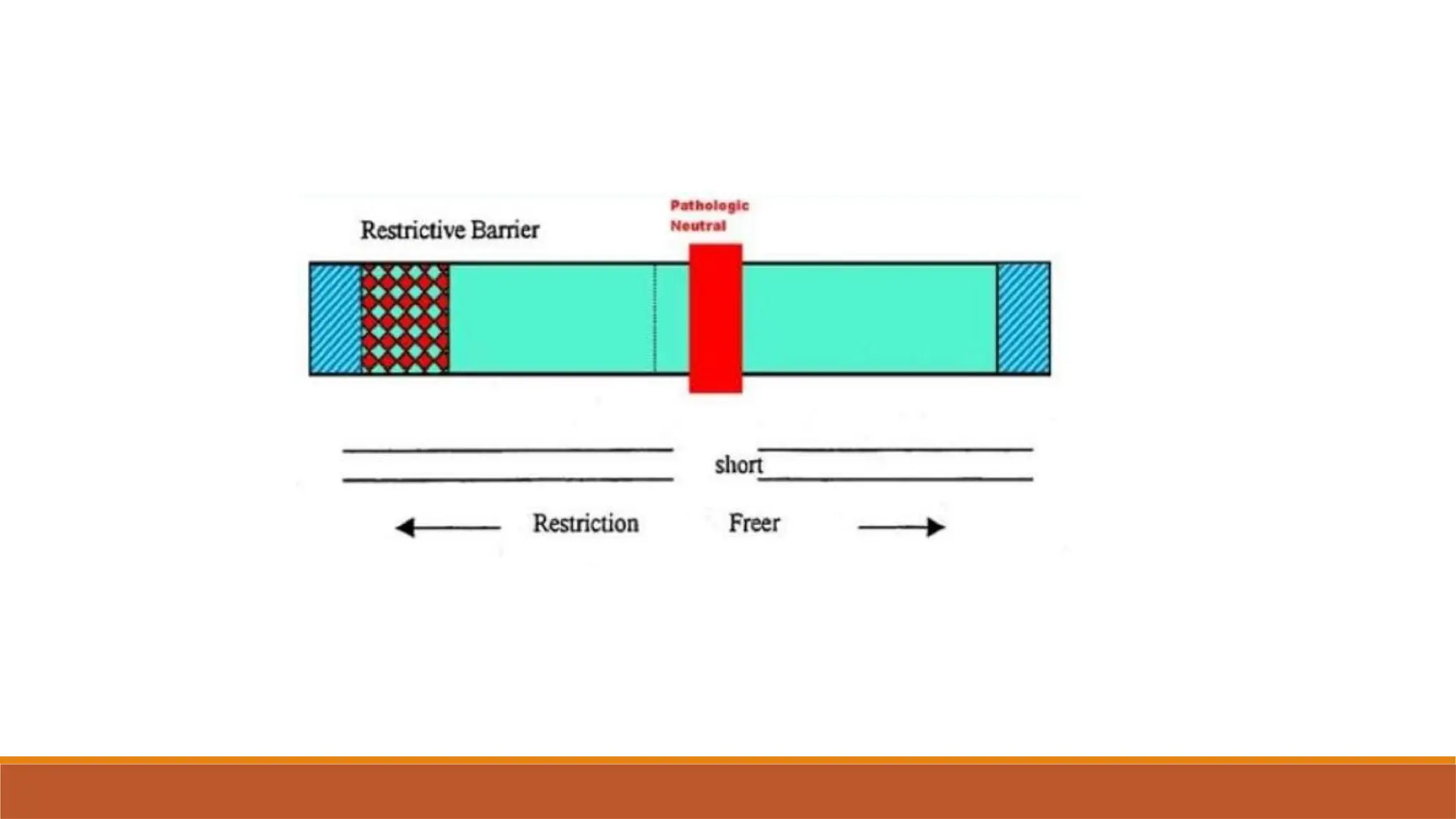
The document outlines barrier concepts in joint mobilization and manipulation, defining three types of barriers: physiological, anatomical, and restrictive. The physiological barrier limits voluntary range of motion, while the anatomical barrier serves as the final limit, beyond which tissue disruption may occur. The restrictive barrier impedes movement within physiological limits and can affect normal joint function, with joint play and various forms of movement being discussed.