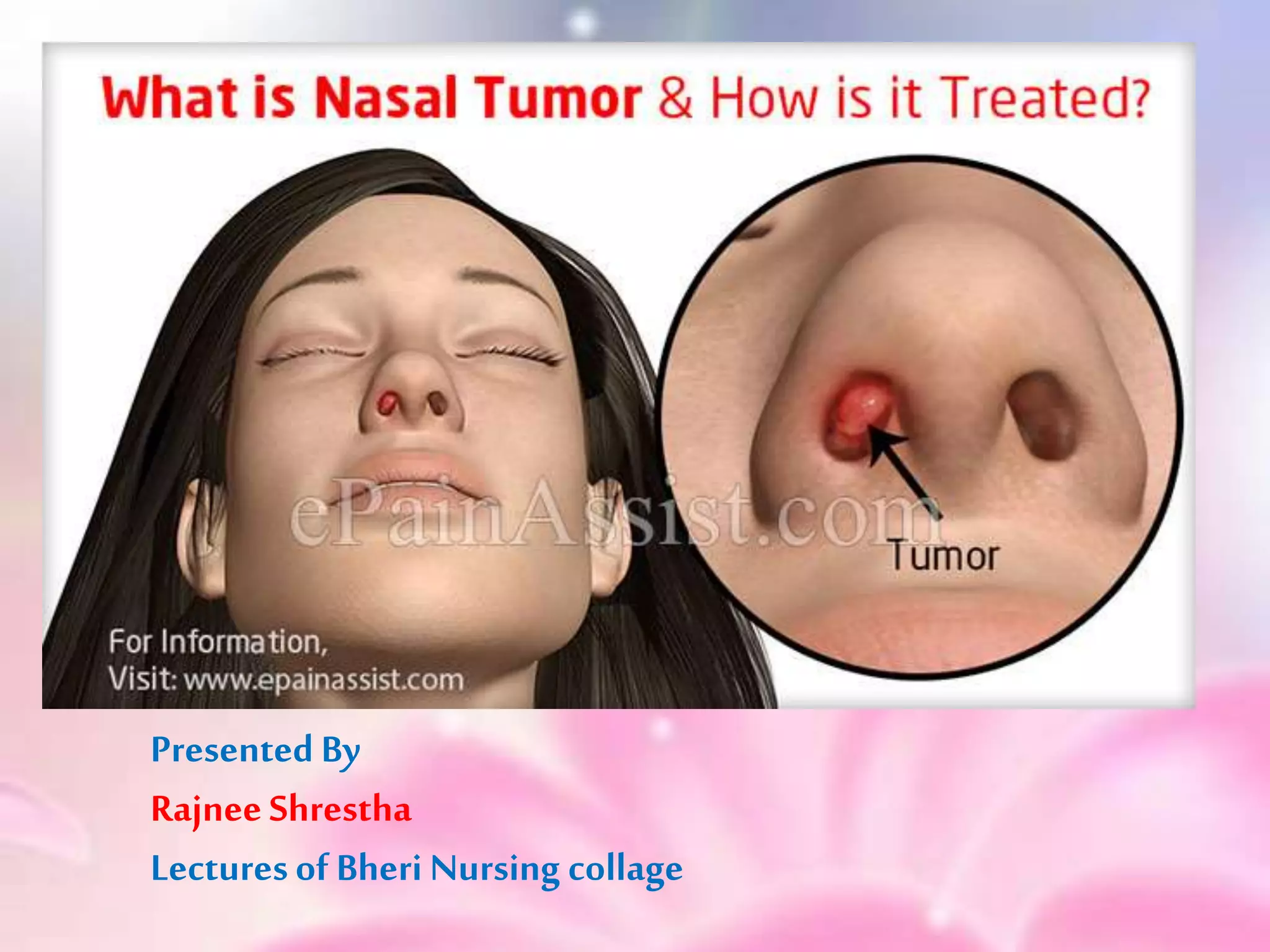
Nasal and sinus tumors can be benign or cancerous growths occurring in the nose or sinuses. Cancerous nasal tumors are rare, with cancers of the sphenoid or frontal sinuses accounting for only 5% of such cancers. Risk factors include smoking, dust and chemical exposures, and men are more commonly affected in their 50s and 60s. Tumors are diagnosed through medical history, physical exam, imaging like MRI or CT, and biopsy. Treatment options depend on the size and spread of the tumor, and may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or endoscopic or open surgical removal.