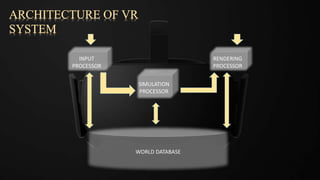
Virtual reality (VR) is designed to immerse users in a computer-generated environment that feels real, achieved through advanced technology like head-mounted displays (HMDs) and various input devices. The document discusses the history of VR, different types of systems, and how VR works, including the hardware and software components necessary for optimal experiences. Additionally, it highlights applications of VR in gaming, education, therapy, military training, automotive design, and healthcare, as well as potential side effects of VR usage.