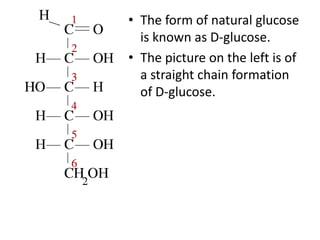
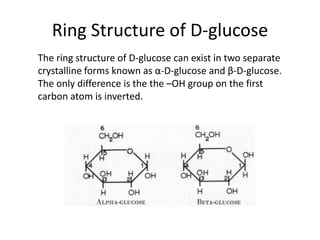
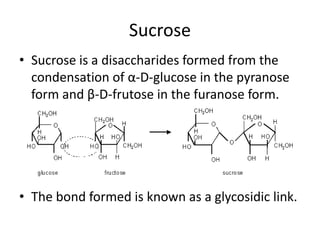
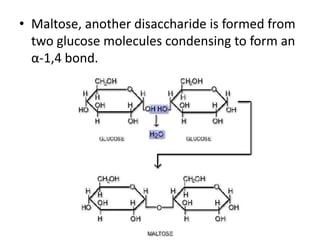
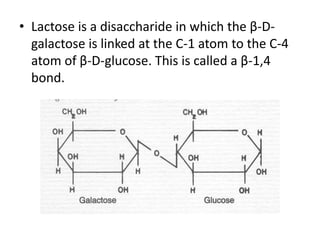
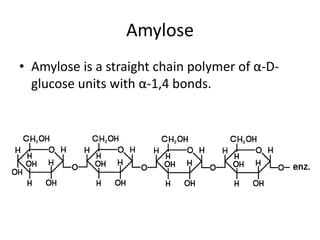
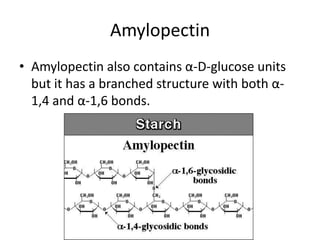
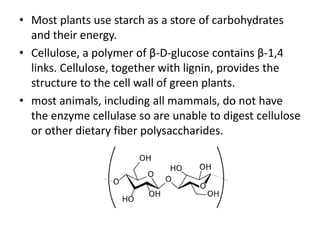
This document discusses carbohydrates including monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. It explains that monosaccharides have formulas of C5H10O5 or C6H12O6 and exist as pentoses or hexoses like glucose. Monosaccharides can form ring structures and optical isomers. Disaccharides like sucrose form from monosaccharide condensation, while polysaccharides like starch are made of many monosaccharide units and provide structure or energy storage. Polysaccharides serve important functions in the body including energy provision, energy storage as glycogen, and as dietary fiber.