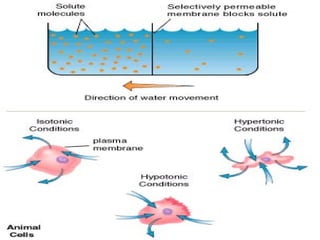
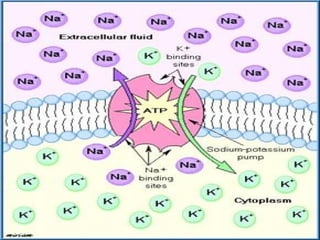
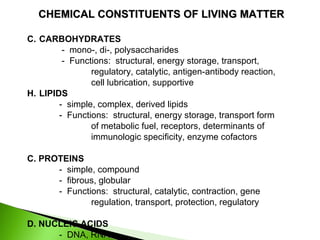
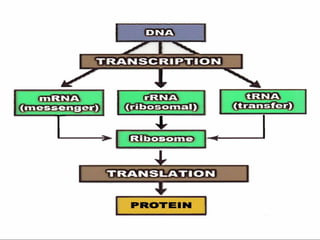
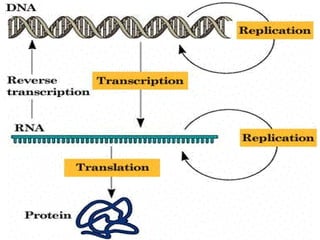
1. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are the major chemical constituents of living matter.
2. Carbohydrates function as structural components, energy storage, transport forms, and in cellular processes like regulation and catalysis.
3. Lipids function as structural components, energy storage, transport forms, receptors, and enzymatic cofactors.












![pH and BUFFER
pH = - log [ H + ]
ACID – donates H+
BASE – accepts H+
ACIDOSIS - high [ H+] , low pH
ALKALOSIS – low [ H+] , high pH
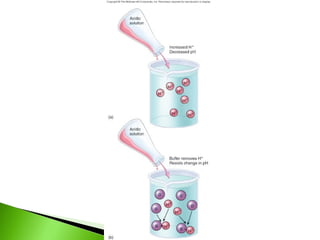
BUFFER - contains an acid and its conjugate base
- resists ph changes
- e.g. BICARBONATE BUFFER SYSTEM
H2CO3
HCO3¯](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicchemistryandchemicalcompositionedited1-120420235403-phpapp01/85/Basic-chemistry-and-chemical-composition-edited-1-18-320.jpg)