The document provides various examples of using R programming for basic calculus, including functions for plotting, differentiation, integration, and solving equations. It includes commands for creating functions, plotting data, modeling relationships, and applying statistical methods. The use of the 'mosaic' and 'manipulate' libraries is demonstrated through practical examples for educational purposes.
![Prepared by VOLKAN OBAN
Basic Calculus in R.
install.packages("mosaic")
library(mosaic)
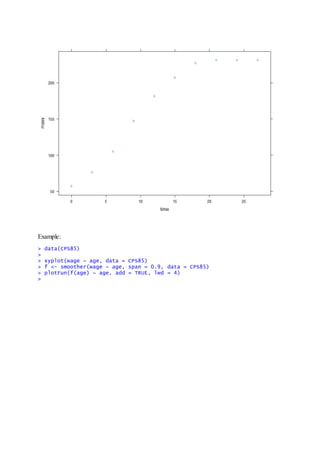
Example:
> f <- makeFun(m * x + b ~ x, m = 3.5, b = 10)
>
> f(x = 2)
[1] 17
>
> g <- makeFun(A * x * cos(pi * x * y) ~ x + y, A = 3)
> g
function (x, y, A = 3)
A * x * cos(pi * x * y)
>
> g(x = 1, y = 2)
[1] 3
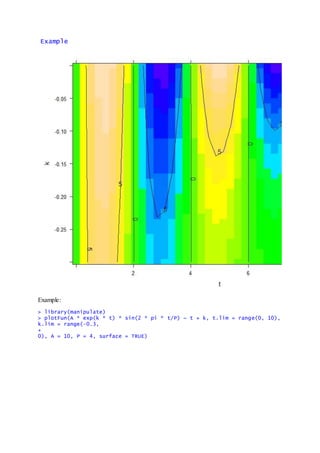
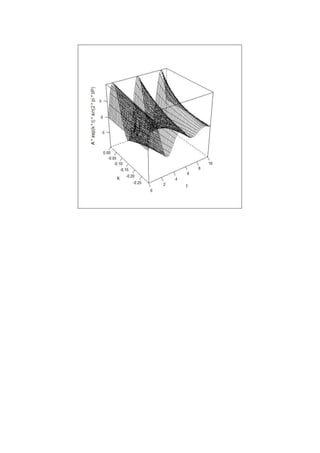
> > plotFun(A * exp(k * t) * sin(2 * pi * t/P) ~ t + k, t.lim = range(0, 1
0), k.lim = range(-0.3,
+
0), A = 10, P = 4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calculus-160923114125/75/Basic-Calculus-in-R-1-2048.jpg)
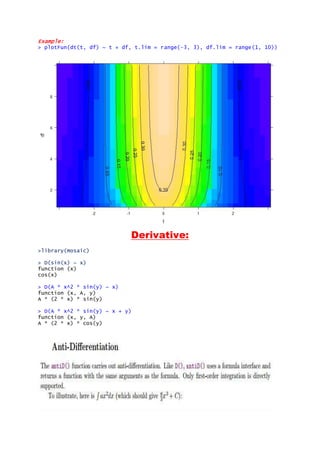
![Example:
> F = antiD(a * x^2 ~ x, a = 1)
> F
function (x, a = 1, C = 0)
a * 1/3 * x^3 + C
> F = antiD(dnorm(x, mean = 6000, sd = 0.01) ~ x, lower.bound = 6000)
> F(Inf) - F(-Inf)
[1] 1
>
Solving..
findZeros(sin(t) ~ t, t.lim = range(-5, 1))
> findZeros(sin(t) ~ t, t.lim = range(-5, 1))
t
1 -6.2832
2 -3.1416
3 0.0000
4 3.1416
Example:
> solve(4 * sin(3 * x) == 2 ~ x, near = 0, within = 1)
x
1 0.1746
2 0.8726
Example:
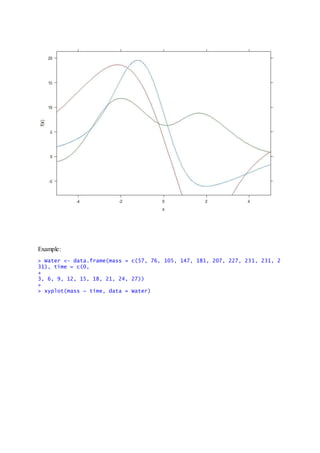
> f <- rfun(~x, seed = 345)
> g <- rfun(~x)
> h <- rfun(~x)
> plotFun(f(x) ~ x, x.lim = range(-5, 5))
> plotFun(g(x) ~ x, add = TRUE, col = "red")
> plotFun(h(x) ~ x, add = TRUE, col = "darkgreen")
>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calculus-160923114125/85/Basic-Calculus-in-R-5-320.jpg)
![Mixed Examples:
1
> f = function(x){ x^2 + 2*x }
>
> f(pi)
[1] 16.15279
2-
> findZeros( sin(x)-0.35 ~ x, x.lim=range(-20,20) )
x
1 -12.2088
2 -9.7823
3 -5.9256
4 -3.4991
5 0.3576
6 2.7840
7 6.6407
8 9.0672
9 12.9239
10 15.3504
3-
> findZeros(sin(x^2)*(cos(sqrt(x^4+3)-x^2))-x+1~x,x.lim=range(1,2))
x
1 1.5576
4-
> f3 = makeFun( sin(x^2) - 100~x)
> f3(x=2)
[1] -100.7568](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calculus-160923114125/85/Basic-Calculus-in-R-9-320.jpg)
![5-
> F = antiD( exp(x^2) ~ x )
> F(x=2) - F(x=-1)
[1] 17.91528
6-Dif.Eq.
> soln <- integrateODE( dx ~ r*x*(1-x/K),x=1, K=10, r=.5, tdur=list(from=0,
to=20))
> soln$x(0:5)
[1] 1.000000 1.548281 2.319693 3.324279 4.508531 5.751209
7-
> plotFun( exp(-t/10)*sin(2*pi*x/5) ~ x&t,x.lim=range(0,5), t.lim=range(0,1
0) )
8-
> newF = antiD(exp(x)*x^2 ~ x, x.from=1)
> F(x=2) #default lower bound is 0
[1] 16.45263](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calculus-160923114125/85/Basic-Calculus-in-R-10-320.jpg)