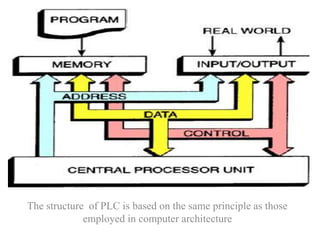
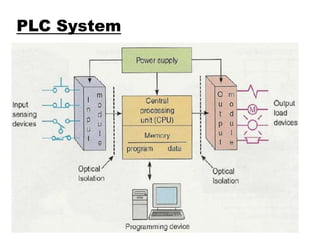
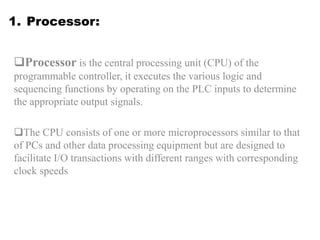
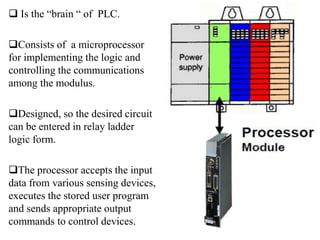
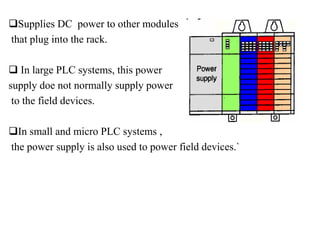
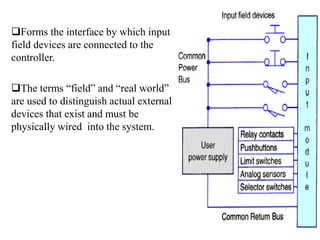
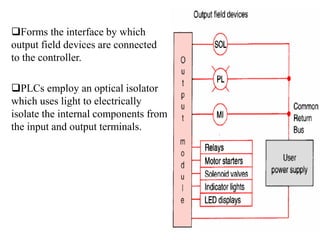
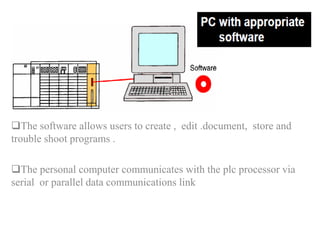
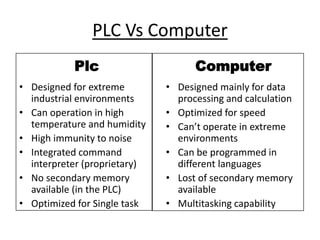
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) were developed to control industrial machinery in a programmable and reliable way. A PLC has a processor that executes stored instructions to control inputs and outputs based on ladder logic programming. It includes a power supply, memory to store the user program, and I/O modules to interface with field devices. PLCs offer advantages over hardwired control systems like easier programming, flexibility, and communication capabilities. They are used widely in industrial applications for tasks like sequencing, timing, counting, and analog control.