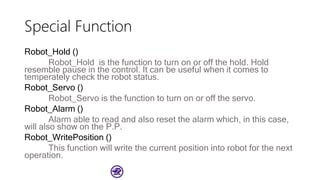
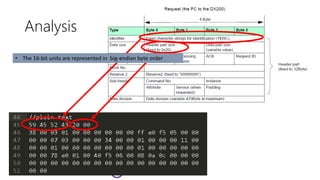
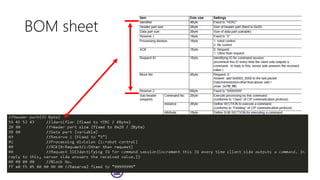
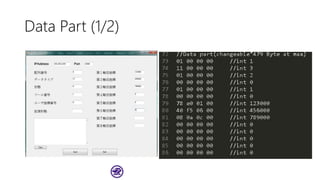
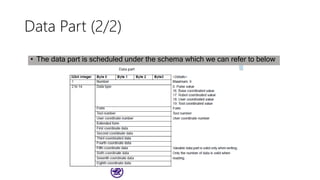
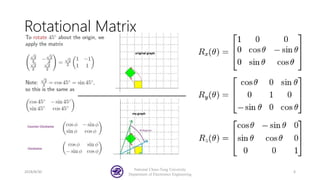
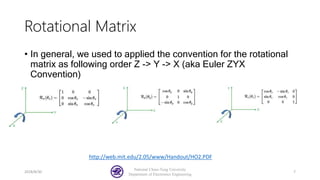
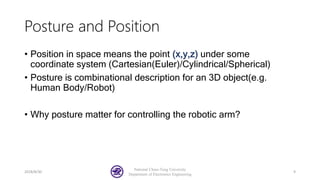
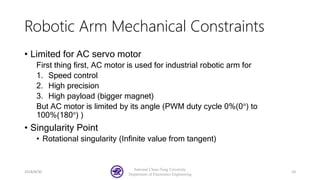
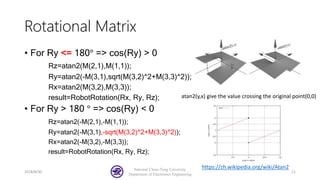
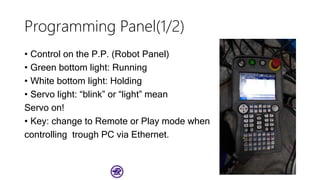
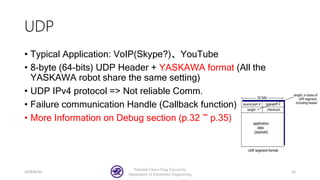
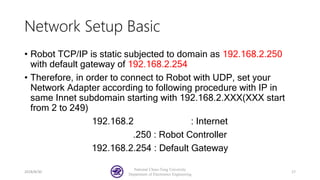
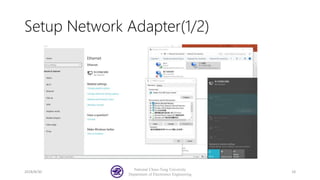
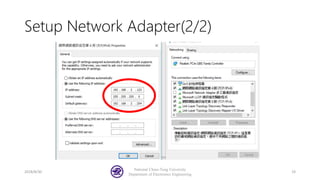
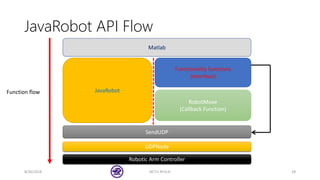
The document serves as a basic tutorial for using a robotic arm, focusing on mathematical theories, programming, and control methods. It covers rotational matrices, programming panels, and the implementation of UDP communication for controlling robotic movements. Additionally, it outlines practical applications and introduces a MATLAB API for further development.






![Eclipse Shortcuts
• [Ctrl + Shift + O]:自動匯入所需要的類別:Auto include
• [Ctrl + Shift + F]:程式碼自動排版 : Auto align
• [Ctrl + Left-click]:查看使用類別的原始碼 : Check the source
code
• [Ctrl+ / ]:將選取的文字多行註解起來 : Comment the code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basic-tutorial-for-robotic-arm-180830151415/85/Basic-Tutorial-for-Robotic-Arm-21-320.jpg)

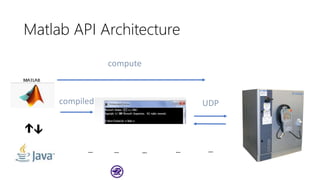
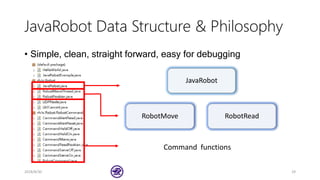
![API Main Function
1. Read the current position with the function of
[Tool] = Read_Position ()
2. Get the position and save it as variable Tool, and than use
the Robot_Move_Angle ()
to move to assign pitch and yaw value.
3. We can read the angle with
[pitch, yaw] = Robot_ReadAngle()
4. Reset the surface back to original point or move to the
Tool with Robot_Move(Tool, speed)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basic-tutorial-for-robotic-arm-180830151415/85/Basic-Tutorial-for-Robotic-Arm-30-320.jpg)