Bladder cancer
- 1. PRESENTED BY: Mr. Vinay Kumar M.Sc. Nursing 1st year HCN.,SRHU BLADDER CANCER
- 2. OBJECTIVES At the end of the class the student will be able to- ☺Define bladder cancer. ☺Enlist risk factor and causes of bladder cancer. ☺List down the clinical manifestation of bladder cancer. ☺Explain the stages of bladder cancer. ☺Enumerate diagnostic evaluation the bladder cancer. ☺Explain the management of bladder cancer.
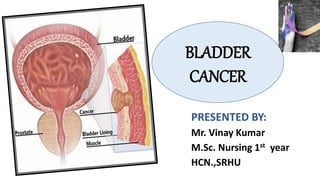
- 4. Urinary bladder Urinary bladder is smooth collapsible muscular sac that store urine temporarily Location Just above and behind the pubic bone
- 5. Size and shape • Urinary bladder is around the size and Shape of pear • Layers • The wall contain three layers of smooth muscle collectively called detrusor muscle and its mucosa is a special type of epithelium know as transitional epithelium
- 6. Opening There is three opening Two is connected with ureter and one is connected with urethra
- 7. Function The bladder largely serves two functions: ֍Temporary store of urine – The bladder is a hollow organ. The walls are very distensible, with a folded internal lining (known as rugae), this allows it to hold up to 600ml. ֍Assists in the expulsion of urine – During voiding, the musculature of the bladder contracts, and the sphincters relax.
- 8. DEFINITION • Bladder cancer is a condition in which cell in the urinary bladder start grow uncontrollably and irregular shape and have a potential to spread in the other parts of body
- 9. Type of bladder cancer on the basis of bladder cell Urothelial or transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Papillary Flat carcinoma
- 10. Urothelial or transitional cell carcinoma • These are transitional cells which are able to change the shape and stretch when the bladder is full • These cell present inside lining of cell • Most common type of carcinoma
- 11. Squamous cell carcinoma • These cell help in changing the shape and bladder • Mainly occur due to prolong on chronic irritation of bladder and also due to long term use of urinary catheterisation. • These are very rare type of bladder cancer.
- 12. Papillary carcinoma • Cylinder ,finger like projection from the inner surface toward the hollow centre of the bladder • papillary cancer is some times called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential and tends to have very good outcomes
- 13. Flat carcinoma • Do not grow towards the hollow parts of the bladder at all • if a flat tumour is only in the inner Layer of bladder cells
- 17. Smoking Alcoholism Tabaco chewing
- 18. Environmental carcinogen Recurrent / chronic bacterial disease infection bladder stone Advance age High urinary ph. High cholesterol and fatly diet Pelvic radiation therapy Cancer of prostate colon and rectum
- 20. • Haematuria • Changes in bladder habits- polyurea dysuria burning sensation
- 21. ꙳Swelling in the feet ꙳Bone pain ꙳Oliguria ꙳Frequent UTI ꙳Being unable to urinate ꙳Lower back pain on affected side ꙳Laws and appetite ꙳Weight loss ꙳Feeling tired or week
- 22. Staging of bladder cancer
- 23. It is describe by AJCC (American joint committee on cancer)TNM system, based on 3 key pieces Of information ♣ T-describe how the main(primary)tumour has growth through the bladder wall and weather it has grown into near by tissues. ♣ N-indicate any cancer spread to lymph nods near the bladder. ♣ M-indicate if the cancer has spread (metastasized)to distend sites such as other Orgon.
- 24. ♣ letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. ♣ Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. ♣ Once a person’s T, N, and M categories have been determined, usually after surgery, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping
- 25. ♣ The earliest stage cancers are called stage 0 and then range from stages I (1) through IV (4). ♣ As a rule, the lower number means less or no spread cancer. ♣ A higher number, such as stage IV, means a more advanced cancer. ♣ Staging is based on the results of physical exam, biopsy, imaging tests, and the results of surgery.
- 26. stage 0a 0is Stage grouping Ta N0 M0 Tis N0 M0 Stage description • Non-invasive papillary carcinoma (Ta). Grown toward the hollow centre of the bladder • No spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) • No Distant sites (M0). • Flat, and non-invasive carcinoma and only Growing in the inner lining layer of the bladder. • No spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) • Distant sites (M0).
- 27. Stage I II Stage grouping T1 N0 M0 T2a or T2b N0 M0 Stage description • Cancer grown into the layer of connective tissue of bladder but not reached the muscle layer of bladder wall (T1). • No spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) • No distant sites (M0). • Cancer grown into inner (T2a) or outer (T2b) muscle layer of the bladder wall, but not passed completely through the muscle of fatty tissue that surrounds the bladder. • The cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) • No distant sites (M0)
- 28. stage IIIa Stage grouping T3a, T3b or T4a N1 M0 stage classification • Cancer has grown in to the muscle layer and into the surrounded fatty tissue of bladder (T3a or T3b). Might spread into the prostate, uterus, or vagina, but it is not growing into the pelvic or abdominal wall (T4a). • spread to nearby lymph nodes (N1) • NO to distant sites (M0)
- 29. Stage IIIb Stage grouping T1-T4a N2 and N3 M0 stage classification • Cancer Grow in layer of connective tissue under the lining of bladder wall (T1) • grow in connective tissue with muscle layer of bladder (T2) grown into fatty tissue layer that surrounds the bladder (T3a or T3b) • It might have spread in to the prostate, uterus or vagina but • not growing in to pelvis or abdominal wall (T4a) • Spread 2 or more lymph nodes in to pelvis (N2) or lymph nodes along the common iliac arteries (N3) • Not spread to distant sites.
- 30. stage Iva IVb Stage grouping T4b N2 and N3 M1 T N M stage classification Grown through bladder wall into the pelvic or abdominal wall (T4b) • Spread 2 or more lymph nodes in to pelvis (N2) or lymph nodes along the common iliac arteries (N3) • spread to nearby distant sites. Might or might not have grown through the wall of bladder in to near by organ. It might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes. It has spread to a distant set of lymph nodes. (M1a) It has spread to 1 or more distant organs.(such as bone, liver or lungs. (M1b)
- 33. Diagnostic evaluation • History collection PAST HEALTH HISTORY PRESENT HEALTH HISTORY • Physical examination • Urinary analysis- for haematuria • Urine cytology- to find the cancer cell in urine
- 34. Urine test for tumour marker Newer test look for substances in the urine that might indicate bladder cancer. These include- Urovision – these show chromosomal changes in bladder cell. BTA Test – These tests look for a substances called bladder tumour –associated antigen (BTA) also known as CFHrp, in the urine.
- 35. • Immunocyte – This tests look at cells in the urine for the presence of substances such as mucin and carcinoma embryonic antigen (CEA) • NMP22 Bladder check – this tests looks for a protein called NM22 in the urine. • Cystoscope – It is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allow to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called cystoscope.
- 37. PET SCAN
- 38. Ultrasonography
- 40. Most common treatment options for bladder cancer are listed below, Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including: • Type, stage, and grade • Possible side effects • The patient’s preferences and overall health
- 41. Intravesical (local)chemotherapy. Drugs delivered into the bladder through a catheter Local treatment only destroys superficial tumour cells that come in contact with the chemotherapy solution. Not for metastasis condition. Mitomycin (Mitozytrex, Mutamycin) and thiotepa are the drugs used most often for intravesical. Systemic chemotherapy.
- 43. Combination of methotrexate, vinblastine, Adriamycin, and cisplatin, for metastatic bladder cancer. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin is now considered a 1st line treatment for bladder cancer. Fluorouracil (Adrocil)- Antimetabolite drugs which inhibit the RNA synthesis Methotrexate- Inhibit both RNA or DNA synthesis.
- 44. Gemcitabine- it inhibit the DNA replication. Antineoplastic, vinca alkaloid-it act on the G phase of mitosis, inhibiting the DNA and RNA synthesis. E.g. vinblastine Anthracycline- it synthesis by steric obstruction. They intercalate between DNA base pairs and triggers DNA cleavage by topoisomerase 2nd . E.g. doxorubicin, valrubicin
- 45. Alkylating agent- Inhibit the cell growth and proliferation. They inhibit the DNA synthesis by proliferation of DNA cross link. e.g. cisplatin, carboplatin PD-1/ PD-L1 inhibitors- these is expressed on the surface of activated T cell under normal condition. PD-L1 interaction inhibit immune activation and reduce T cell cytotoxic activity when bound. E.g.- Atezolizumab, Nivolumab
- 47. Transurethral bladder tumour resection (TURBT). Used for diagnosis, staging, as well as treatment. Anaesthetic is given to block the awareness of pain. Inserts a cystoscope through the urethra into the bladder. Then removes the tumour using a tool with a small wire loop, a laser, or fulguration (high-energy electricity).
- 48. Cystectomy Removal of the whole bladder and possibly nearby tissues and organs. For men, the prostate and urethra also may be removed. For women, the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and part of the vagina may be removed. In addition, lymph nodes in the pelvis are removed for both men and women. This is called a pelvic lymph node dissection.
- 49. Urinary diversion. If the bladder is removed, create a new way to pass urine out of the body. One way is,use a section of the small intestine or colon to divert urine to a stoma or ostomy (opening) on the outside of the body. • Then patient wear a bag that attached to the stoma to collect and drain urine. • Increasingly, use the part of the small or large intestine to make a urinary reservoir, which is a storage pouch that sits inside the body. • Then pouch is connect to the urethra that is called neobladder.
- 51. 2nd way is, to use an internal (inside the abdomen) pouch made of small intestine is created and connected to the skin on the abdomen or umbilicus (belly button) through a small stoma. In this patients do not need to wear a bag. Patients drain the internal pouch multiple times a day by inserting a catheter through the small stoma and immediately removing the catheter.
- 53. • Also called biologic therapy, designed to boost the body’s natural defences to fight the cancer. • It is made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function.
- 54. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), Standard immunotherapy drug similar to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. ֍ Placed directly into the bladder through a catheter (intravesical therapy). ֍ That stimulates the immune system to destroy the tumour. BCG can cause flu-like symptoms, chills, mild fever, fatigue, a burning sensation in the bladder, and bleeding from the bladder.
- 55. Interferon (Roferon-A, Intron A, Alferon) is another type of immunotherapy that can be given as intravesical therapy. Sometimes combined with BCG if using BCG alone does not help treat the cancer
- 56. ☺Immunotherapy block a protein called PD-1. ☺ PD-1 is found on the surface of T-cells, which are a type of white blood cell that directly helps the body’s immune system fight disease. ☺Because PD-1 keeps the immune system from destroying cancer cells, ☺ stopping PD-1 from working allows the immune system to better eliminate the disease.
- 59. ♣ Use of high-energy x-rays or other particles to destroy cancer cells. ♣ Radiation therapy is usually not used by itself as a primary treatment for bladder cancer, but it may be given in combination with chemotherapy.
- 60. Types of radiation therapy 1. External beam radiation therapy 2. internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy.
- 61. External beamradiation therapy • Common type of radiation treatment is called external-beam radiation therapy, given from a machine outside the body. • Machine is called linear accelerator
- 62. Internal radiation therapy • Radiation therapy is given using implants, it is called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. • In this a radioactive seed is inserted in bladder(radioisotope like cobalt- 60)
- 64. Major side effects are- • Anaemia • Thrombocytopenia • Constipation • Diarrhoea • Fertility issue in both male and female • Alopecia • Peripheral neuropathy • Sexual health issue in both men and women • Urinary and bladder problem.
- 65. Care for side effects • Stop the chemotherapy and consult the physicians. • Take the concern before continue the treatment • Palliative care or supportive care
- 67. Assessment ♣ Pain ♣ Anxiety ♣ Impaired urinary elimination ♣ Ineffective coping mechanism ♣ Sexual disfunction ♣ Disturbed body image
- 68. Nursing diagnosis Acute pain related to disease process as evidence by patient verbalization Goal- to control pain Intervention- • Assess the location, intensity duration of pain. • Encourage to maintain bed rest. • Administer the prescribed medication (analgesic)
- 69. Impaired urinary elimination related to bladder cancer as evidence by patient verbalization Goal- to maintain the urinary elimination pattern Intervention • Observe the amount, colour, and frequency of urination • Administer the prescribed medication • Educate the eliminate regarding disease process
- 70. Anxiety related to disease process and haematuria as evidence by patients query regarding disease process. Goal- to minimize the anxiety of patient Intervention • Assess the patient general condition • Check the patient knowledge level regarding disease level • Listen the patient carefully • Educate patient regarding disease condition
