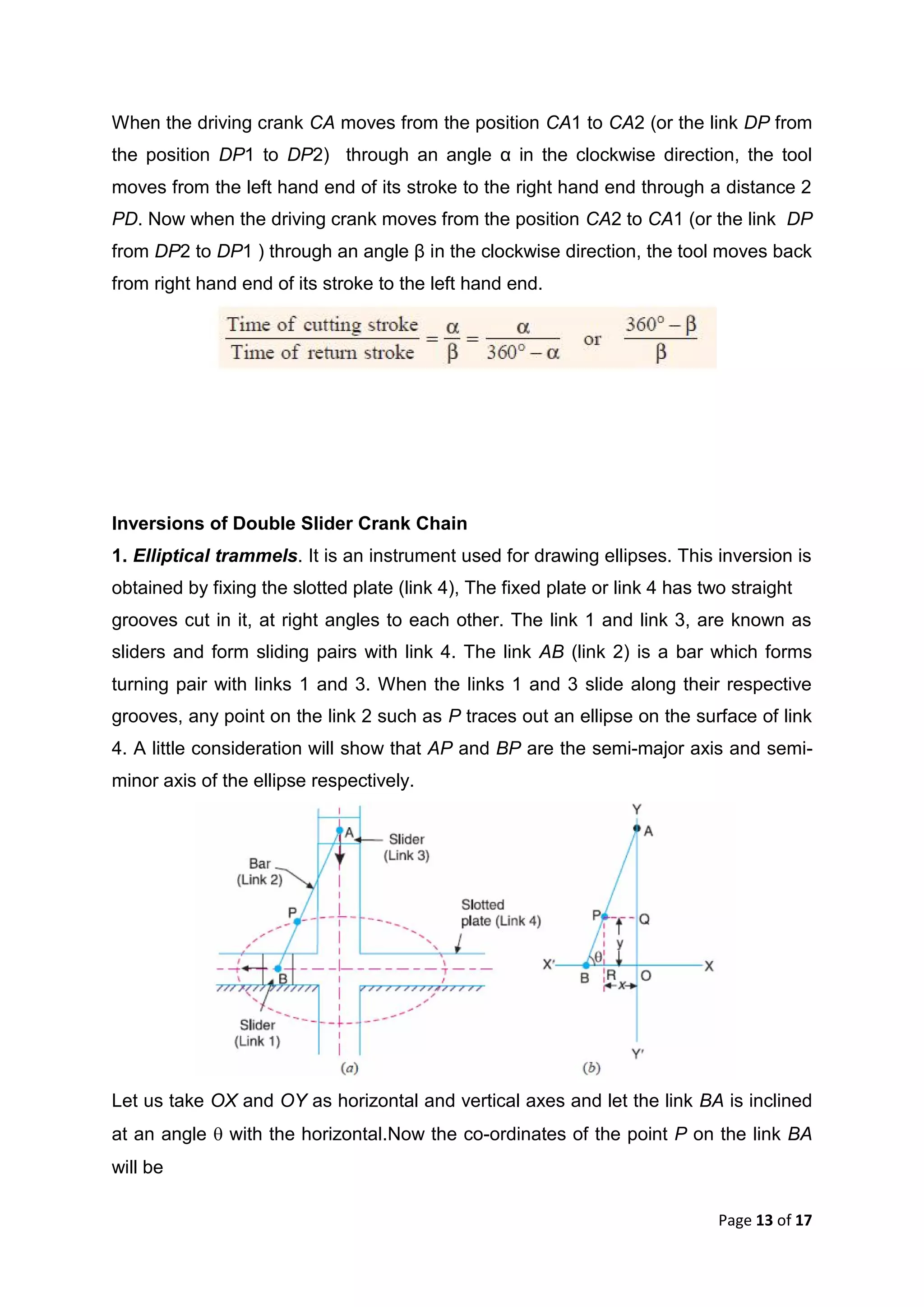
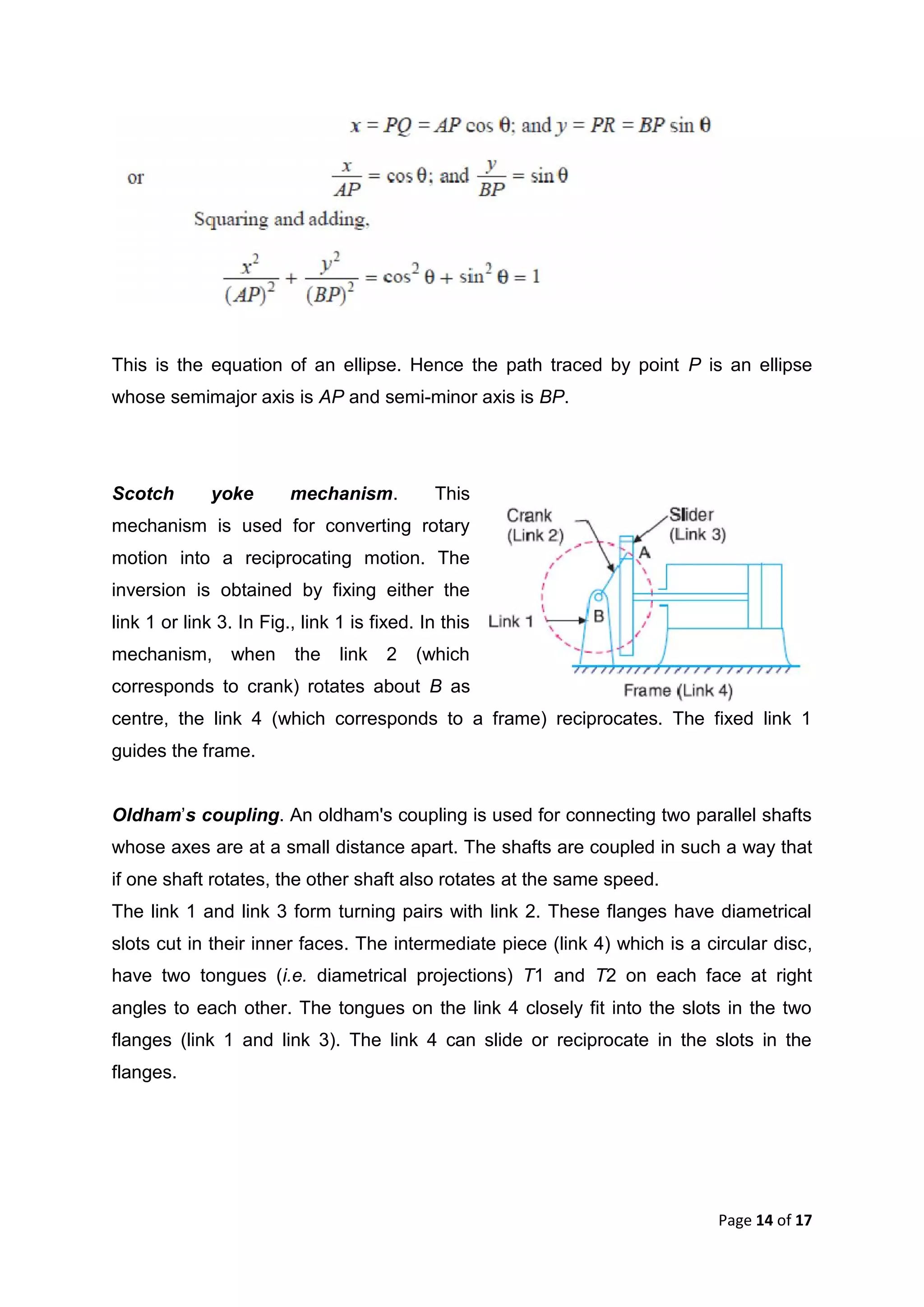
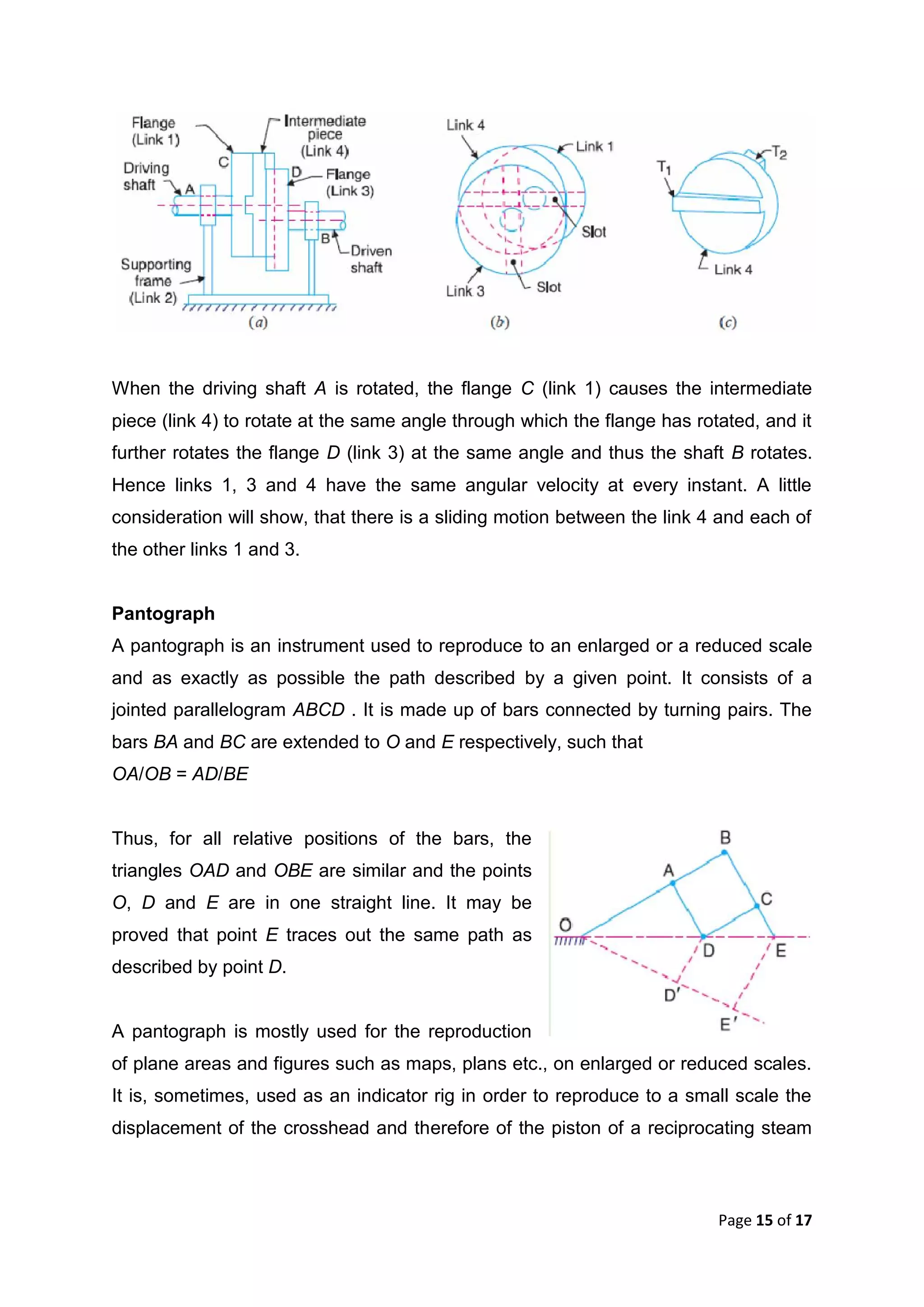
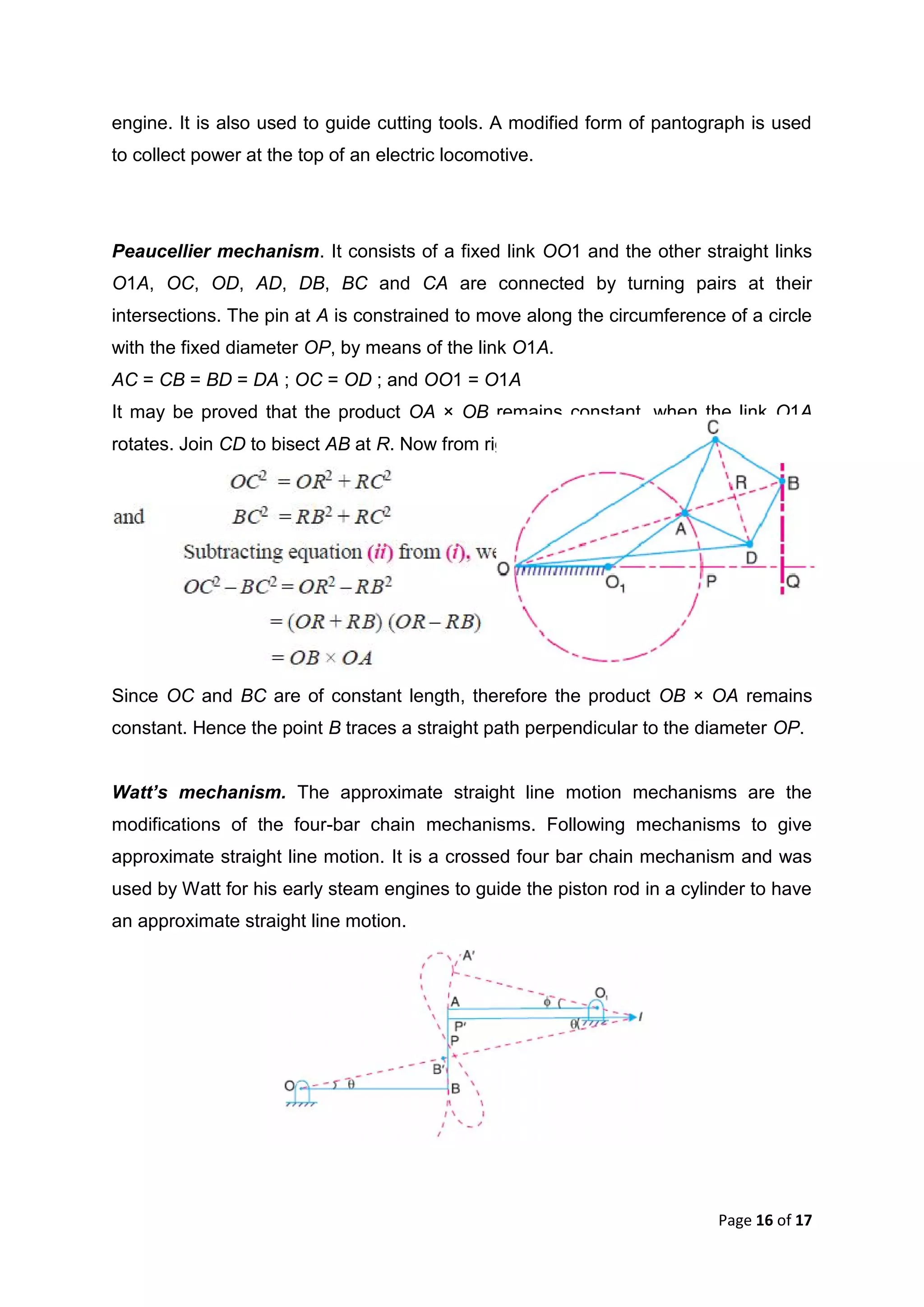
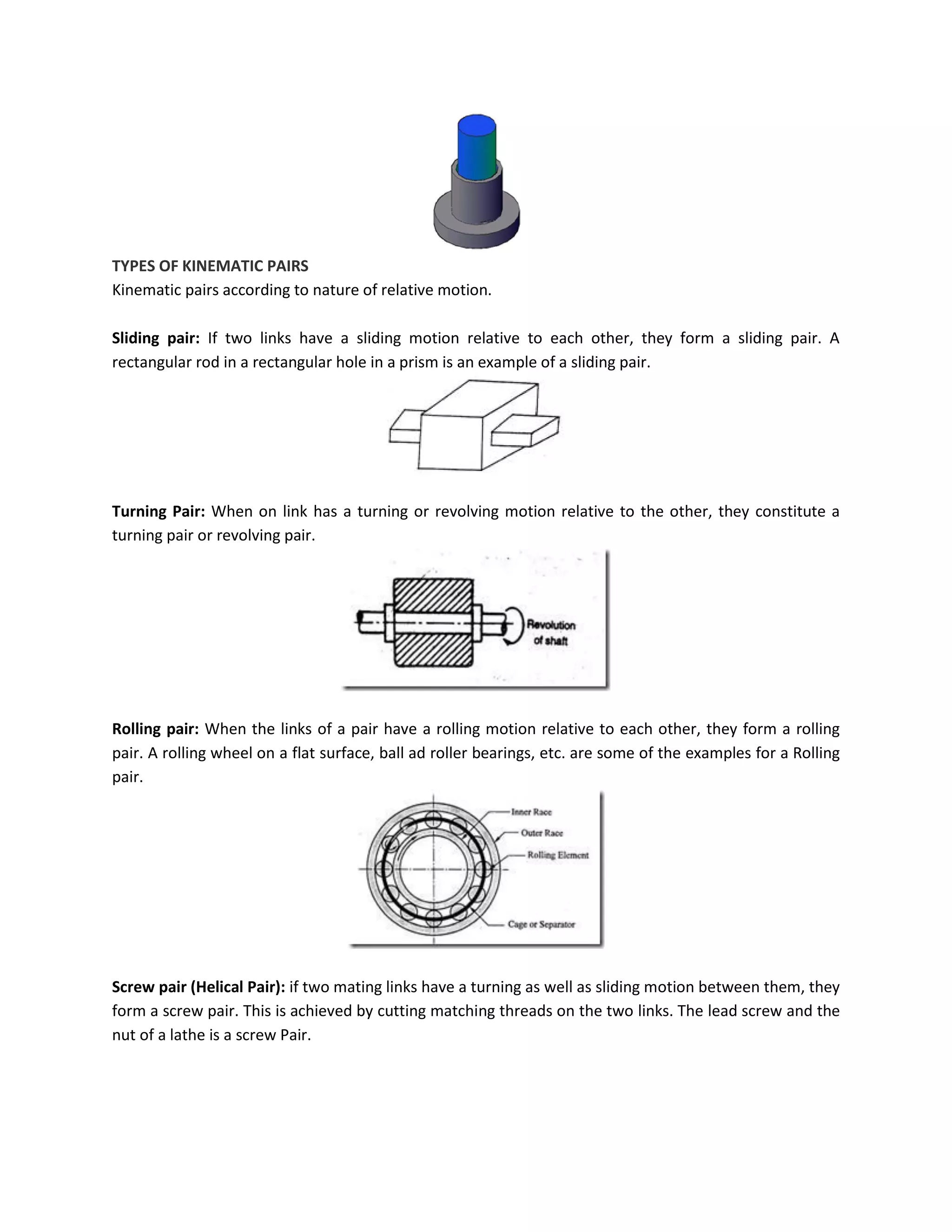
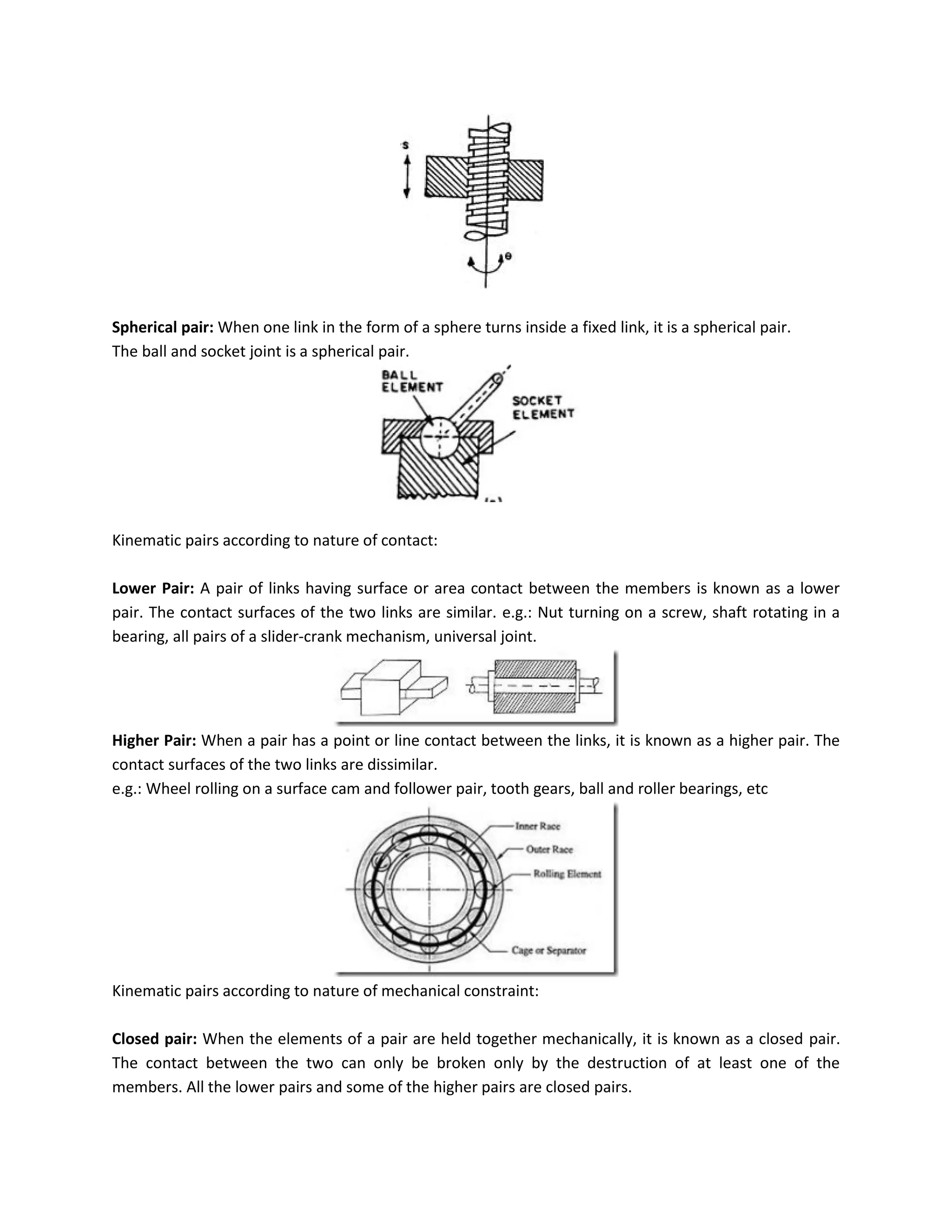
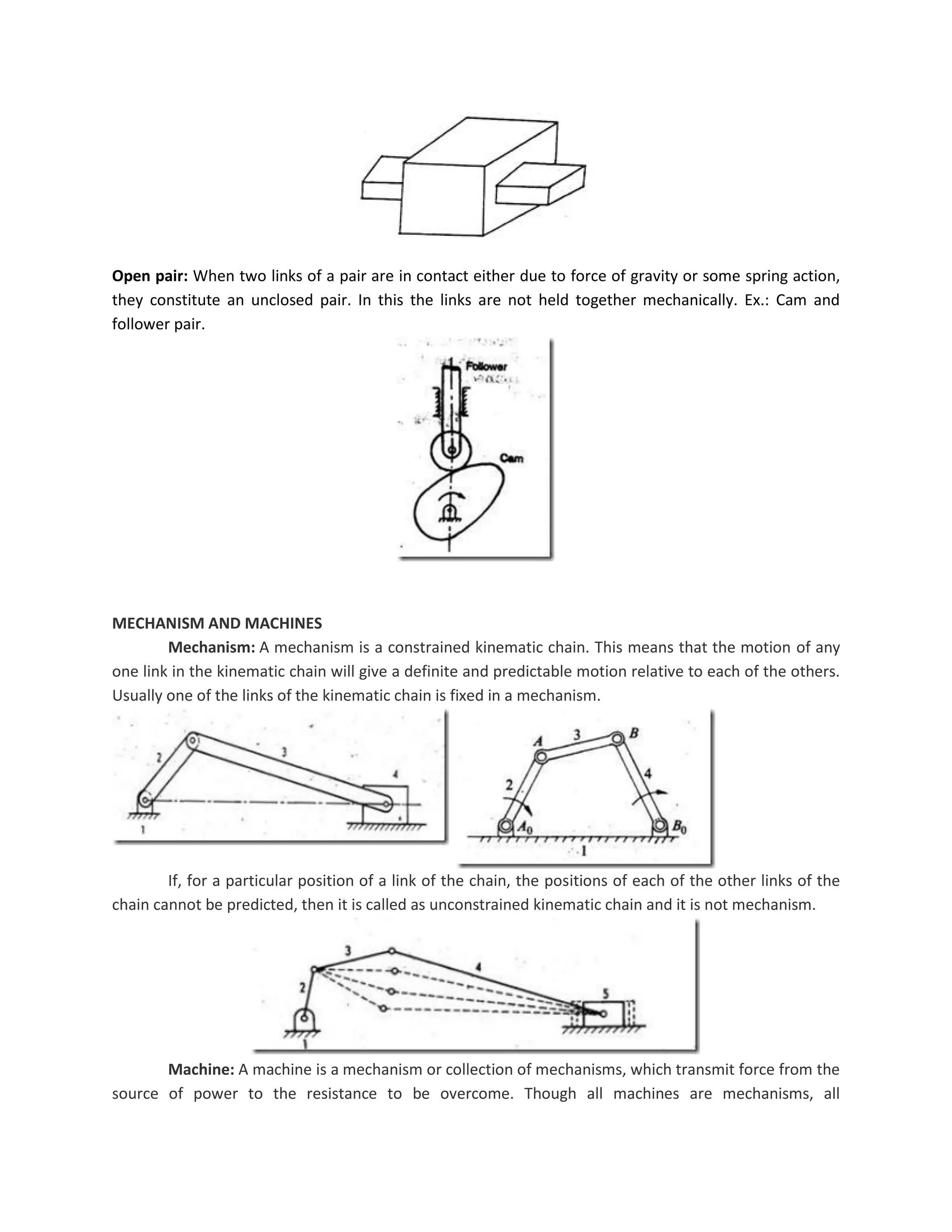
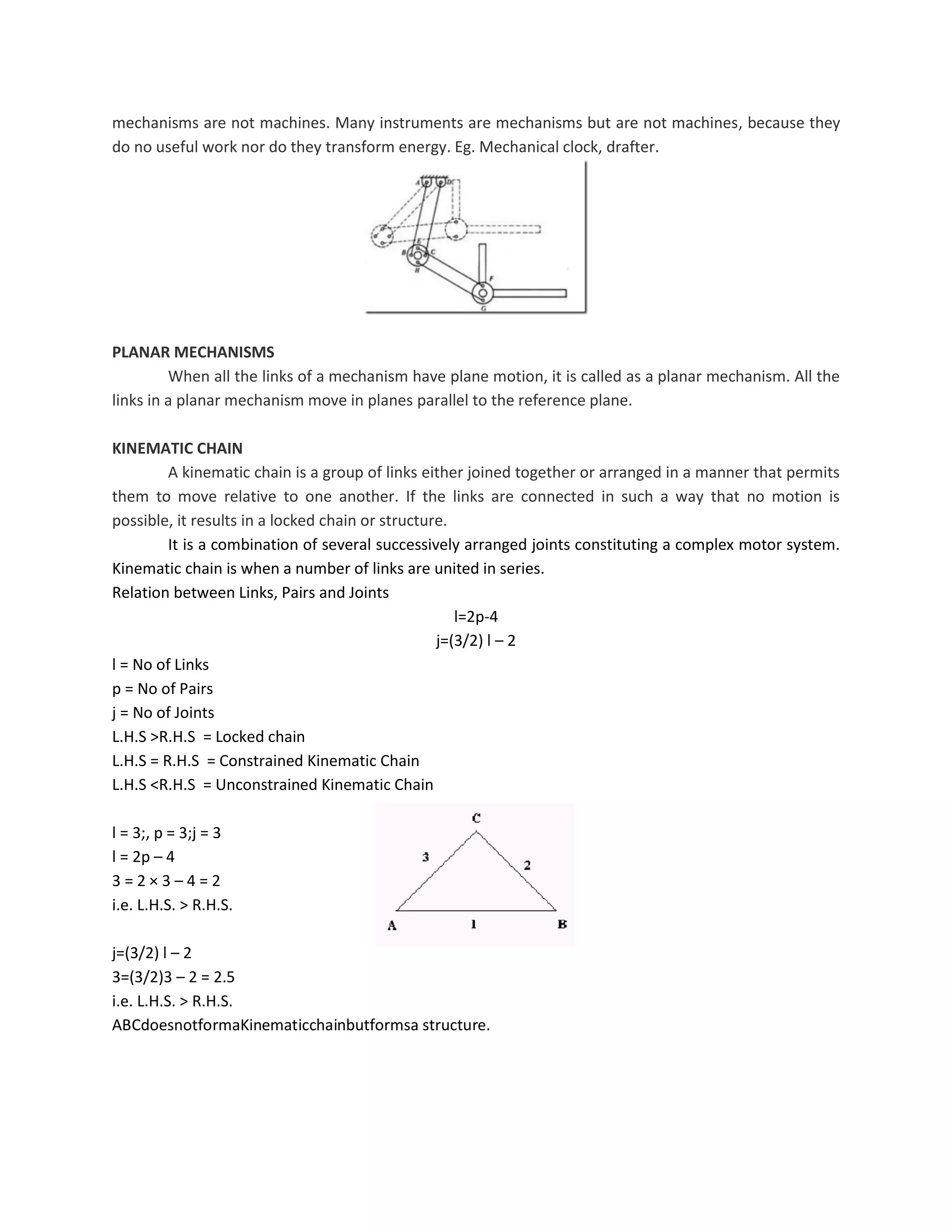
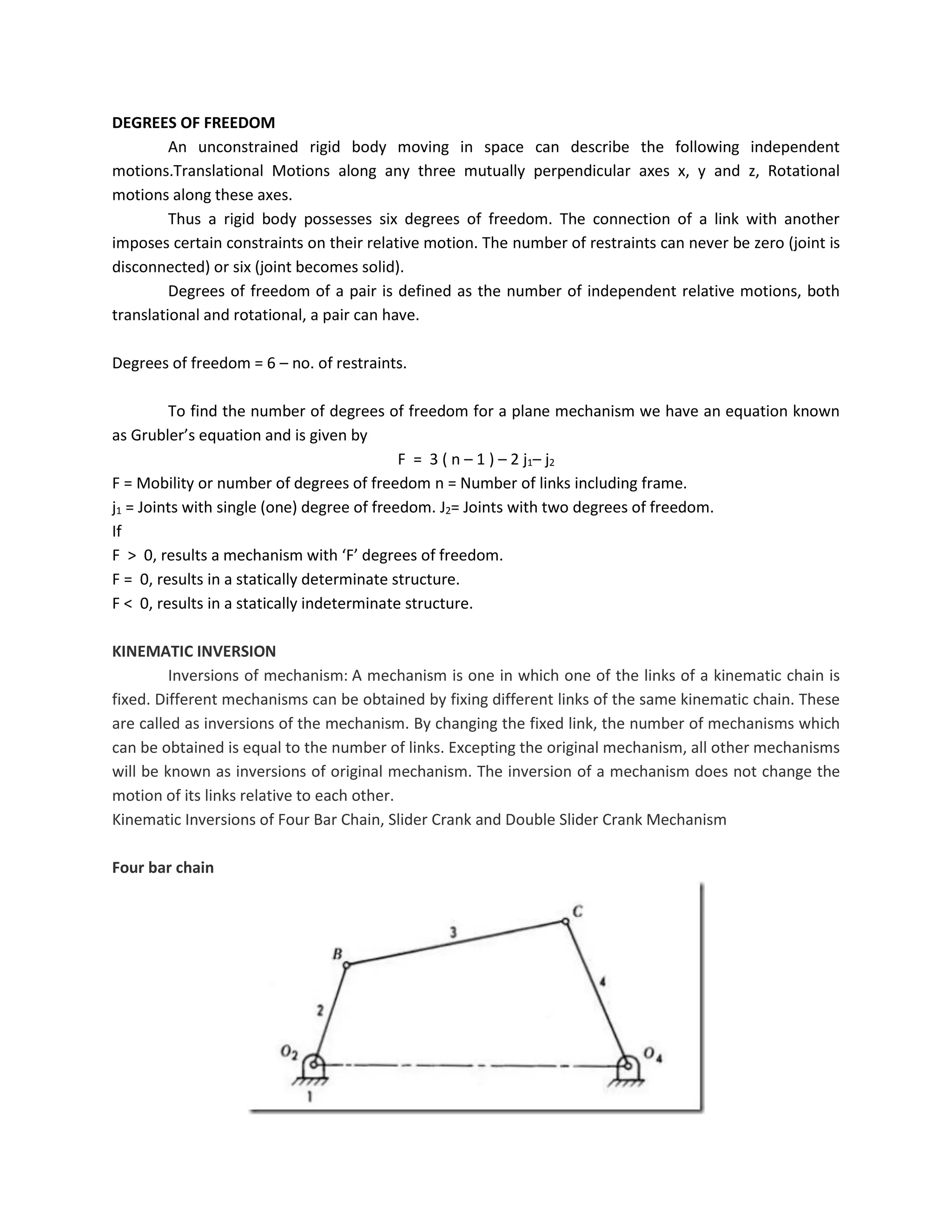
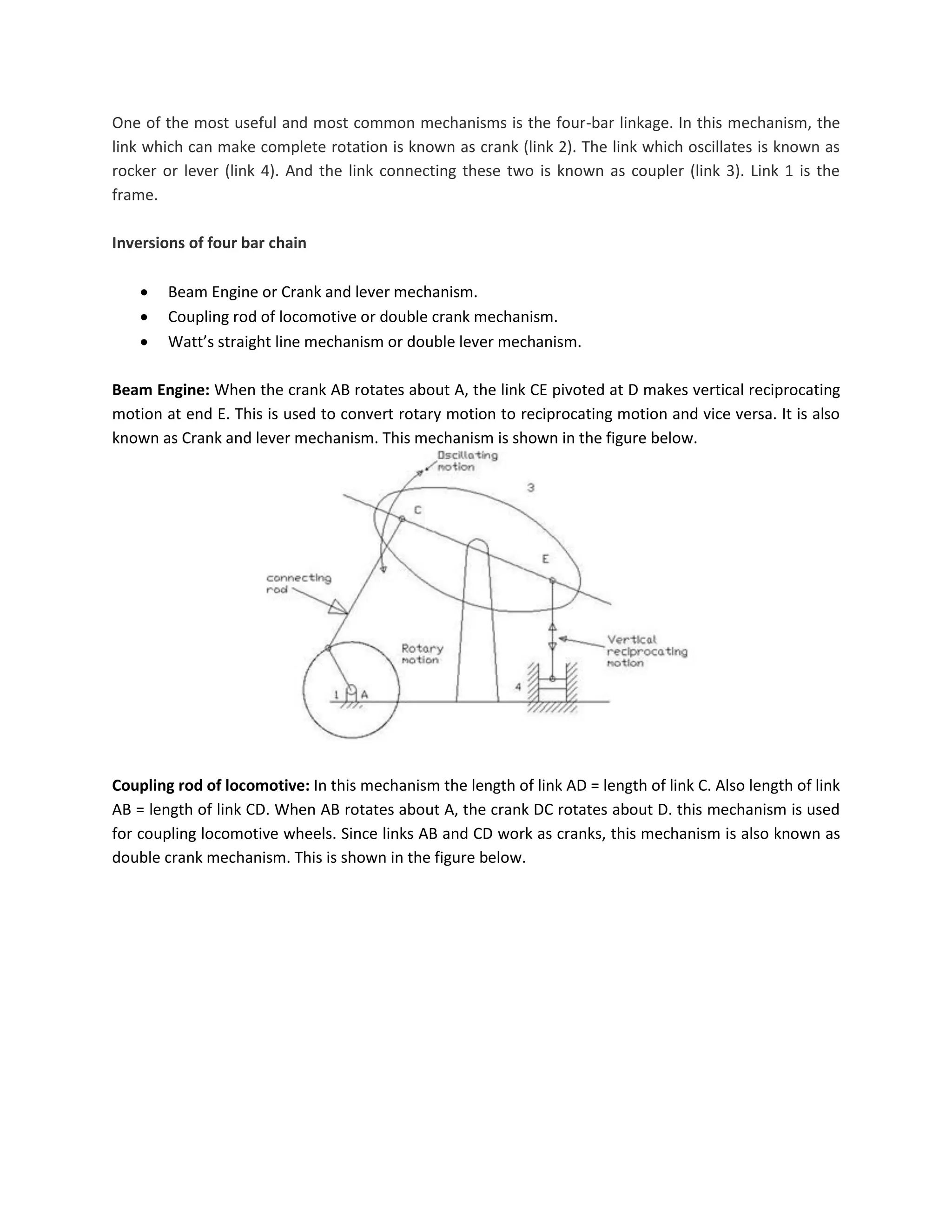
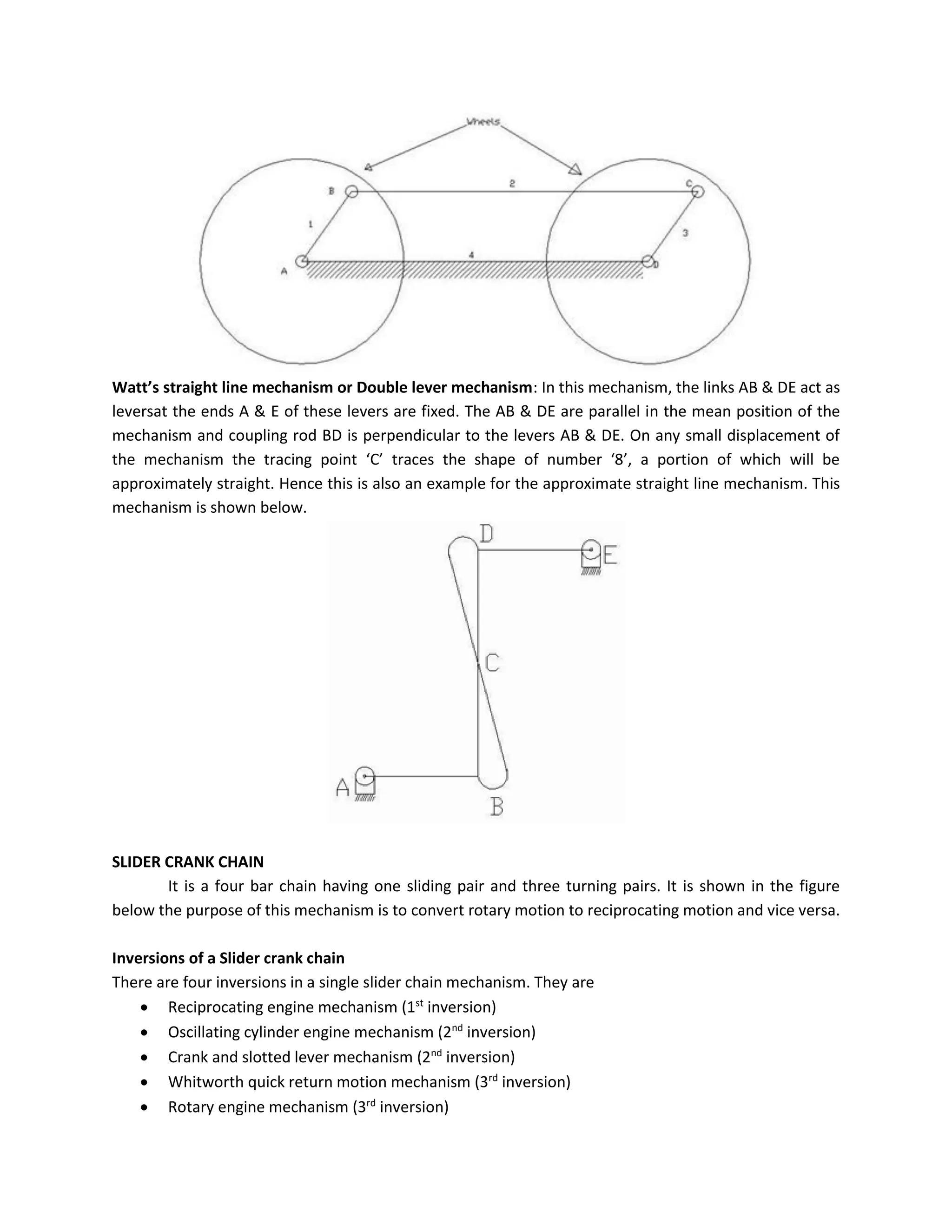
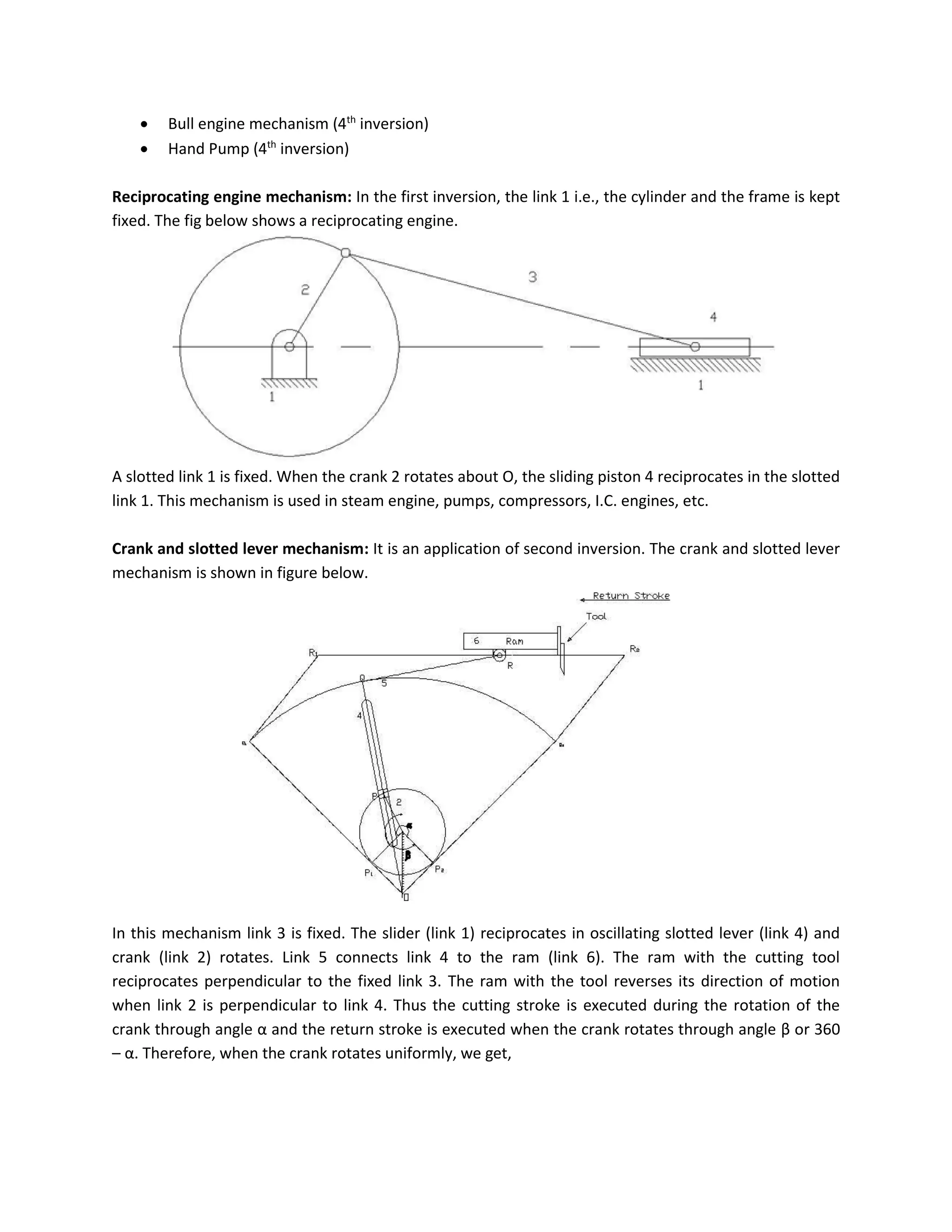
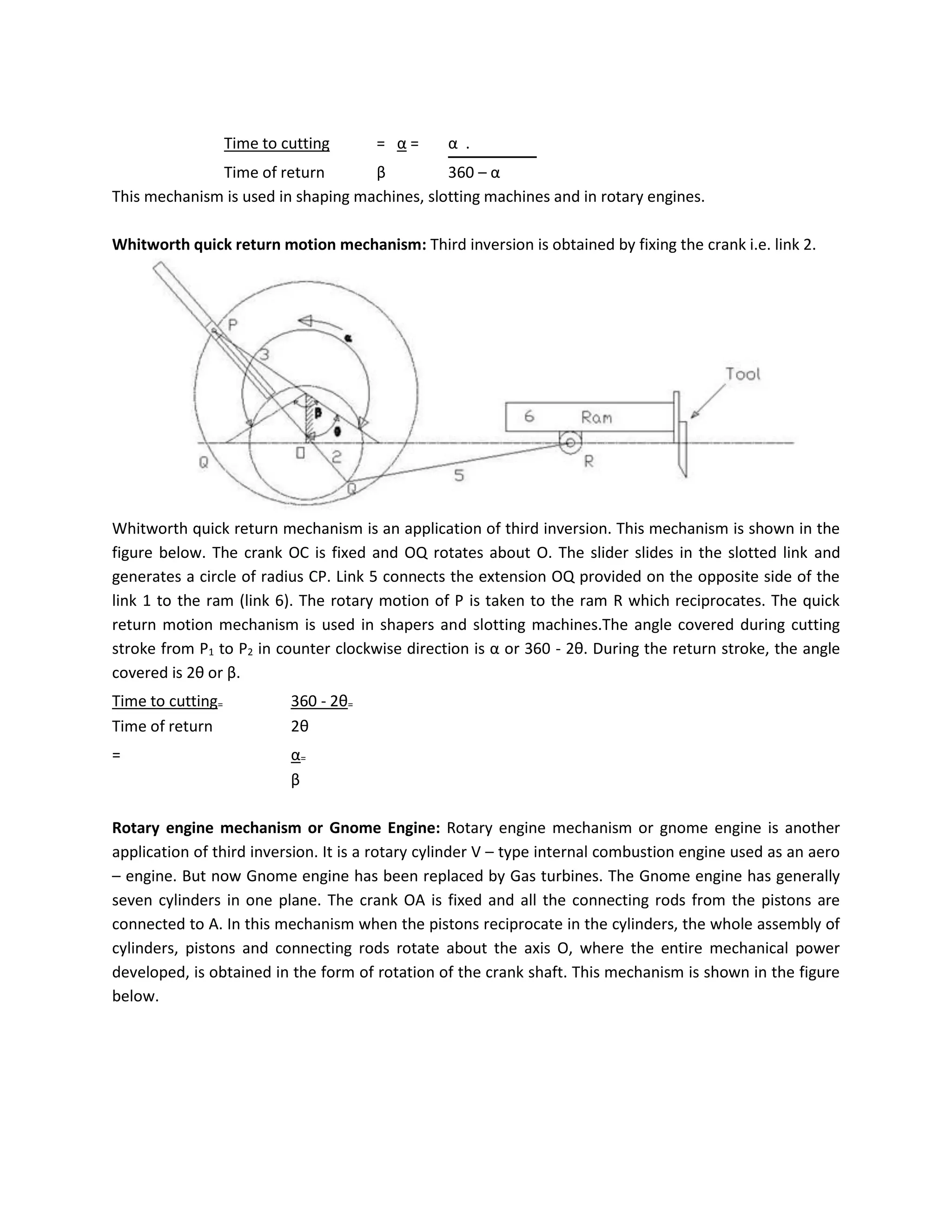
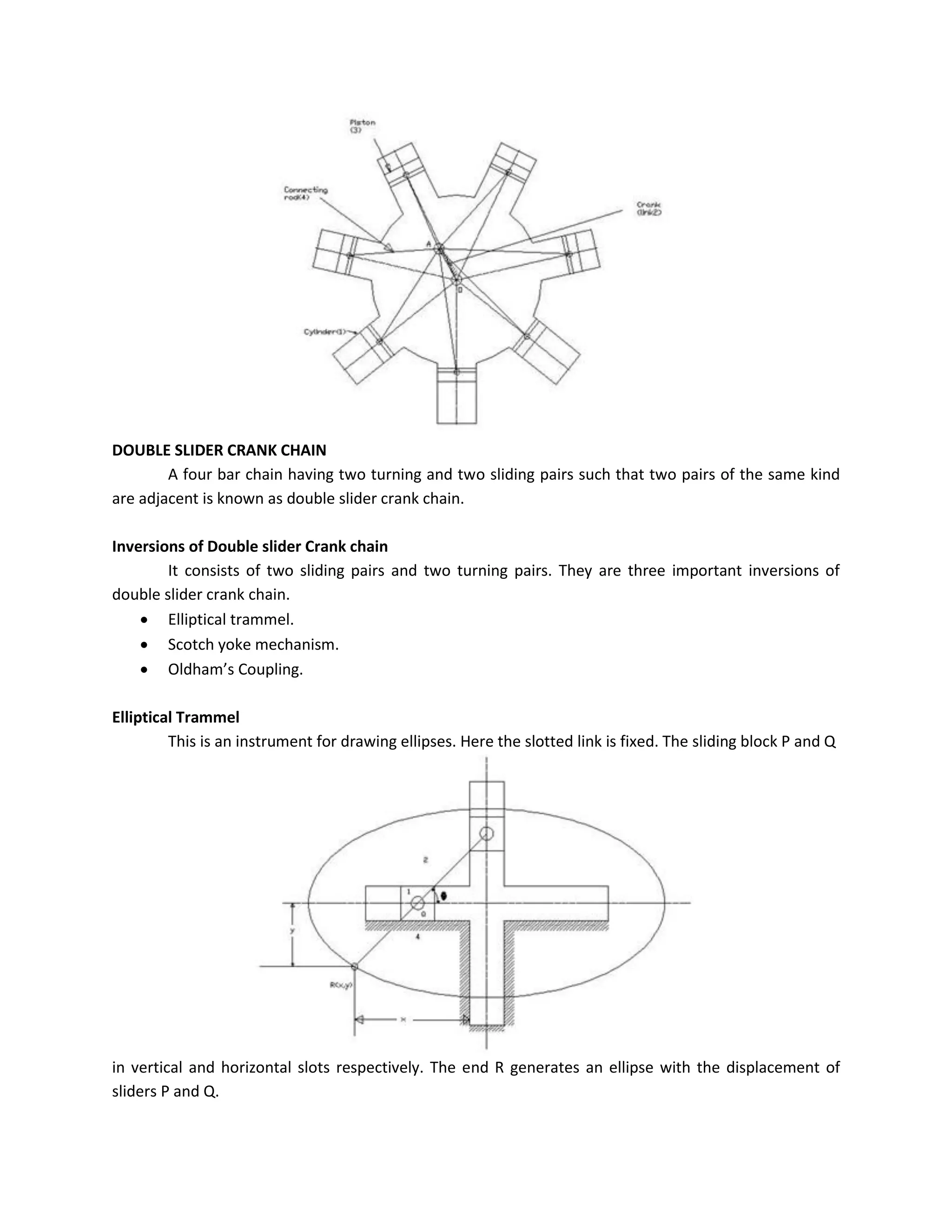
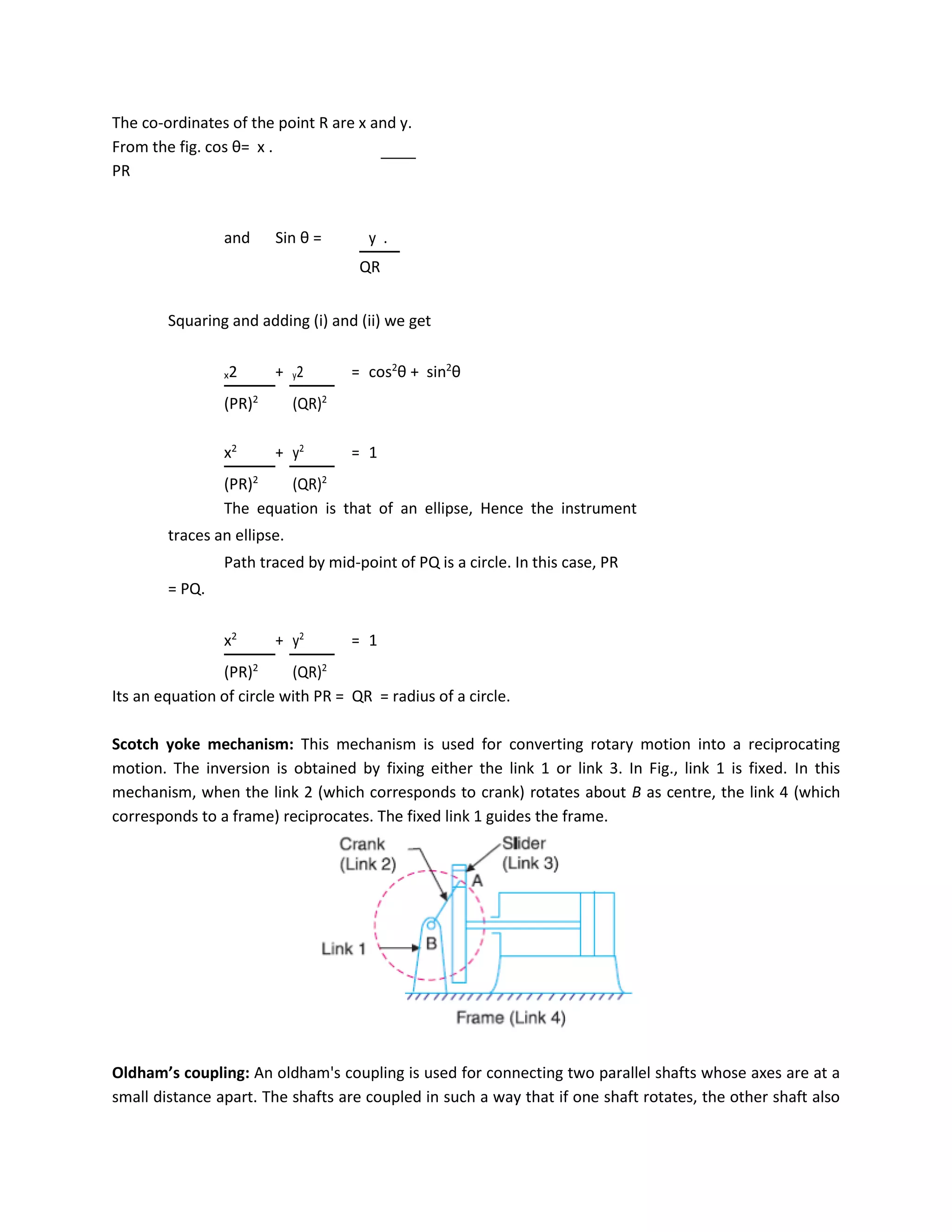
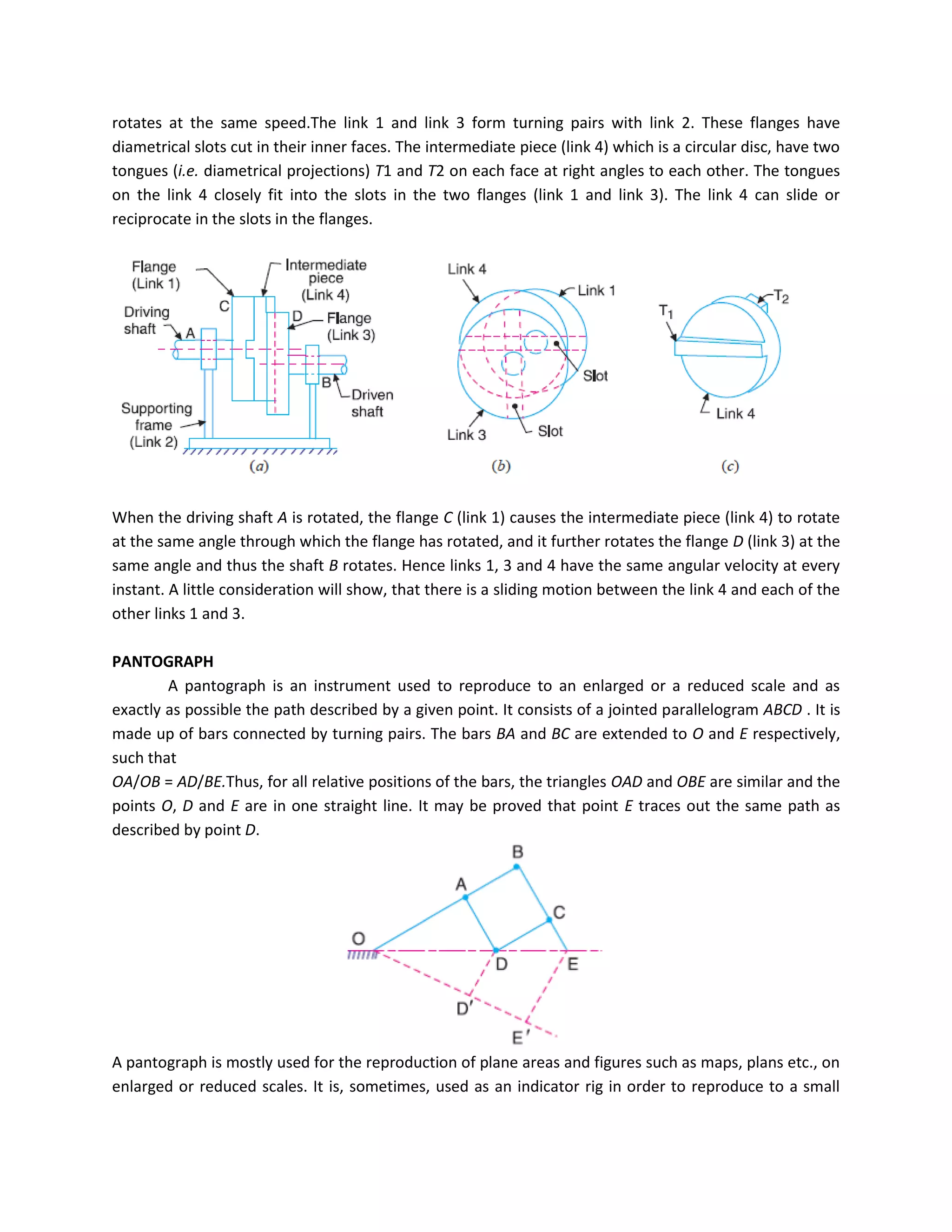
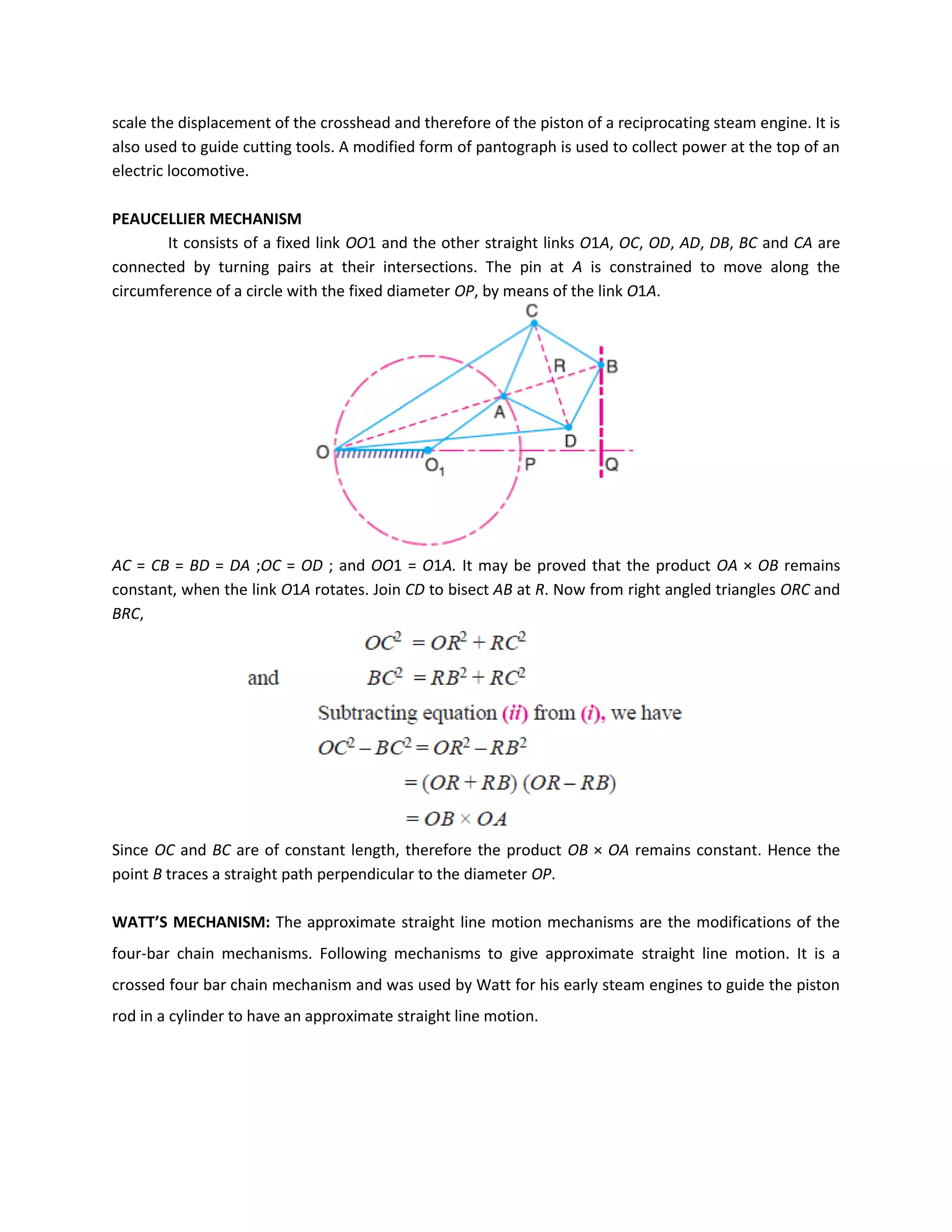
This document discusses kinematic elements and pairs that are components of machines. It defines a kinematic link as any part that moves relative to another, and types of links include rigid, flexible, and fluid. Kinematic pairs constrain the relative motion between two links, and types of pairs are classified by the motion (sliding, turning, rolling, etc.) and contact (lower or higher). A kinematic chain combines multiple pairs so each link belongs to two pairs. When one link is fixed, it forms a mechanism that can transmit or transform motion. Common mechanisms are discussed like four-bar linkages and inversions obtained by fixing different links.