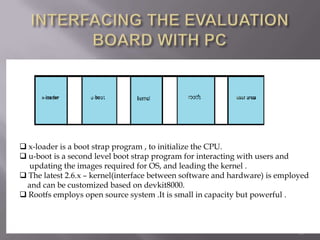
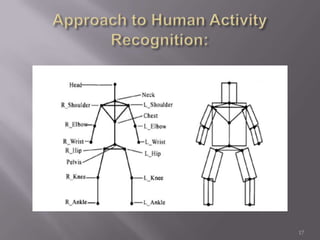
The document discusses human activity recognition from video data using computer vision techniques. It describes recognizing activities at different levels from object locations to full activities. Basic activities like walking and clapping are the focus. Key steps involve tracking segmented objects across frames and comparing motion patterns to templates to identify activities through model fitting. The DEV8000 development kit and Linux are used to process video and recognize activities in real-time. Applications discussed include surveillance, sports analysis, and unmanned vehicles.