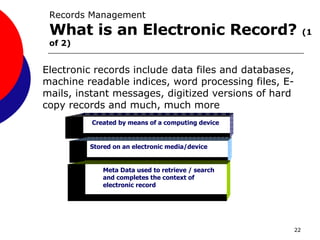
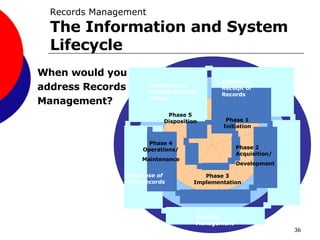
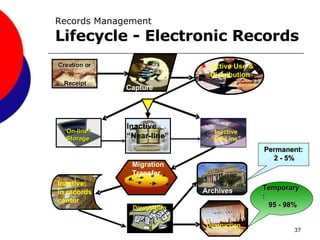
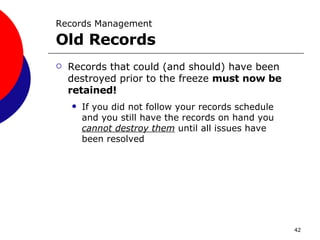
This document provides guidance on records management for the TRICARE Management Activity (TMA). It discusses what constitutes a TMA record, the records lifecycle, impacts of record freezes, and when records can be destroyed. It emphasizes the importance of properly managing both paper and electronic records in accordance with relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal and organizational issues.