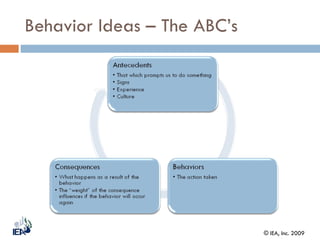
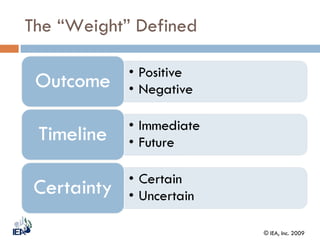
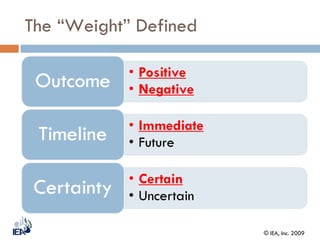
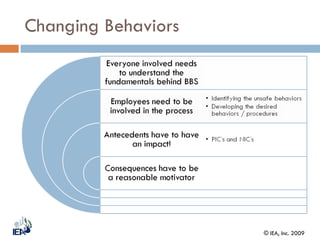
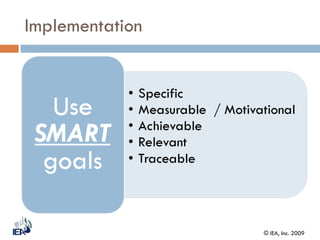
This document discusses Behavior Based Safety (BBS), a program aimed at improving safety by focusing on behaviors. It provides an overview of BBS, explaining that BBS involves employees, drives safety improvement, and can lead to positive cultural changes when implemented correctly. However, BBS requires being part of an overall safety process and culture, and is not a replacement for compliance, training, or hazard removal. The document then discusses key aspects of implementing a successful BBS program, such as defining behaviors to observe and improve, understanding what drives both safe and unsafe behaviors, providing positive reinforcement, and focusing on achievements rather than failures.












![Contact Info Email: [email_address] Phone: 507-281-6661 Cell: 507-884-6691 LinkedIn http://www.linkedin.com/in/timpuyleart](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbsoverview-124447660659-phpapp02/85/BBS-Overview-20-320.jpg)