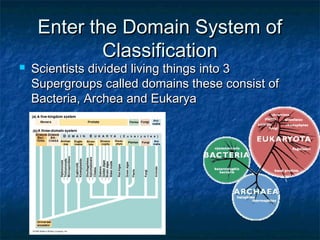
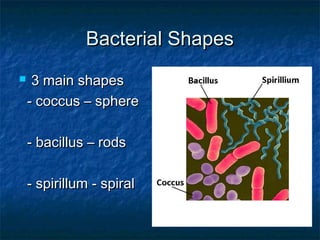
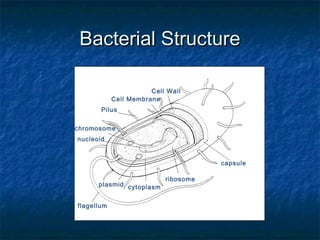
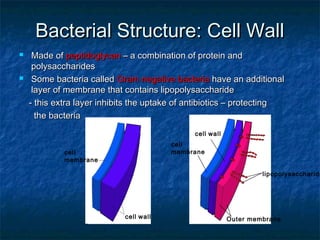
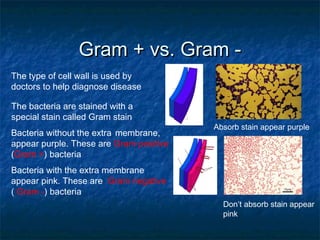
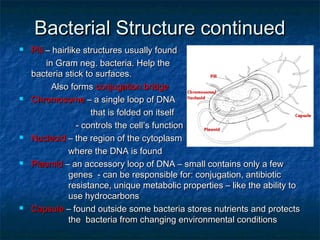
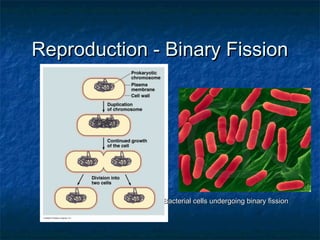
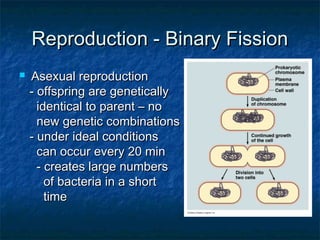
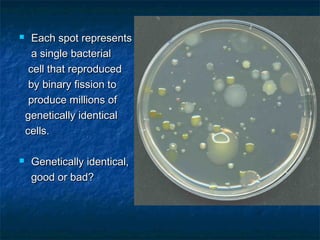
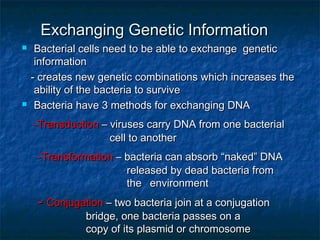
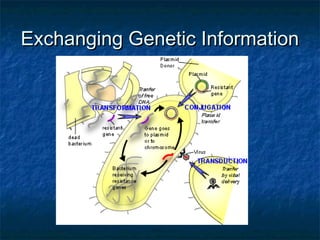
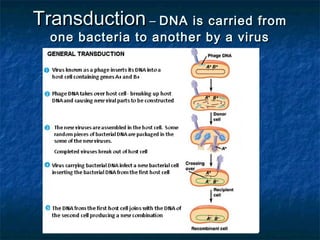
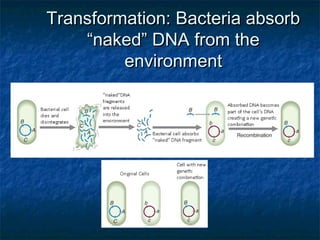
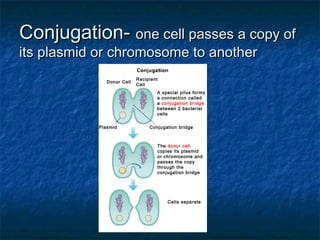
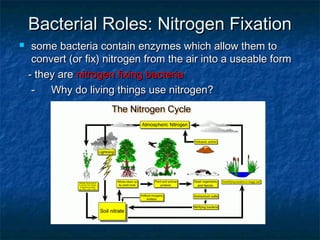
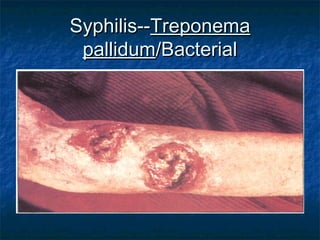
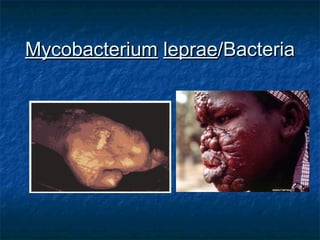
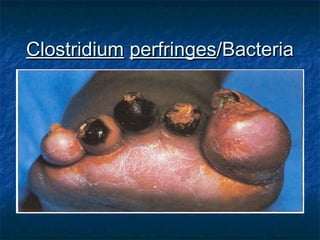
Prokaryotes like bacteria and archea make up the human microbiome, comprising 1-3% of the human body mass. Bacteria are some of Earth's oldest life forms and come in various shapes. They have diverse metabolic functions and can live in extreme environments. Some bacteria engage in symbiotic relationships with humans and support functions like digestion. While many bacteria are beneficial, certain pathogens can cause diseases. Advances like antibiotics revolutionized medicine but their overuse led to increased antibiotic resistance in bacteria.