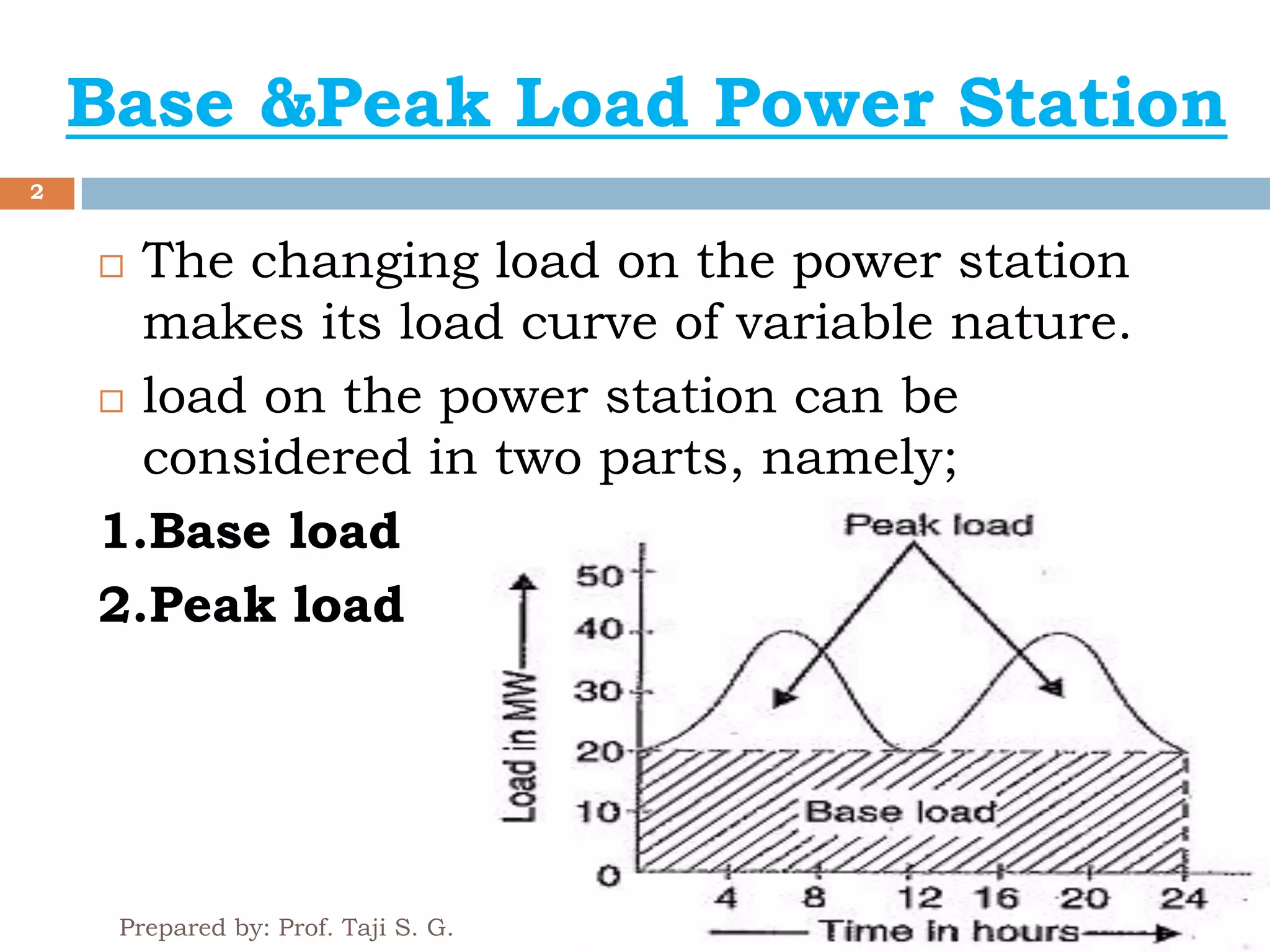
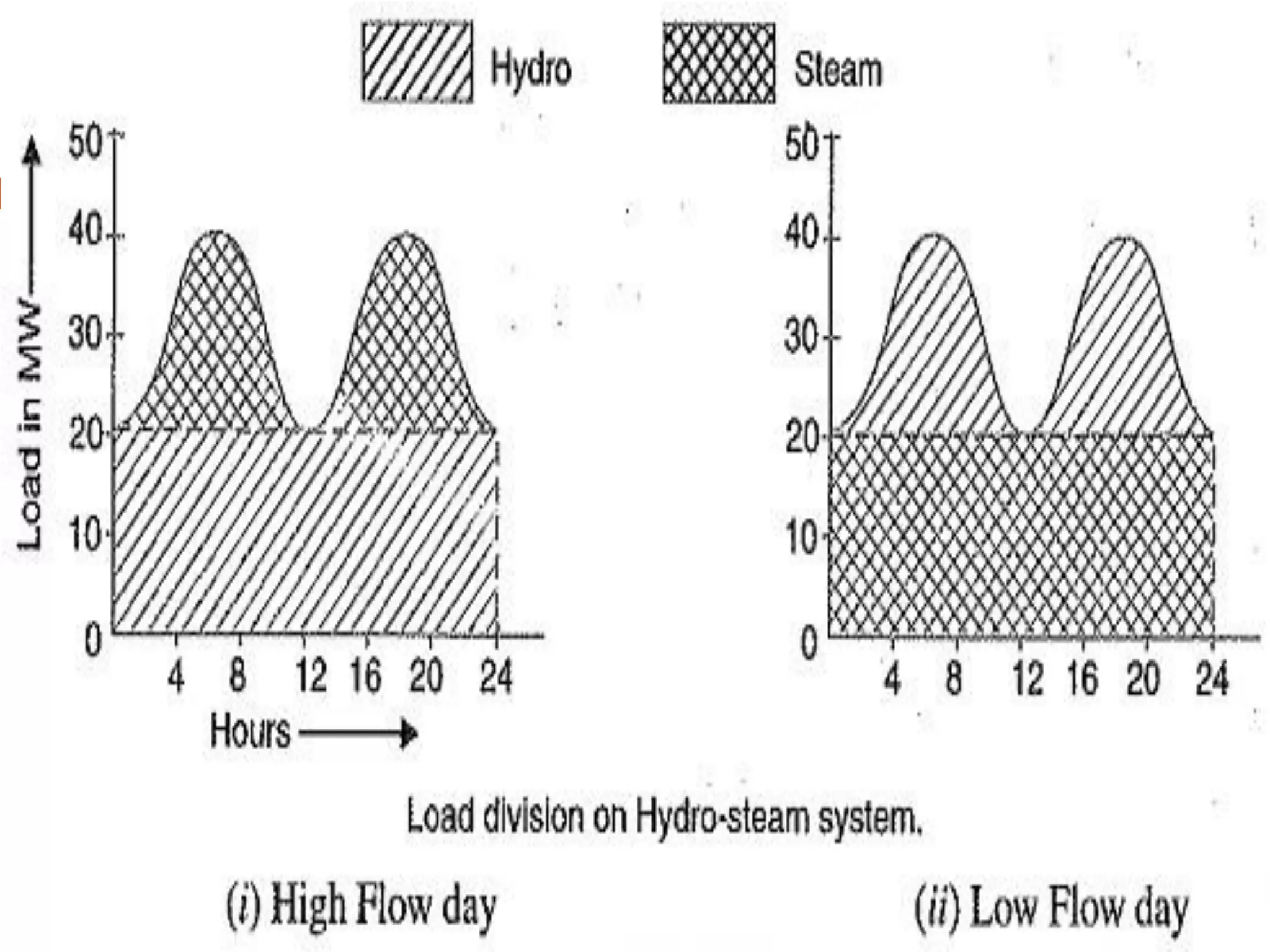
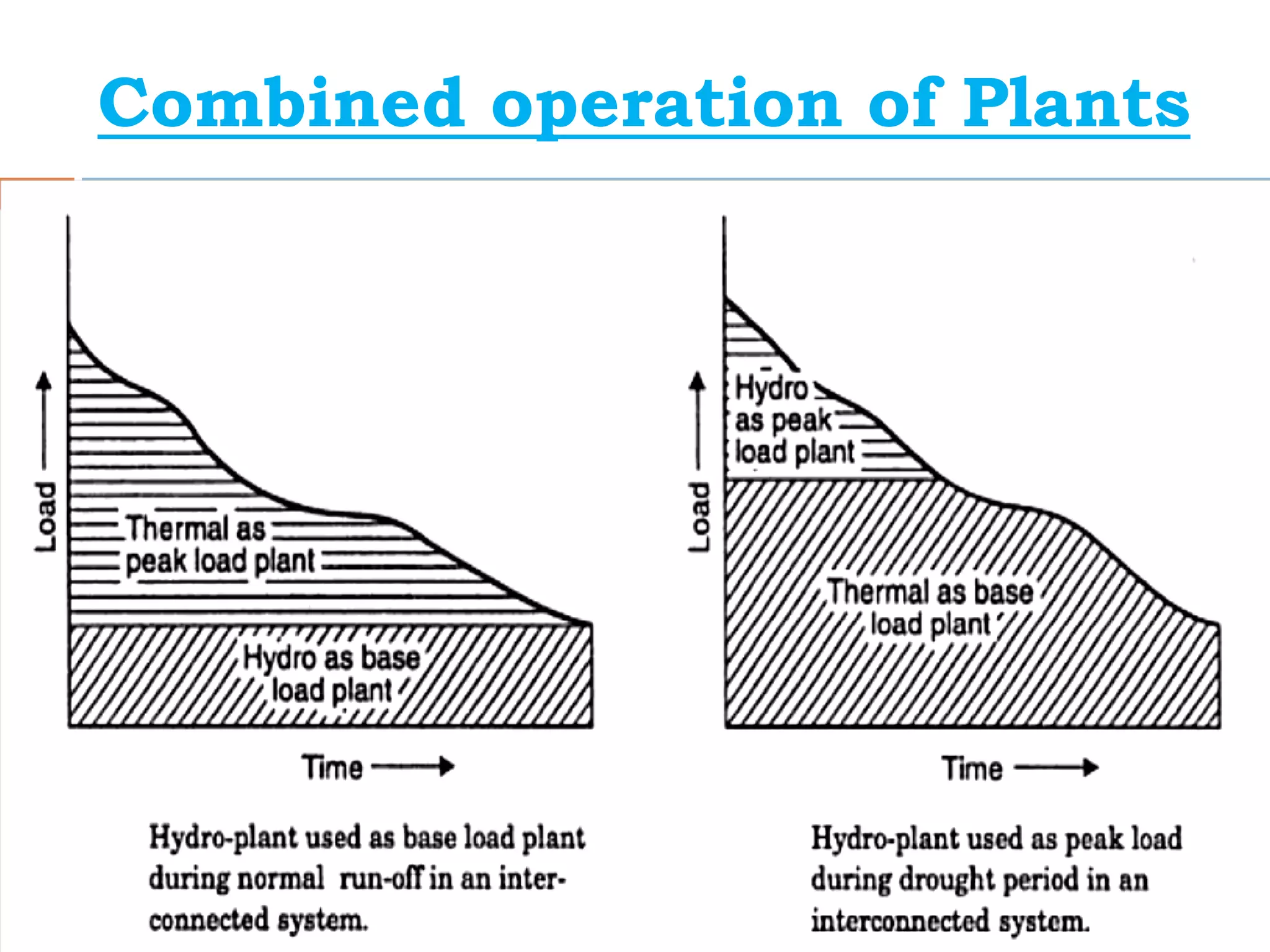
The document outlines the operational dynamics of base load and peak load power stations, emphasizing their roles in meeting fluctuating energy demands efficiently. It discusses the advantages of an interconnected grid system, such as sharing peak loads, utilizing older plants, and ensuring more economical operation. Additionally, it covers the combined operation of hydroelectric and thermal plants to optimize energy allocation and maintain reliability while reducing costs.