Embed presentation
Downloaded 60 times



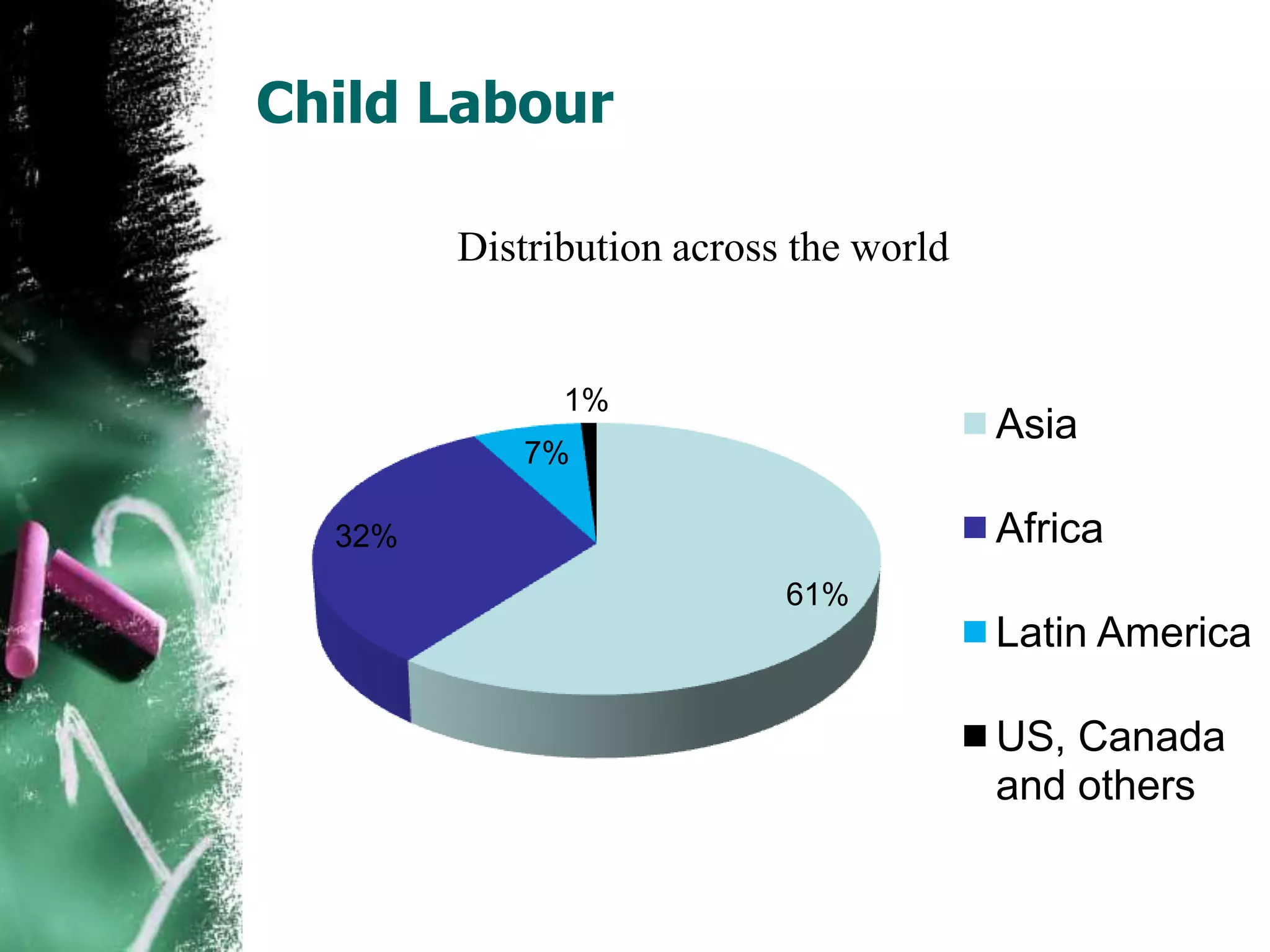















Child labour is a growing problem worldwide, with over 250 million children between the ages of 5 and 14 involved. Asia accounts for the majority at 61%, while Africa is next at 32%. The International Labour Organization defines child labour as work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful. The key causes of child labour are poverty, overpopulation, ignorance and illiteracy. Some of the worst forms involve exploitation, trafficking, use in armed conflicts, and prostitution. Eradicating child labour requires steps like increasing education access, income transfers, and interventions, along with strong laws and enforcement.

















