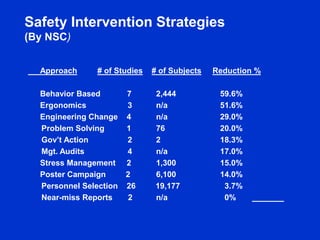
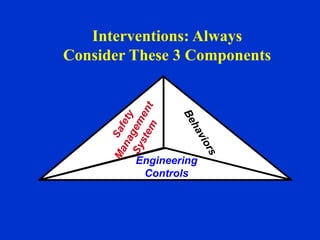
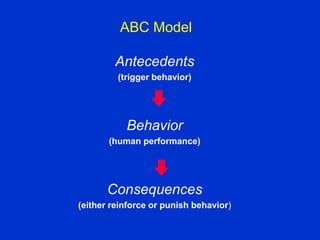
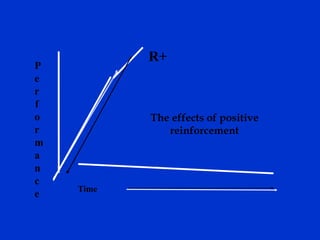
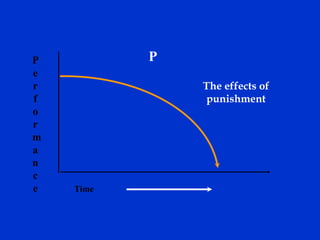
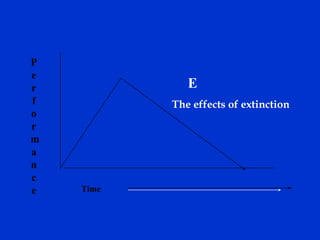
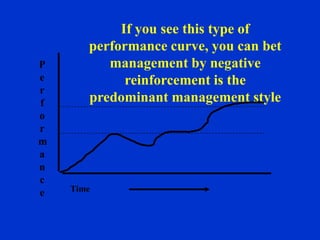
The document discusses behavior-based safety (BBS) as a superior approach compared to traditional safety programs, highlighting the importance of understanding employee behavior and implementing positive reinforcement. It critiques common misconceptions in safety management and emphasizes the need for a proactive safety culture driven by continuous improvement and accountability. Effective BBS requires careful observation, clear definitions of safe versus at-risk behaviors, and meaningful employee involvement to achieve significant reductions in incidents.