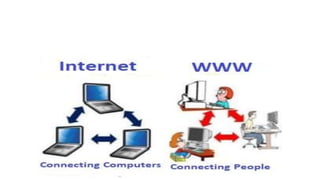
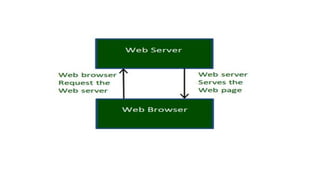
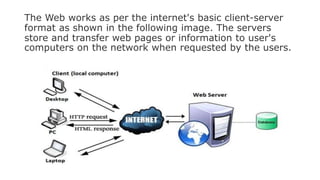
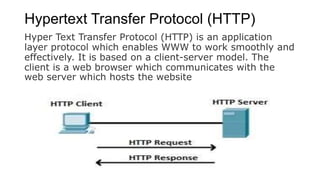
The World Wide Web (WWW) is an information space that allows access and navigation of documents through hyperlinks over the internet. Created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, it distinguishes itself from the internet by being a collection of interlinked web resources identified by URIs. The web operates using a client-server model, enabled by protocols such as HTTP, and features dynamic and interactive components across various platforms.