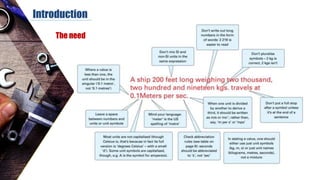
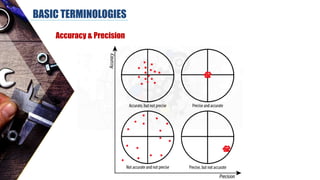
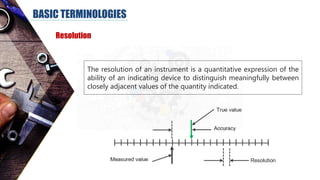
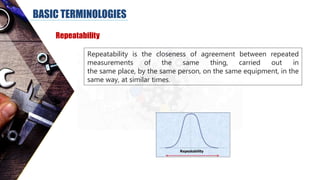
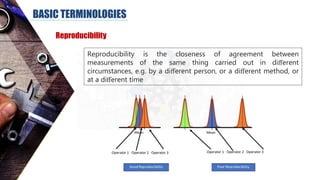
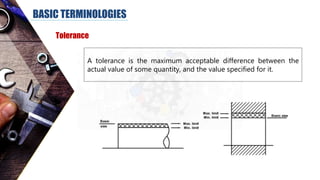
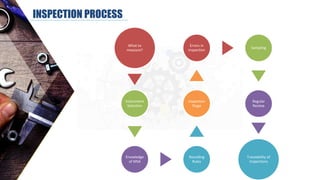
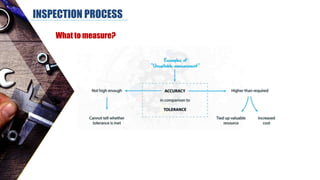
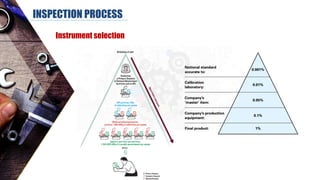
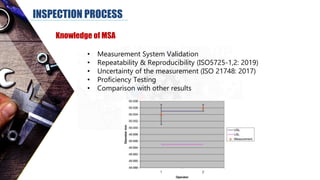
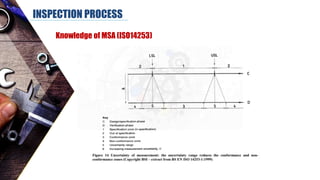
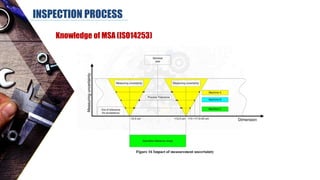
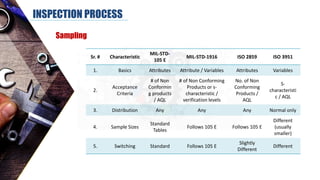
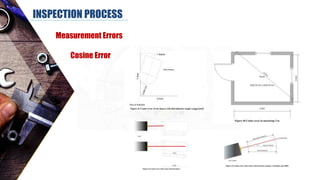
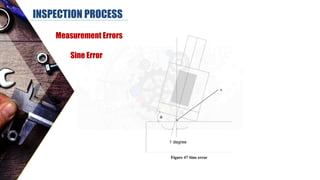
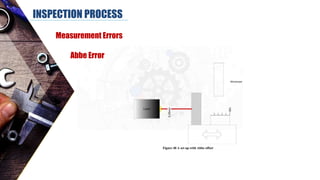
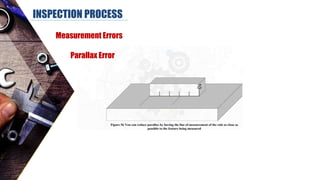
The document discusses dimensional metrology, which includes fundamental concepts such as accuracy, precision, and measurement errors, along with the importance of validation and verification in measurement processes. It outlines the inspection process, types of measurements, and essential terminology related to measurement systems. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for regular review and the adherence to standards to ensure measurement reliability and consistency.