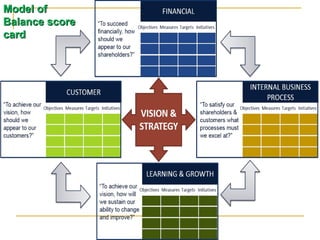
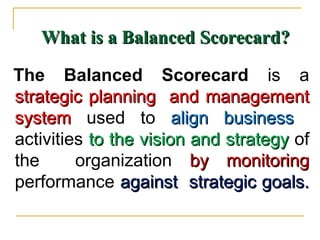
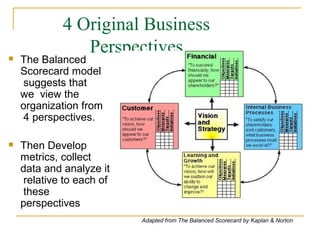
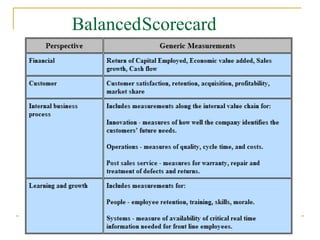
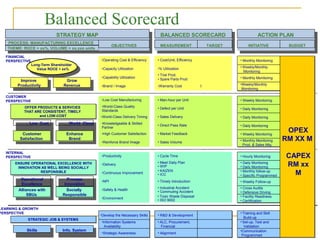
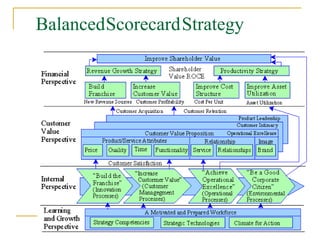
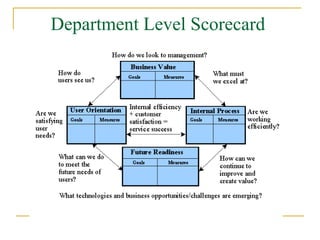
The document discusses the balanced scorecard approach. It begins by defining the balanced scorecard as a strategic planning and management system used to align business activities with an organization's vision and strategy by monitoring performance against goals. It describes the balanced scorecard as having four perspectives - financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. These perspectives allow an organization to measure performance holistically rather than focusing solely on financial measures. The document outlines some key factors for successful implementation of a balanced scorecard and provides examples of balanced scorecards at both the organizational and departmental levels. It also discusses some potential pitfalls in using the balanced scorecard approach.