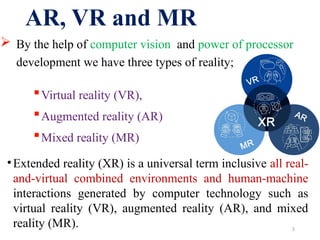
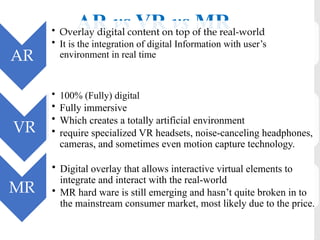
The document discusses augmented reality (AR), its comparison with virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR), and its applications across various fields like education, medicine, and engineering. AR enhances the real environment by overlaying digital content, enabling interaction with both virtual and real objects. It highlights the architecture of AR systems, their functionalities, and examples of implementation in different disciplines.