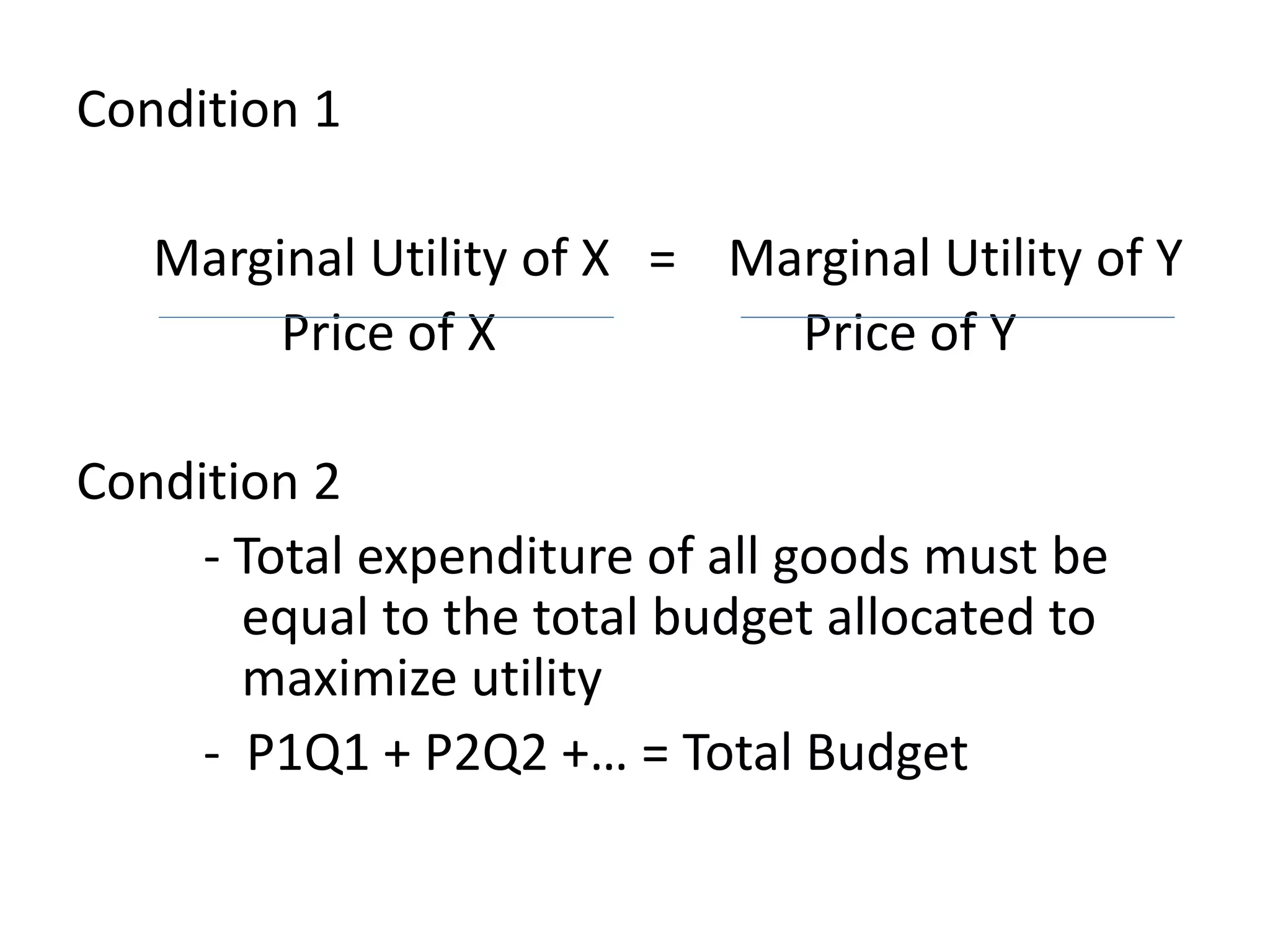
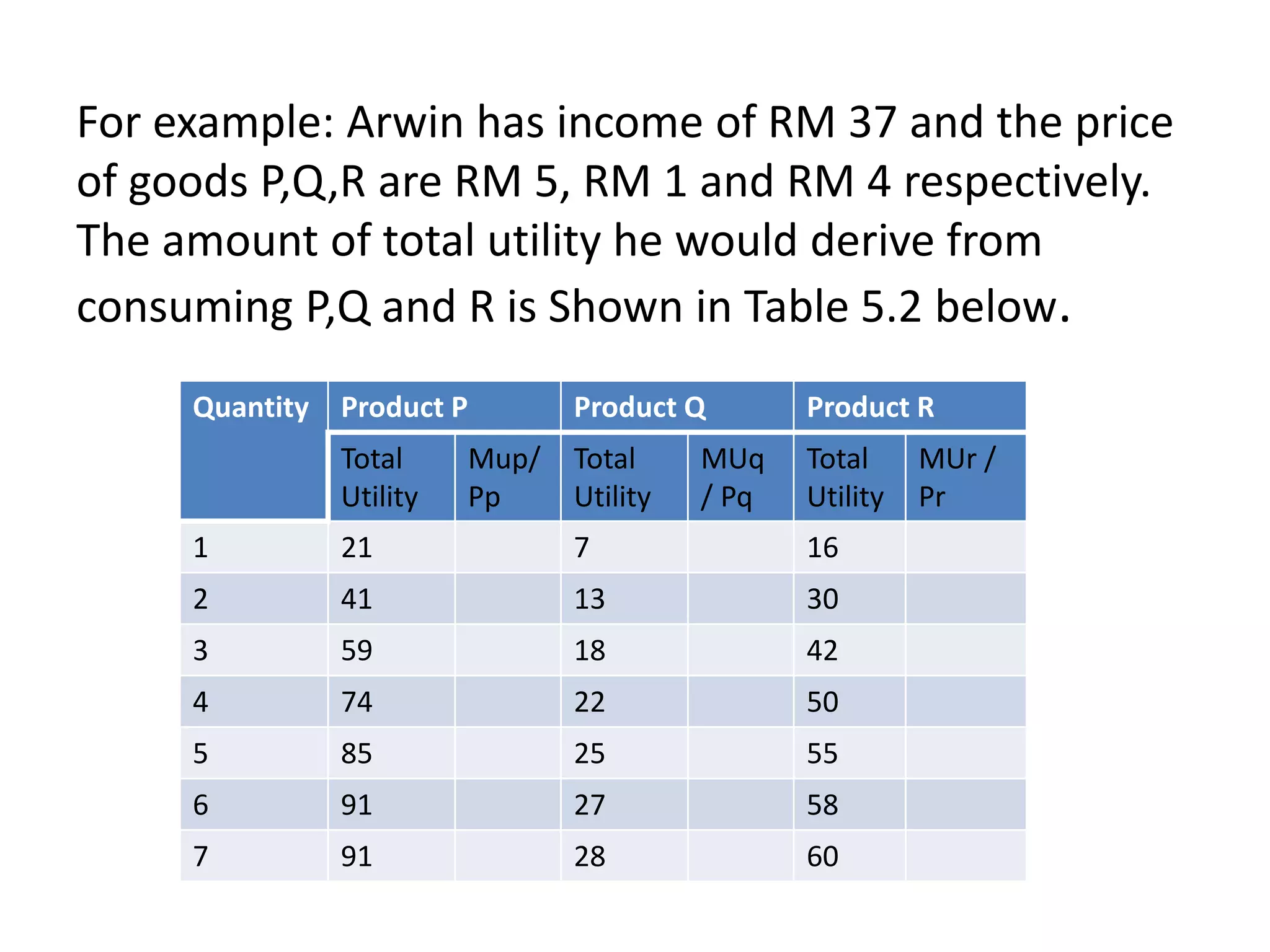
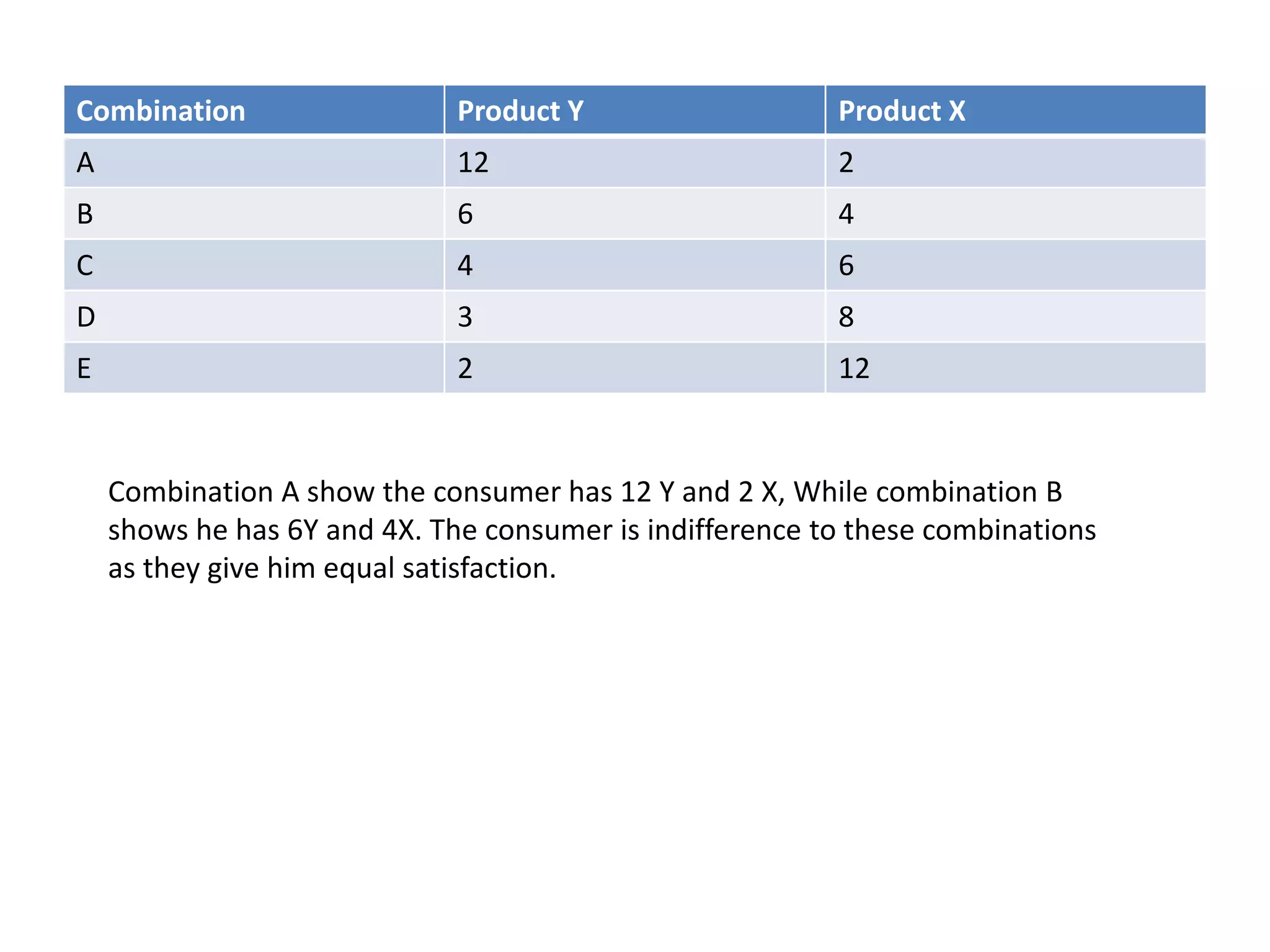
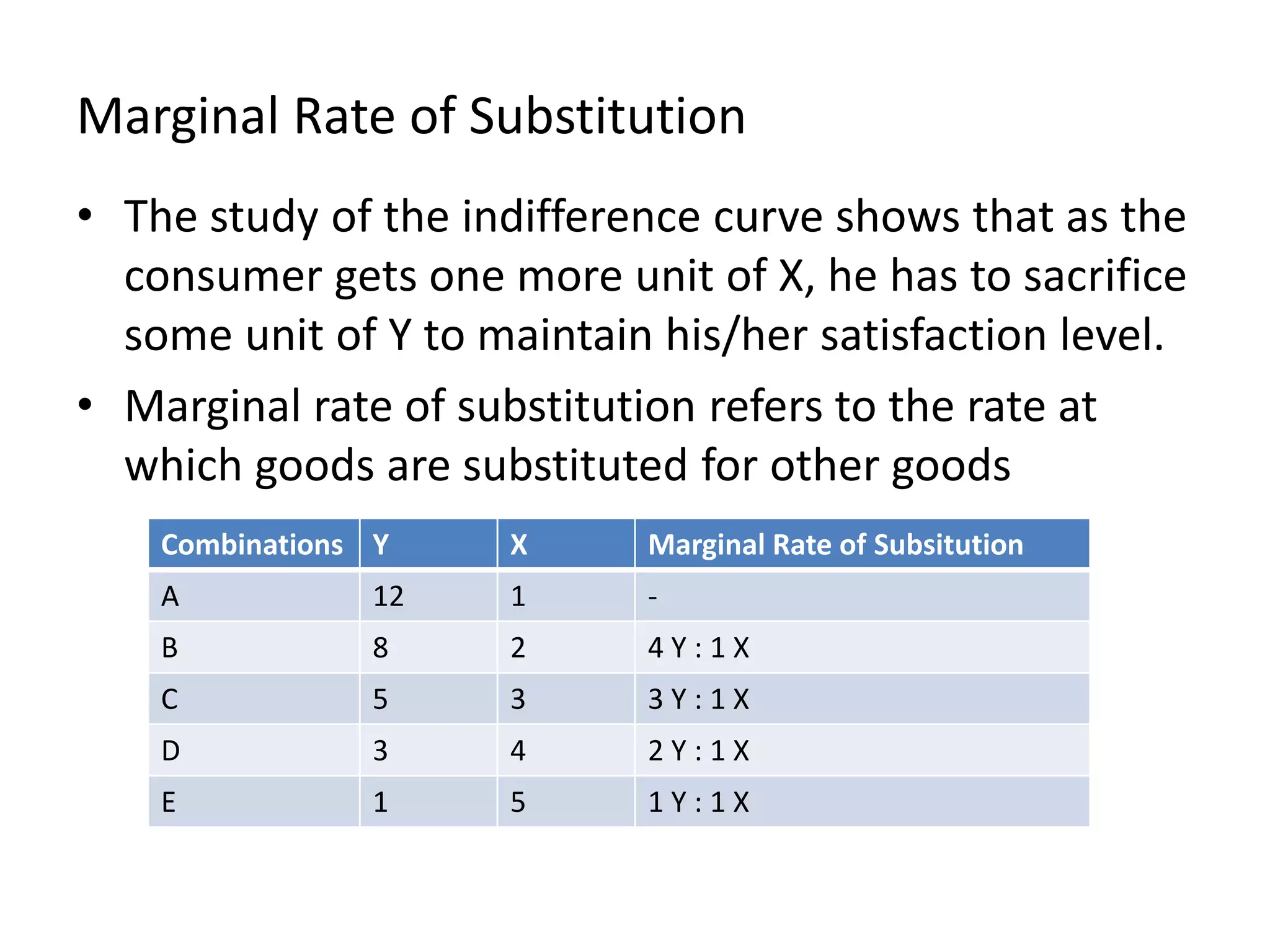
This document discusses consumer behavior theory and the two approaches to understanding consumer utility - the cardinal and ordinal approaches. It explains key concepts like total utility, marginal utility, indifference curves, and the conditions for consumer equilibrium. The cardinal approach uses measurements of utility to analyze concepts like diminishing marginal utility and the law of equi-marginal utility. The ordinal approach uses indifference curves and budget constraints to show consumer equilibrium without measuring exact utility amounts.