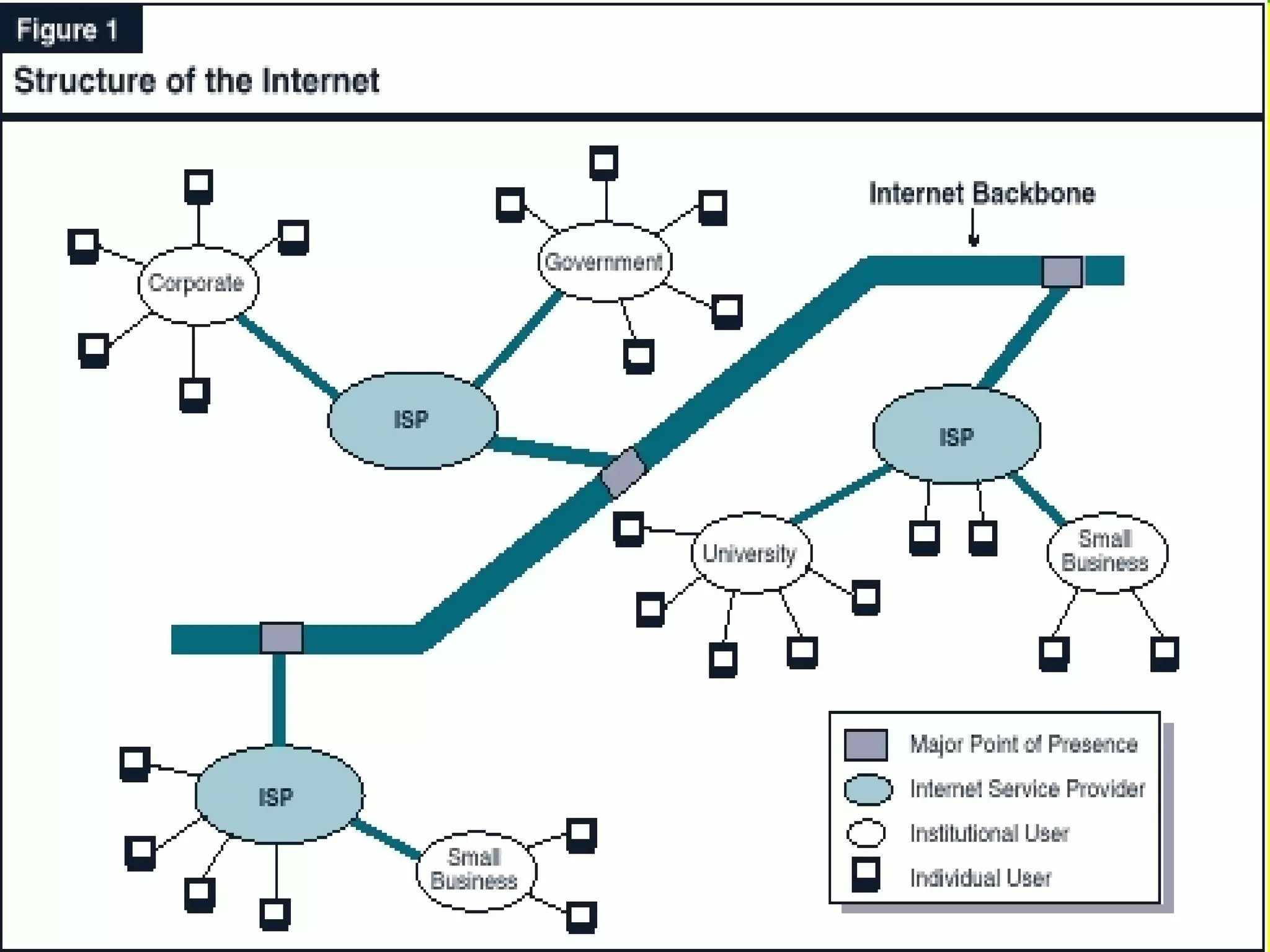
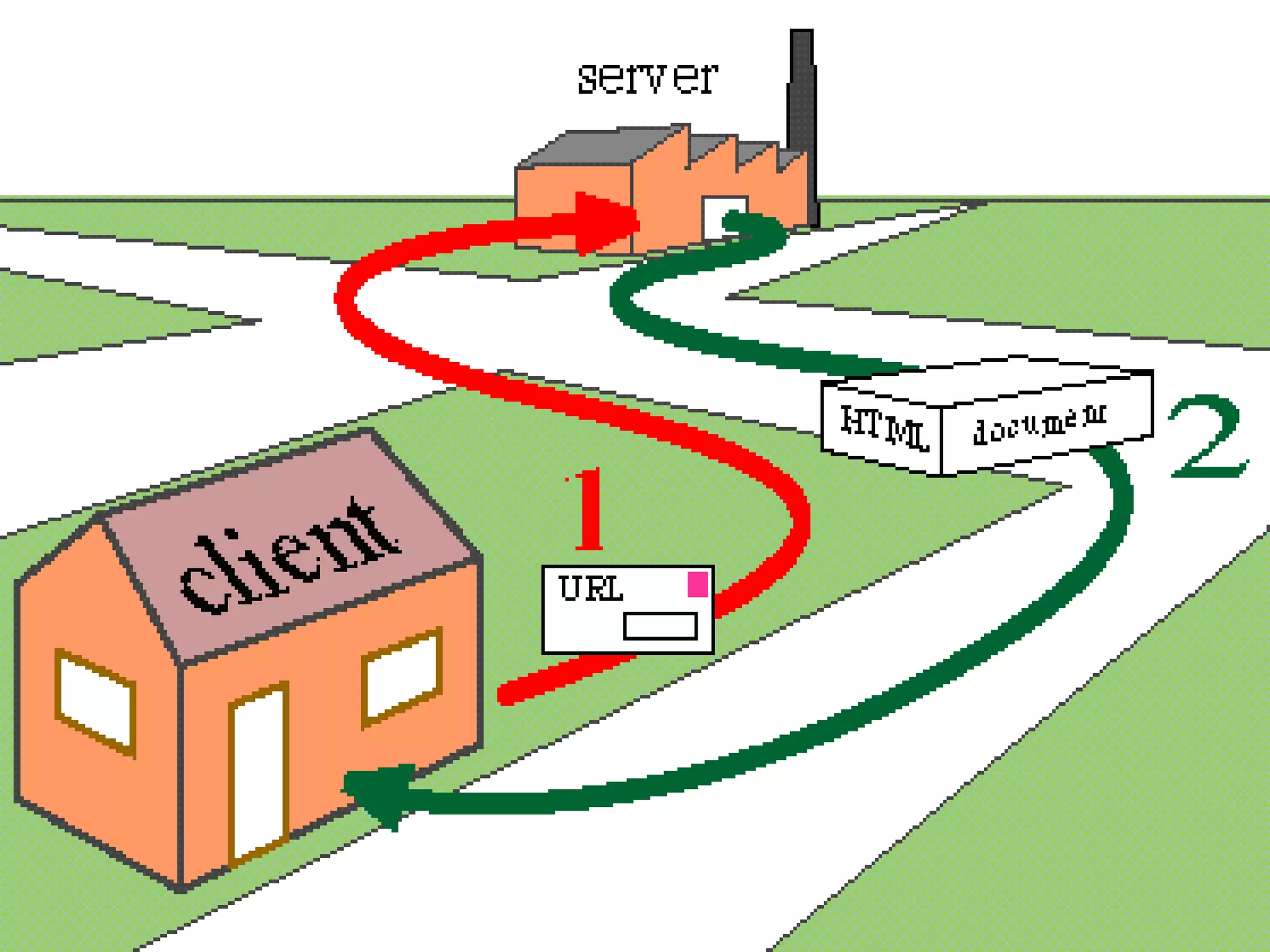
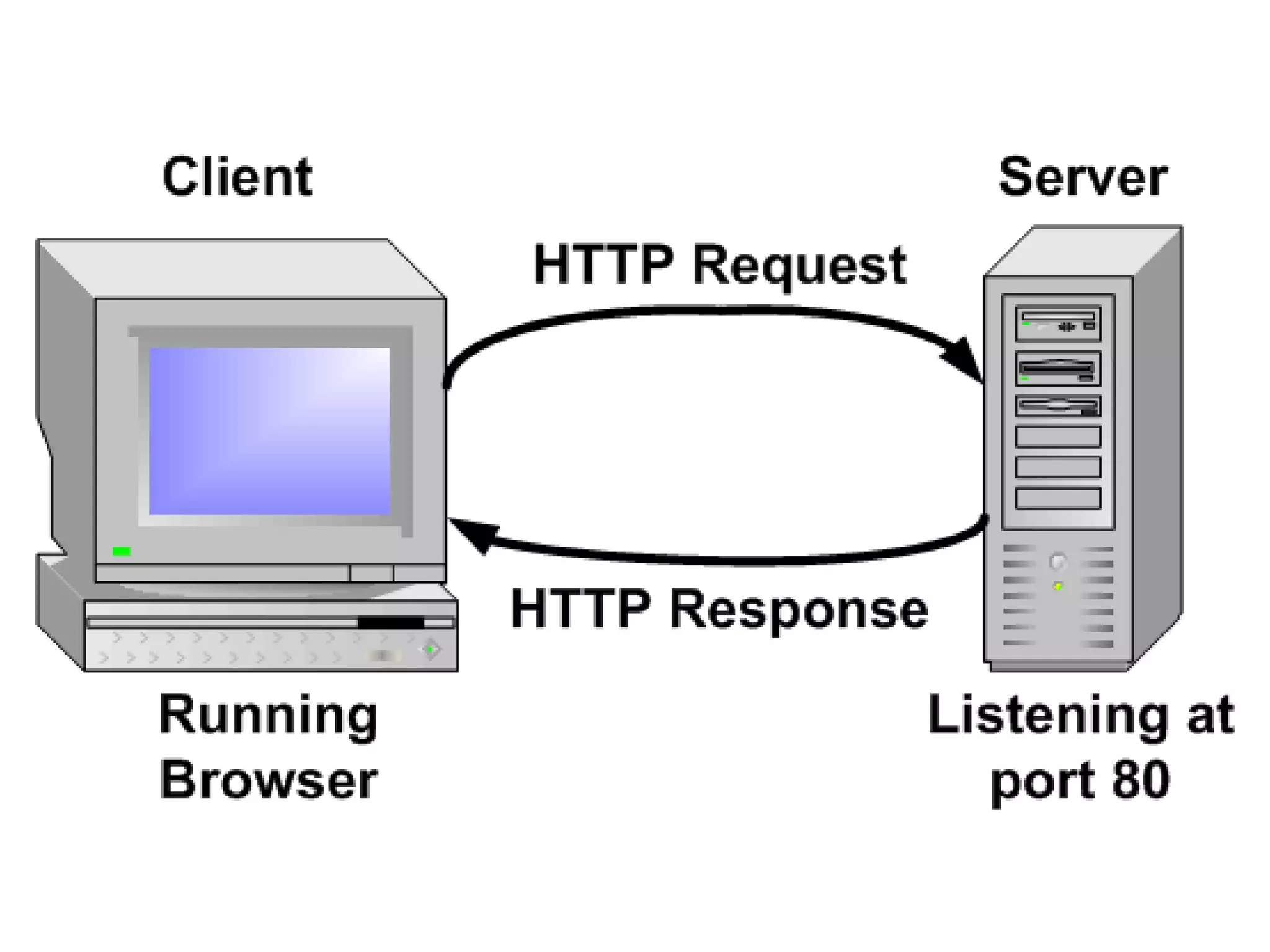
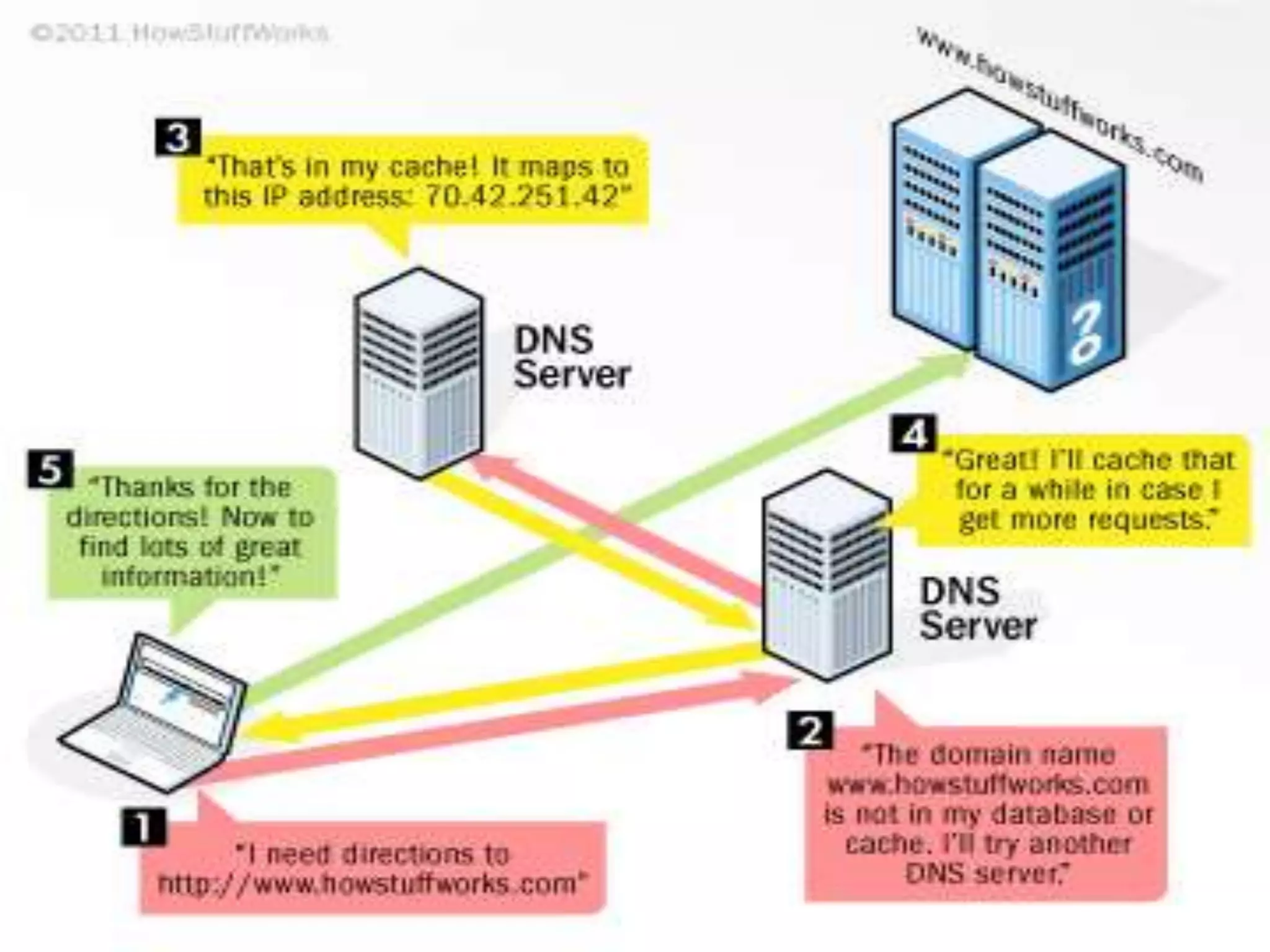
The document outlines the evolution of the internet backbone, beginning with the NSFNET in 1987 and the development of high-speed connections by organizations like IBM and MCI. It discusses the creation of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 as a system for accessing documents, utilizing key components like URLs, HTTP, and hypertext for easy navigation. Additionally, it explains the domain name system (DNS) that translates internet domain names into IP addresses.