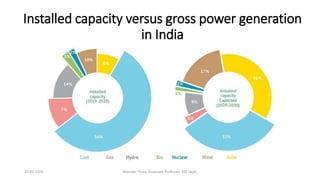
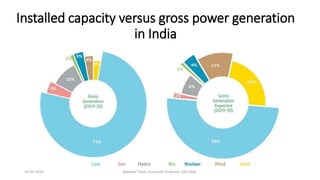
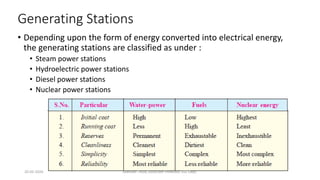
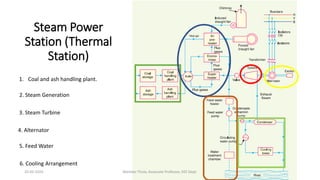
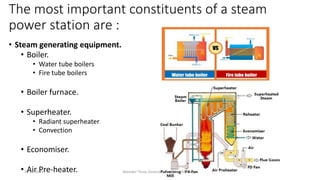
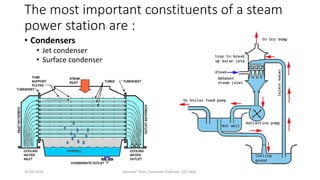
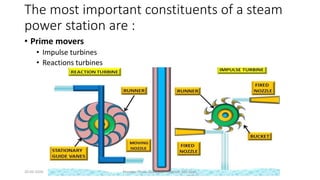
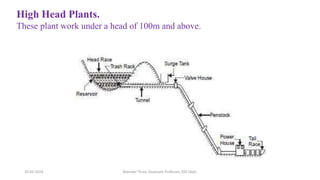
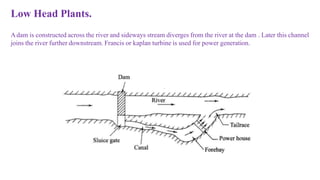
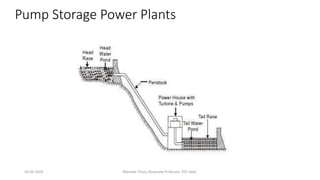
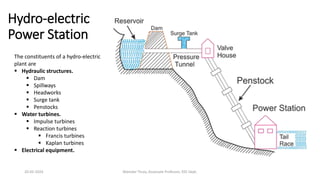
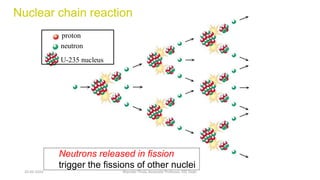
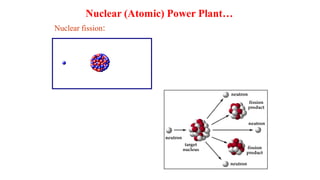
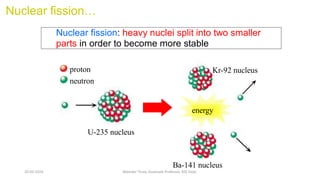
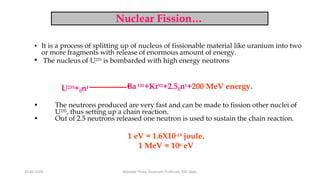
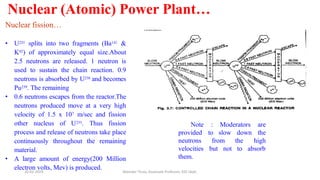
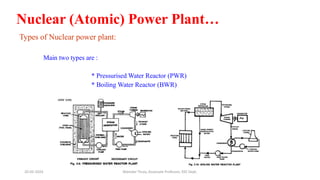
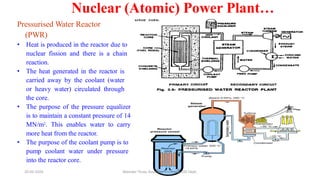
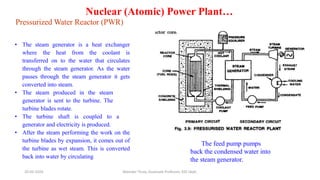
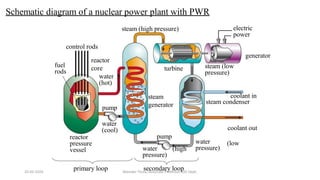
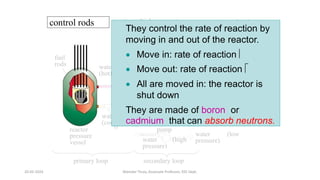
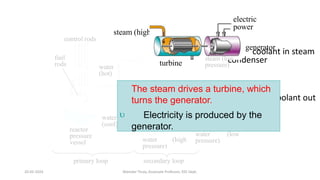
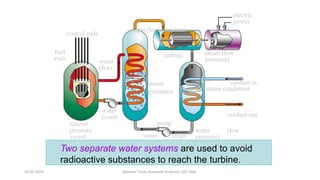
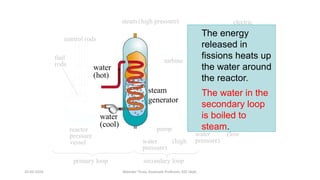
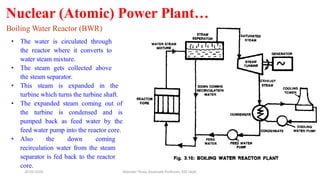
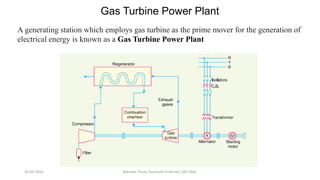
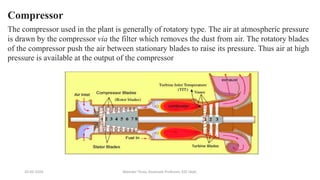
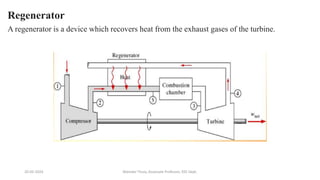
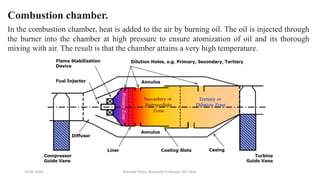
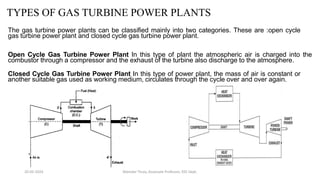
The document discusses different types of power generating stations including steam, hydroelectric, nuclear and gas turbine power plants. It focuses on providing details about steam power stations and hydroelectric power stations. For steam power stations, it describes the key components, factors considered for site selection, efficiency, advantages and disadvantages. For hydroelectric power stations, it discusses the classification based on head, storage and load, factors considered for site selection and the basic components. It also provides a brief overview of the working of nuclear power plants.