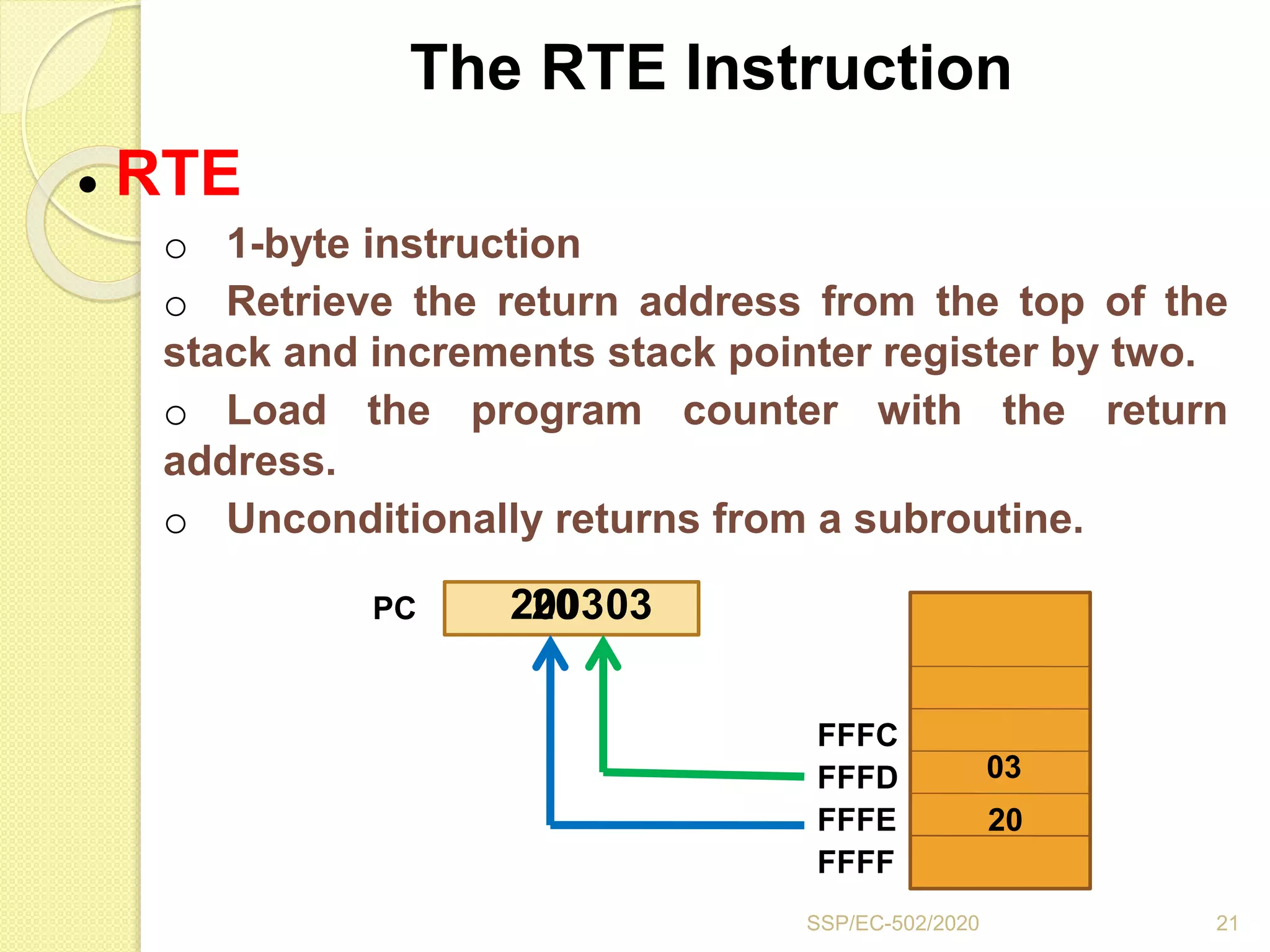
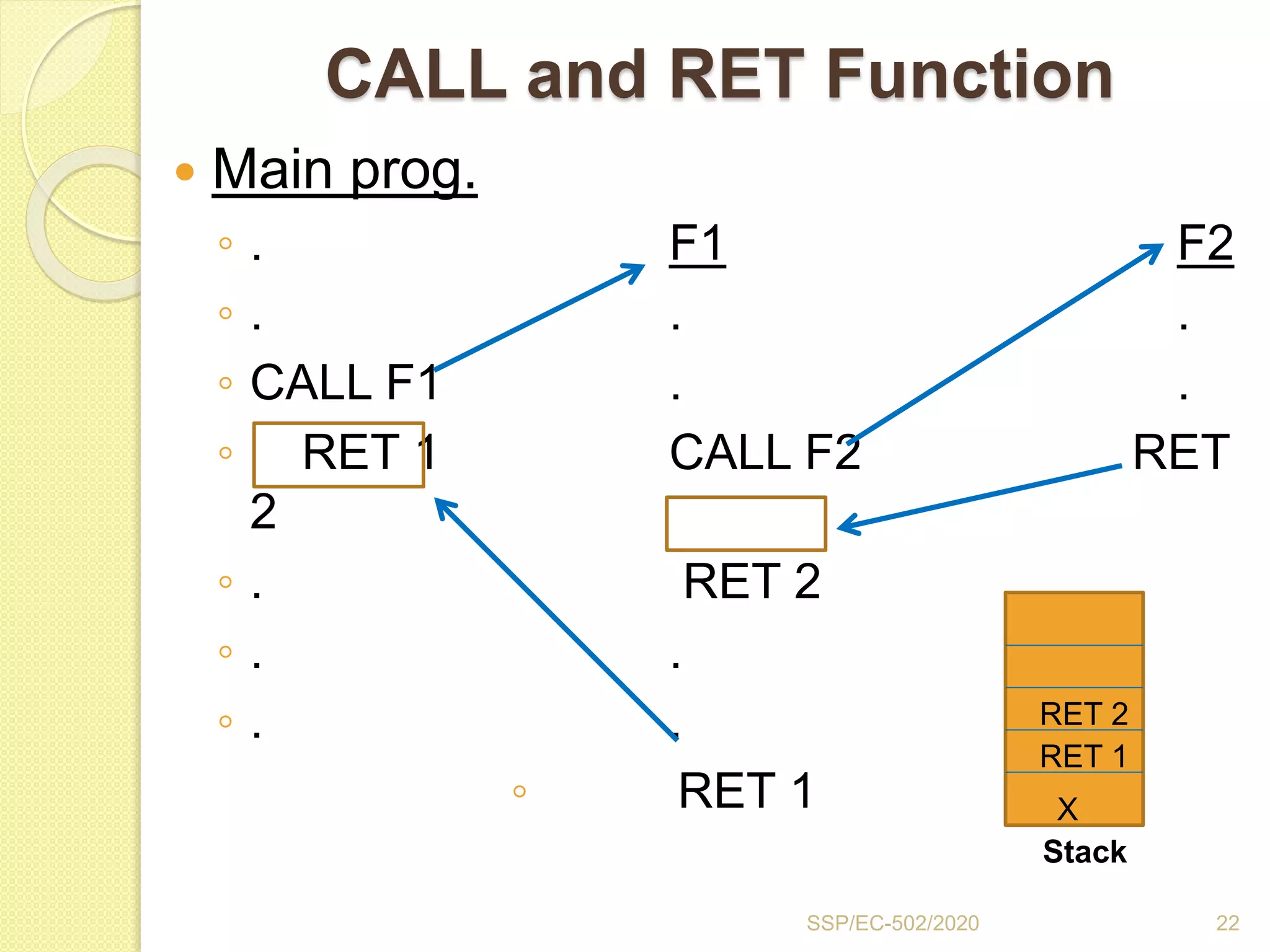
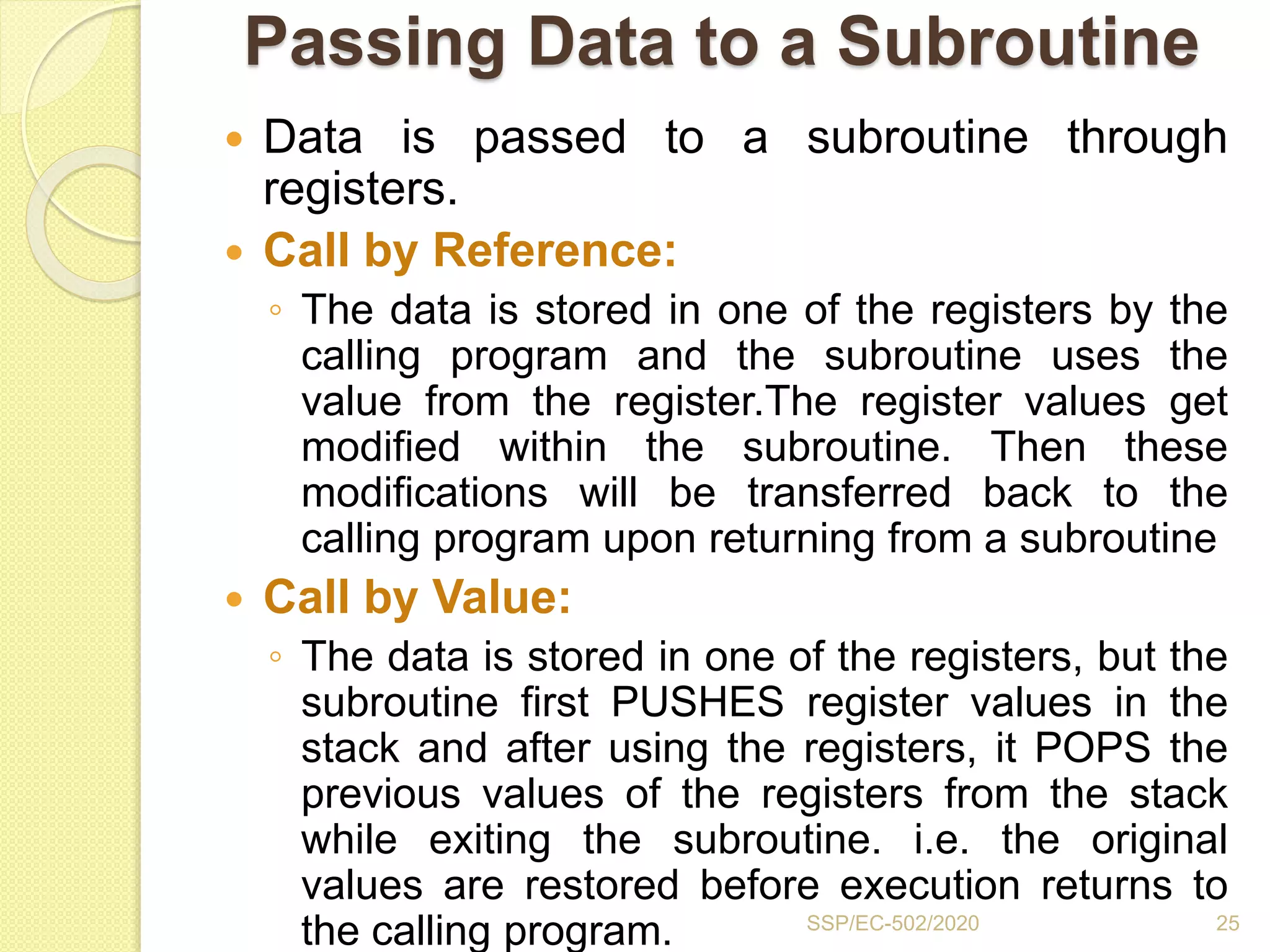
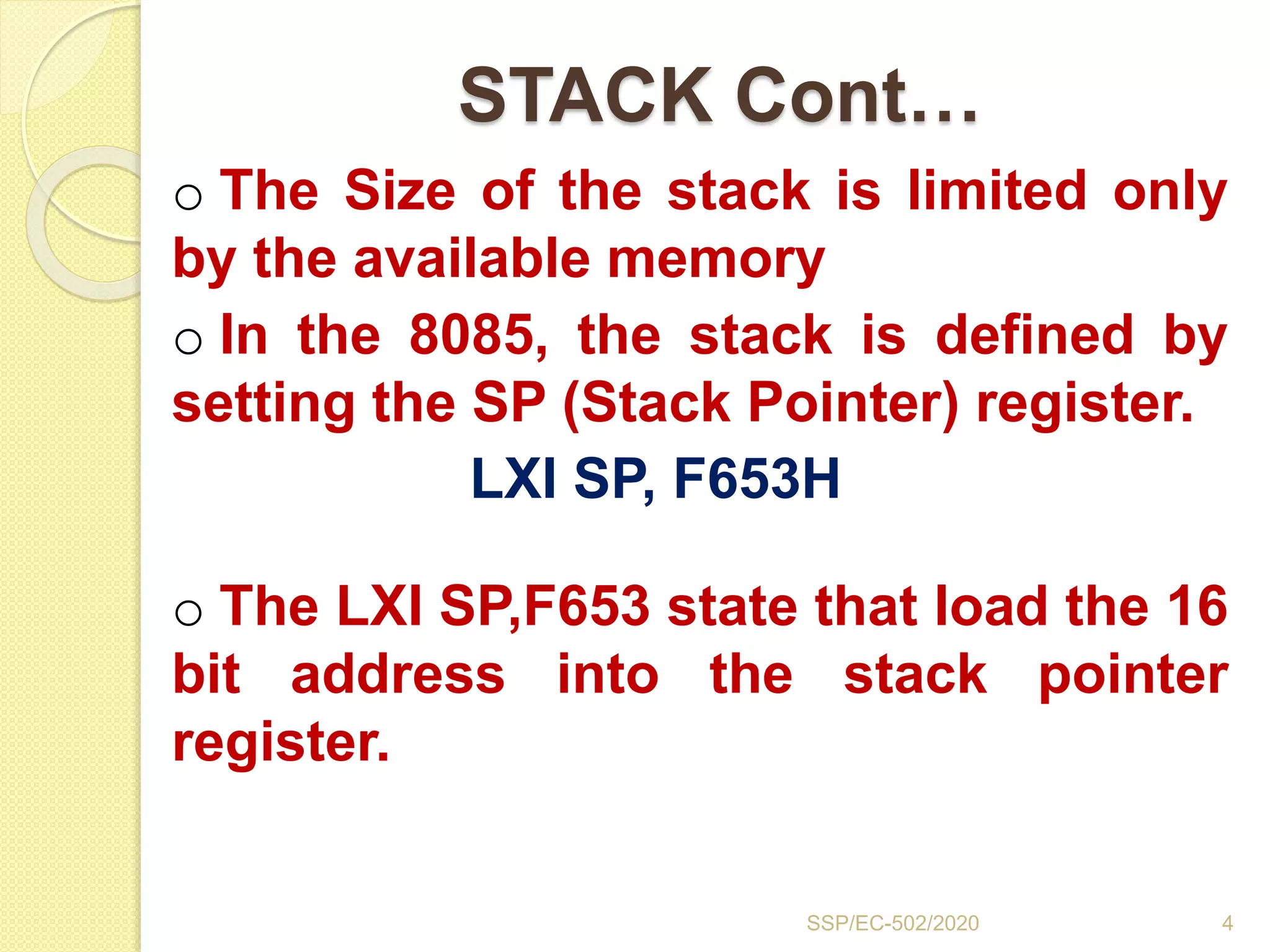
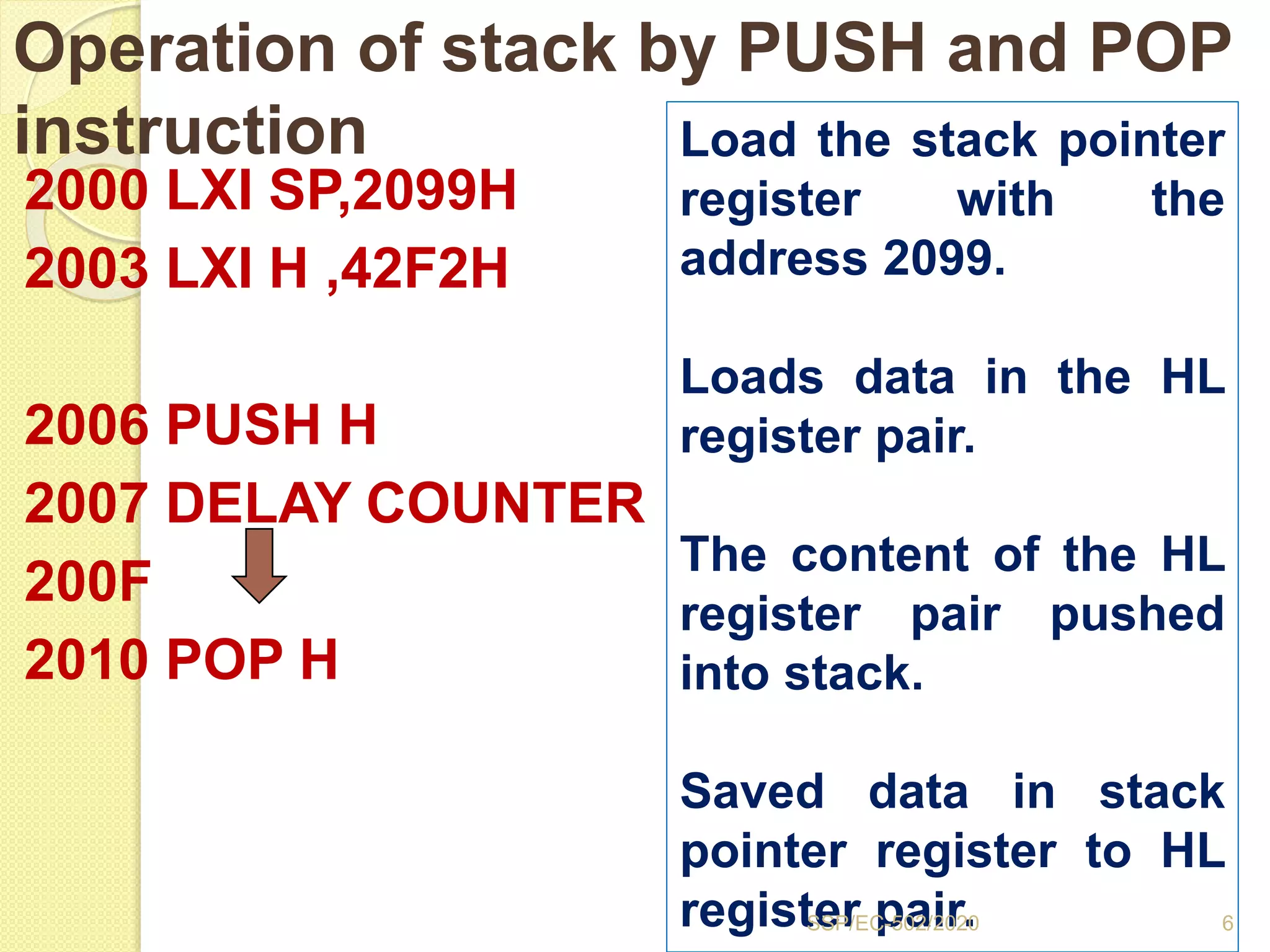
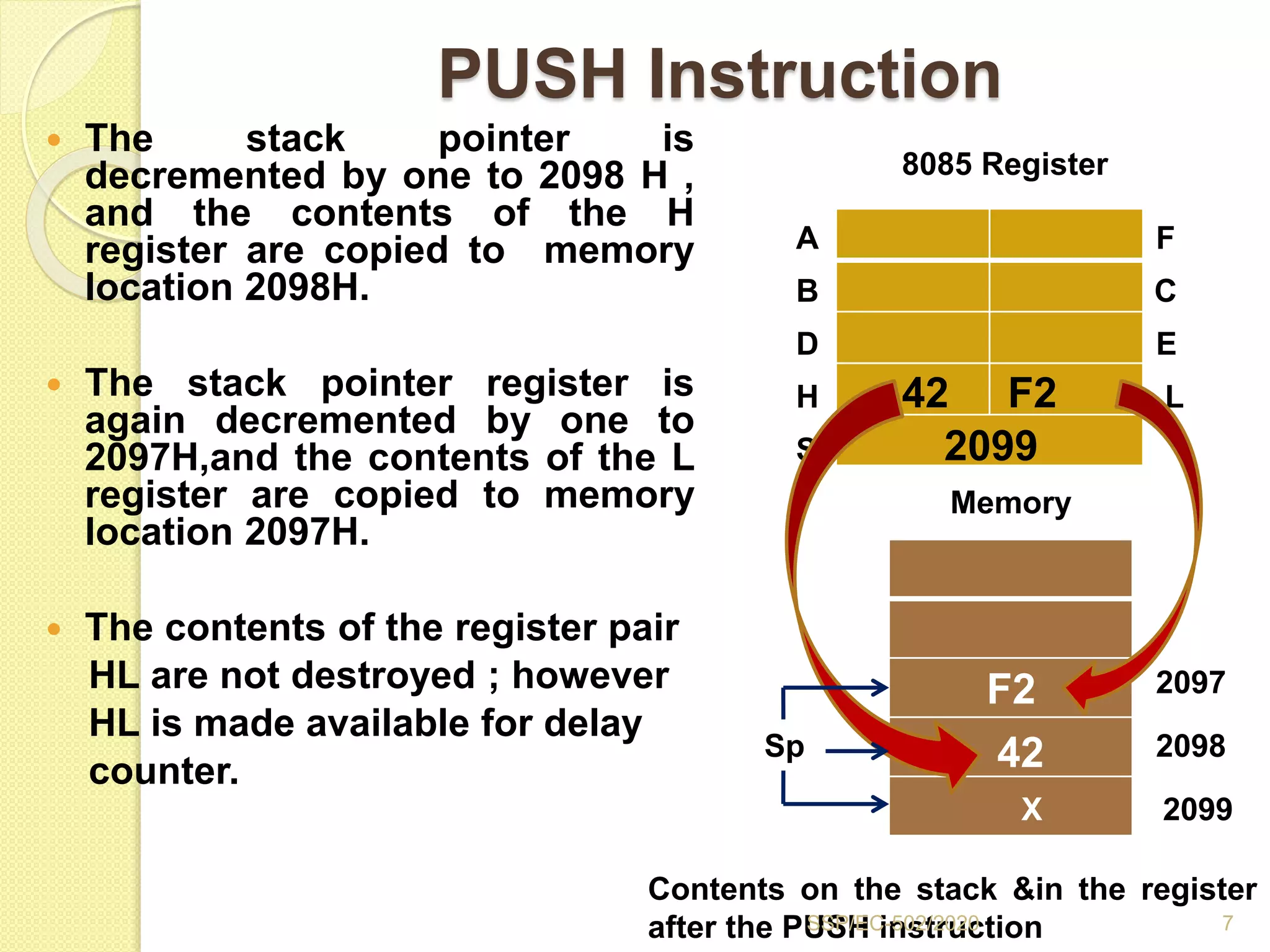
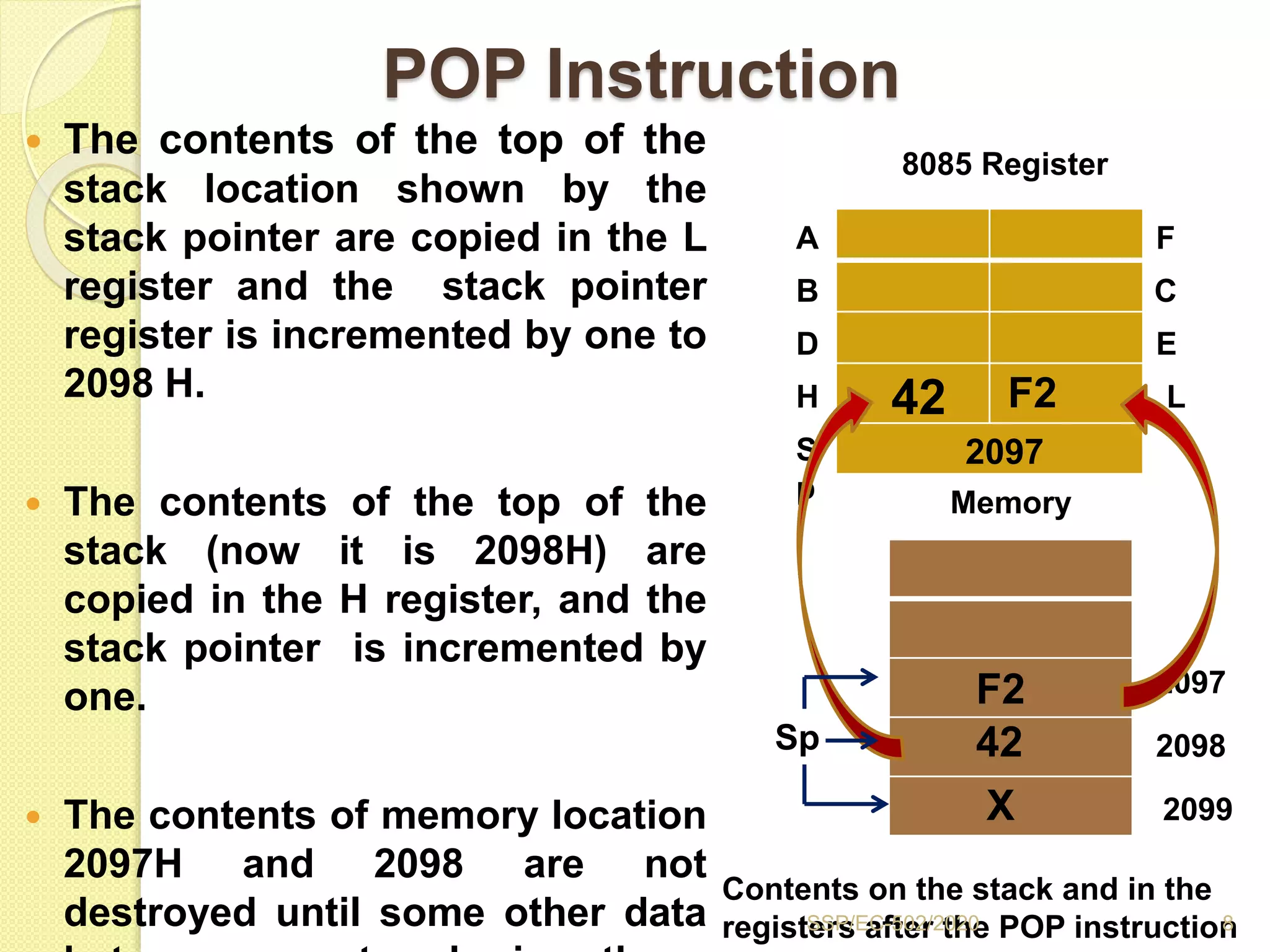
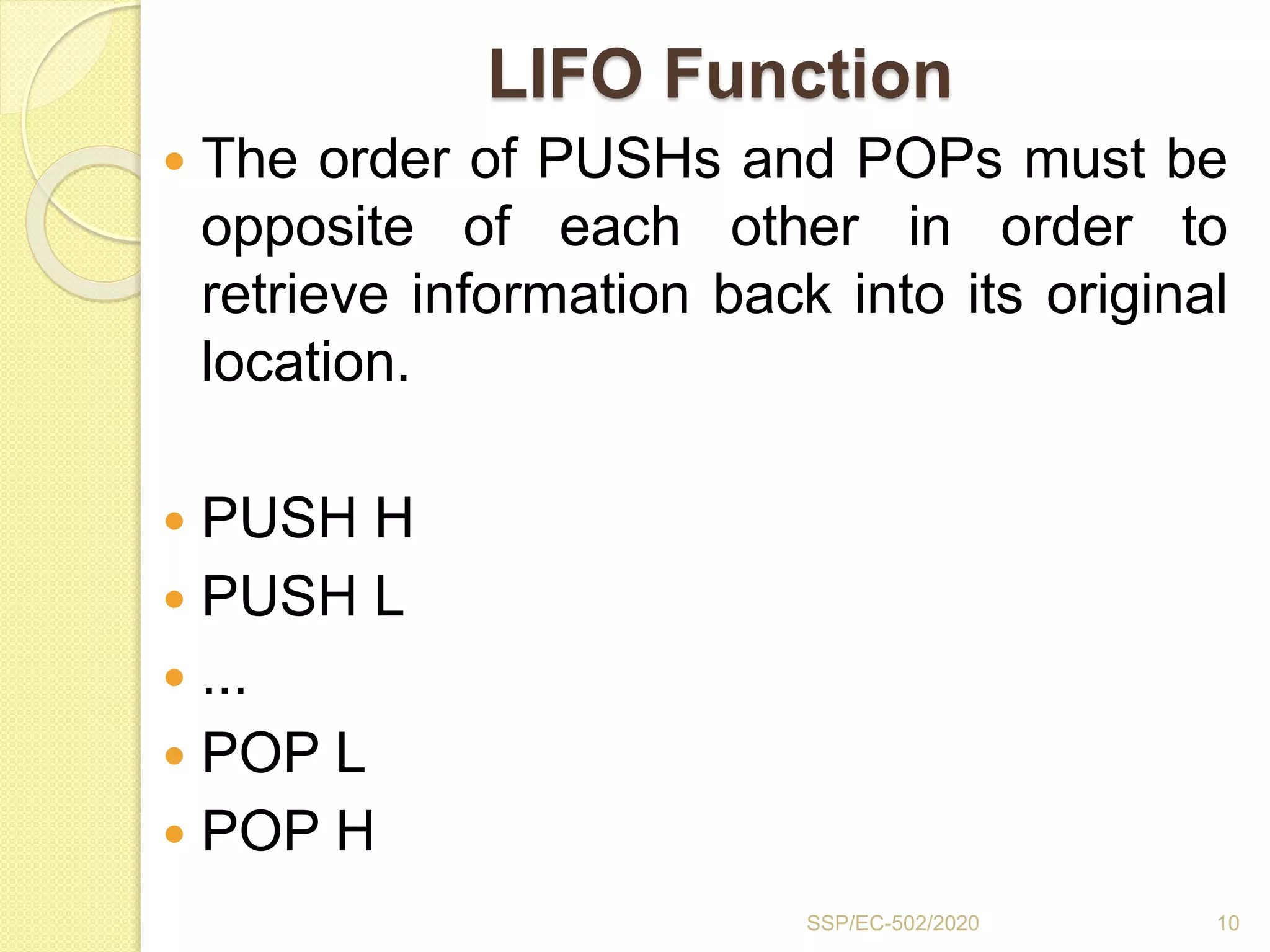
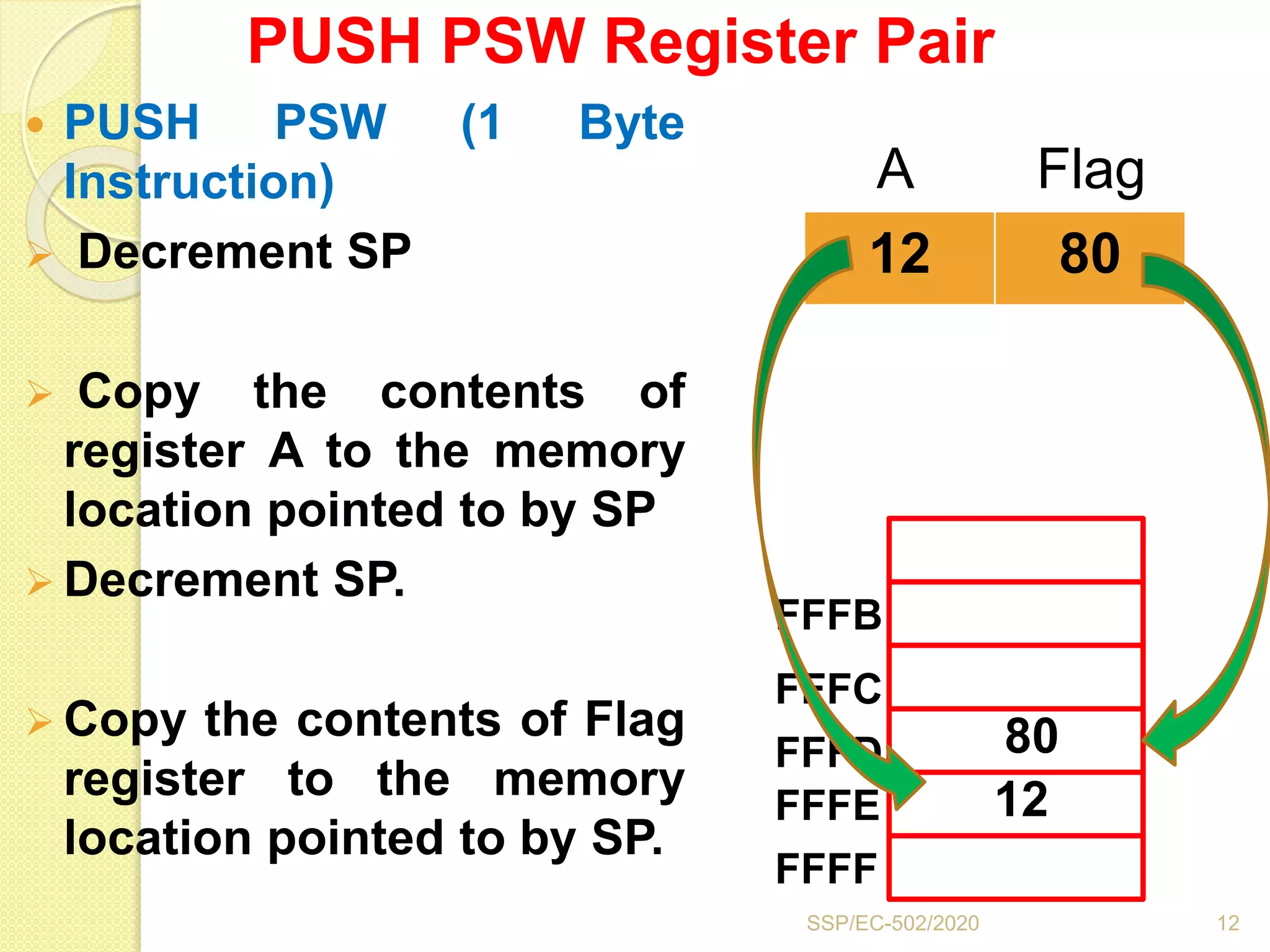
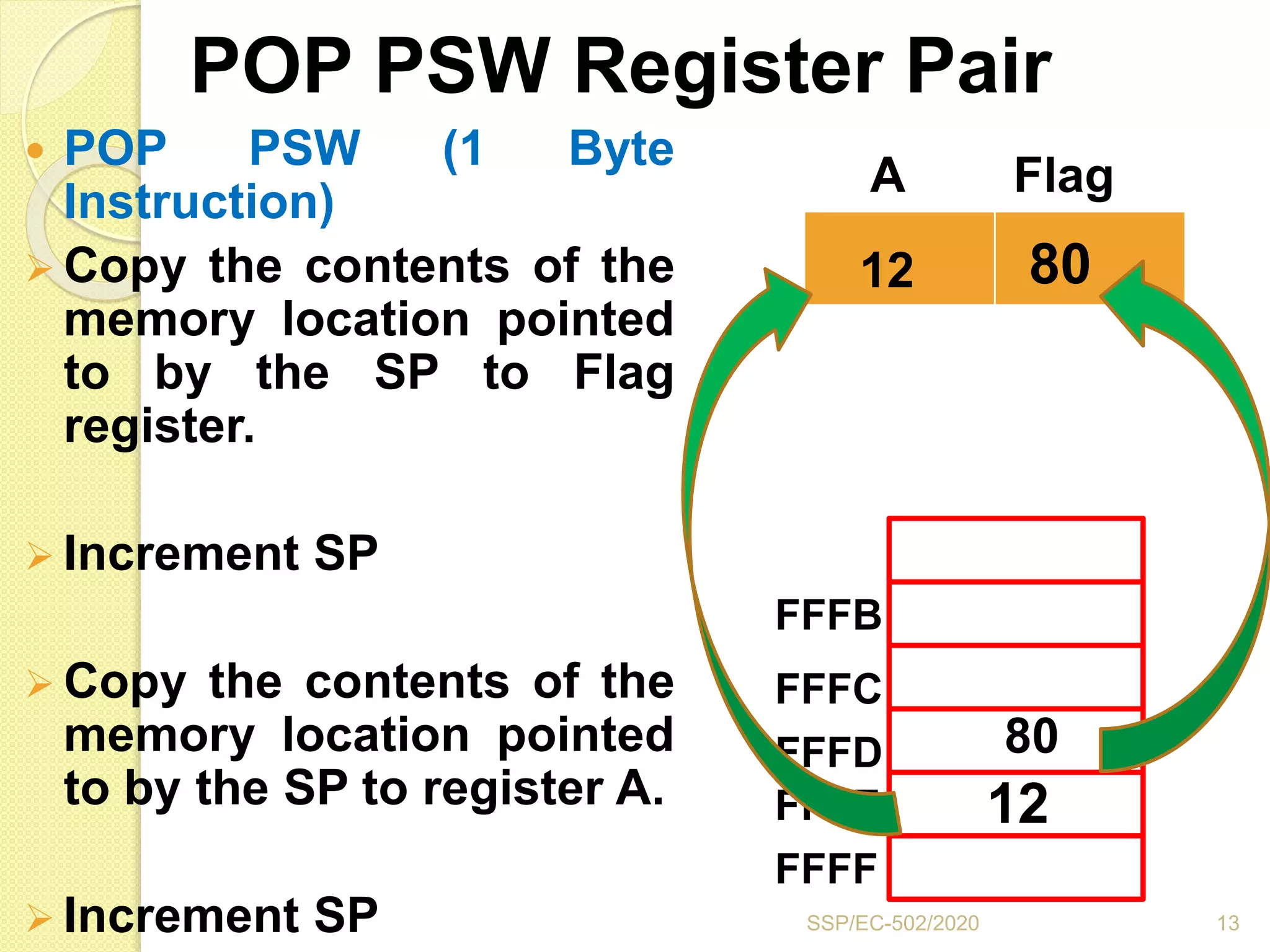
The document discusses stacks and subroutines in 8085 microprocessors. It describes how the stack is an area of memory used for temporary storage of information in a LIFO manner using a stack pointer register. Information is stored on the stack using the PUSH instruction and retrieved using POP. Subroutines allow commonly used code to be executed from different locations in a program by using the CALL instruction to transfer program flow to the subroutine and the RET instruction to return to the main program. Parameters can be passed between the main program and subroutines using registers or memory locations.











![The CALL instruction
● CALL 4000H
o 3-byte instruction.
o Push the address of the instruction immediately
following the CALL onto the stack and decrement the stack
pointer register by two.
o Load the program counter with the 16-bit address
supplied with the CALL instruction.
o Jump Unconditionally to memory location.
FFFF
FFFE
FFFD
FFFC
20 03
40 00
CALL 4000
[W] [Z] Register
PC
03
20
19SSP/EC-502/2020
400
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-200316090056/75/Stack-and-subroutine-19-2048.jpg)
![The CALL instruction cont…
MP reads the subroutine address from the
next two memory location and store the
higher order 8 bit of the address in the W
register and stores the lower order 8 bit of
the address in the Z register.
Push the address of the instruction
immediately following the CALL onto the
stack [ Return address].
Load the program counter with the 16-bit
address supplied with the CALL
instruction from WZ register.
20SSP/EC-502/2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-200316090056/75/Stack-and-subroutine-20-2048.jpg)