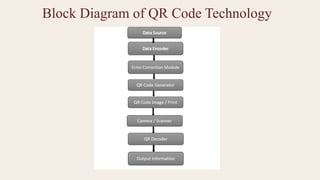
QR Code (Quick Response Code) technology is a two-dimensional barcode system that enables fast, efficient, and reliable data storage and retrieval. It was invented in 1994 by Denso Wave, Japan, initially for tracking automobile parts. Unlike traditional one-dimensional barcodes, QR codes store data both horizontally and vertically, allowing them to hold a large amount of information in a compact form.
Barcode technology evolved from simple UPC codes with limited data capacity to advanced formats like Code 39 and Code 16K. QR codes represent a major improvement, as they can store thousands of numeric, alphanumeric, and binary characters, including URLs and payment data, making them more efficient and flexible.
A QR code is made up of black squares arranged on a white background. Special alignment patterns allow scanning from any direction, enabling fast 360-degree scanning using smartphones or QR readers. Built-in error correction ensures that data can still be read even if the code is partially damaged.
QR codes can store various types of data such as website links, plain text, contact details (vCard), Wi-Fi credentials, location data, event information, and digital payment details. This versatility makes them useful across many applications.
The key benefits of QR codes include quick and contactless access, reduced manual data entry, faster payments and ticketing, low cost, and ease of use. However, they also pose risks such as malicious QR codes, privacy concerns, and dependency on smartphones and internet access. Safe usage requires scanning only trusted codes.
QR codes are widely used in marketing, digital payments, retail, logistics, healthcare, and transportation. Globally, they play a major role in systems such as UPI in India, mobile payments in China, digital certificates in the EU, and public services worldwide.
In conclusion, QR code technology is an essential part of modern digital systems. With future integration into AI, IoT, Blockchain, and AR, QR codes will continue to support smarter, secure, and more interactive digital experiences.