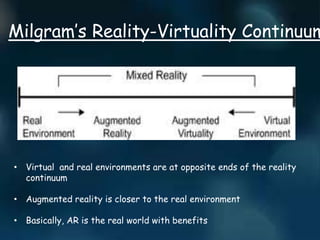
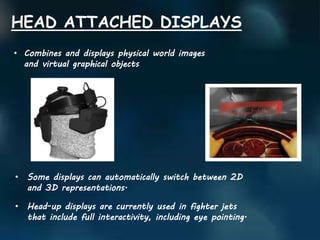
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the real world by adding interactive virtual elements, contrasting with virtual reality's fully immersive environments. AR applications span various fields including advertising, education, and medical, providing users with enhanced information and experiences. Key technologies include handheld devices, spatial displays, and future innovations such as AR-enabled contact lenses and 'holodecks'.