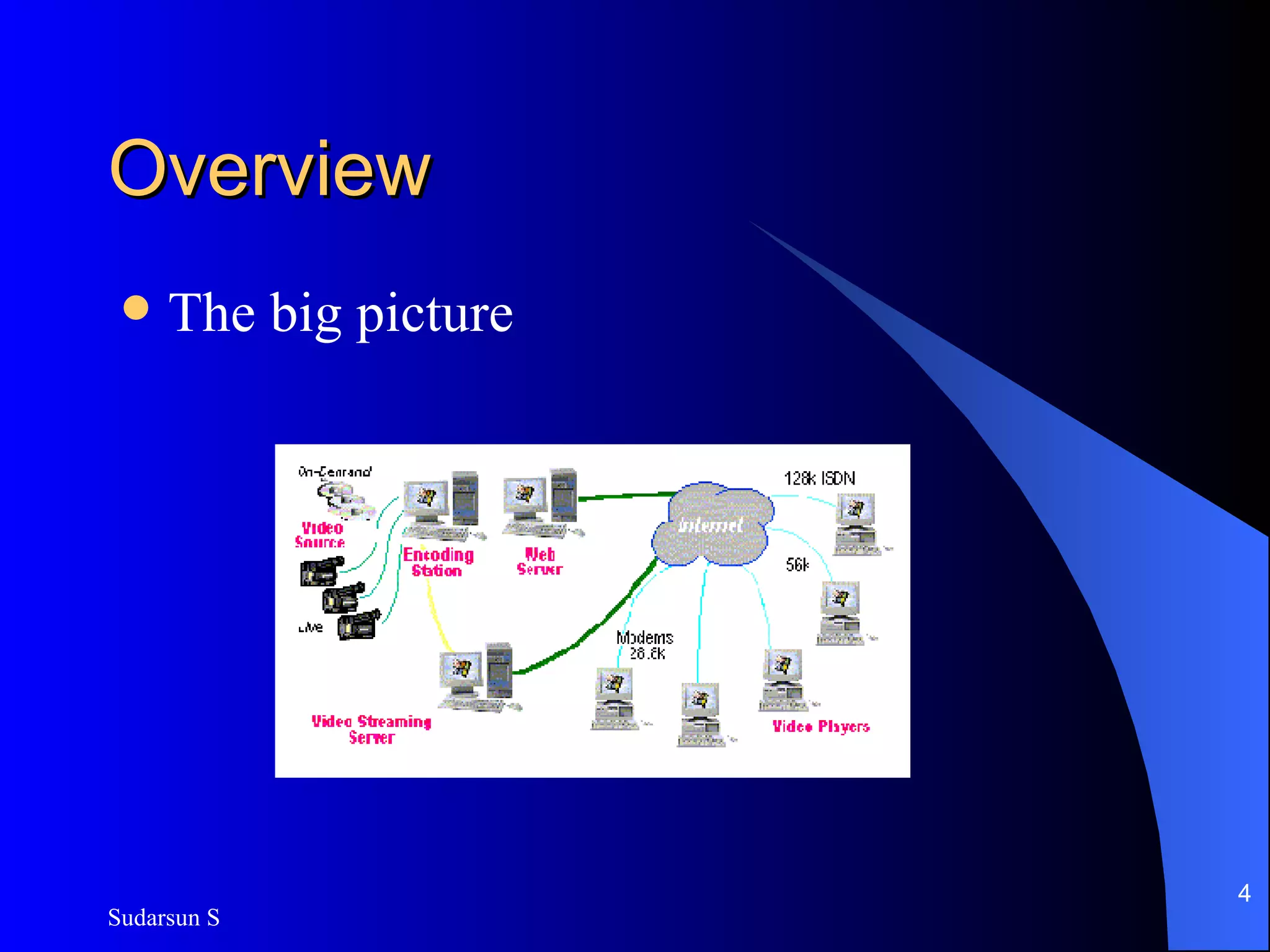
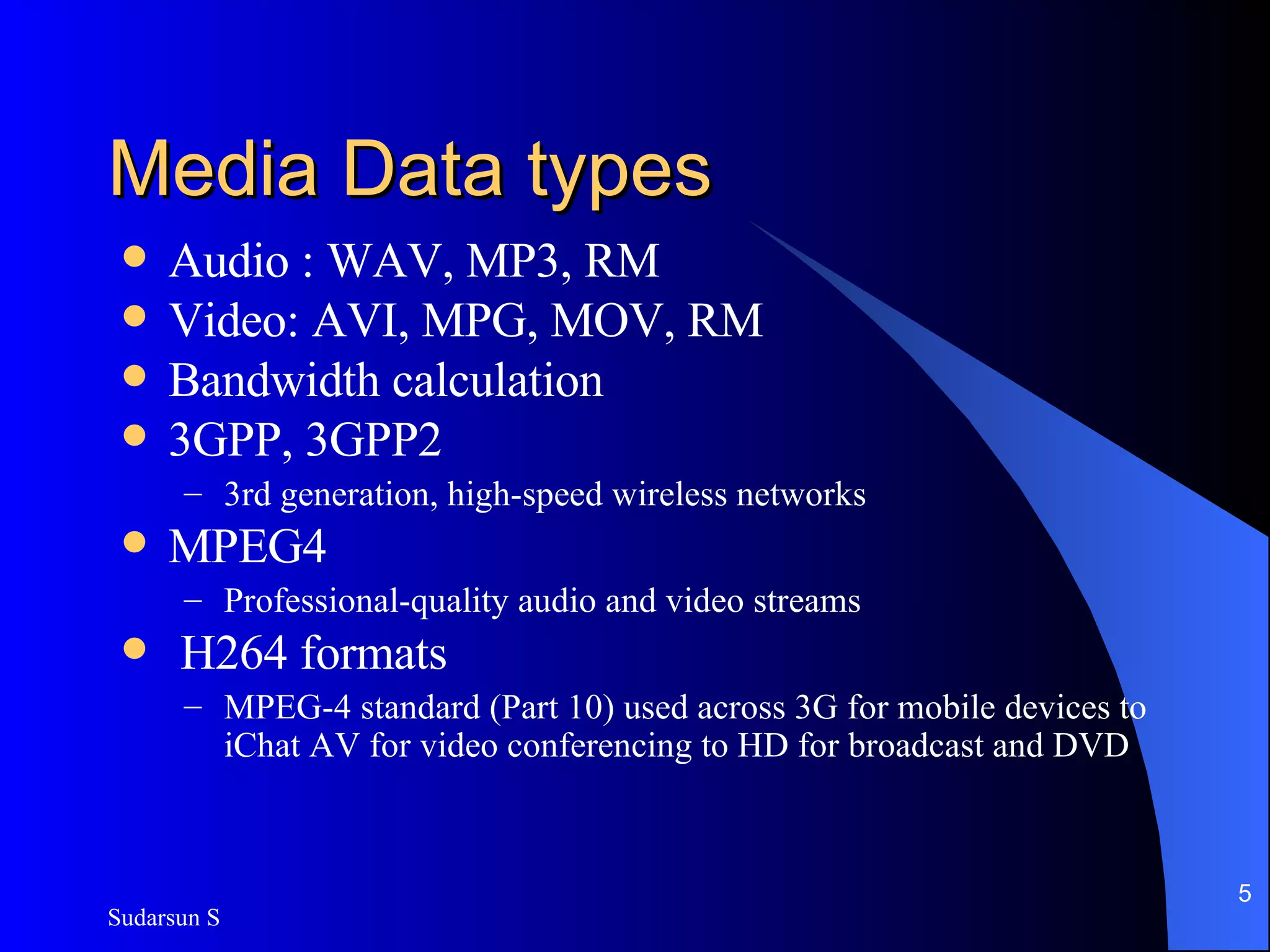
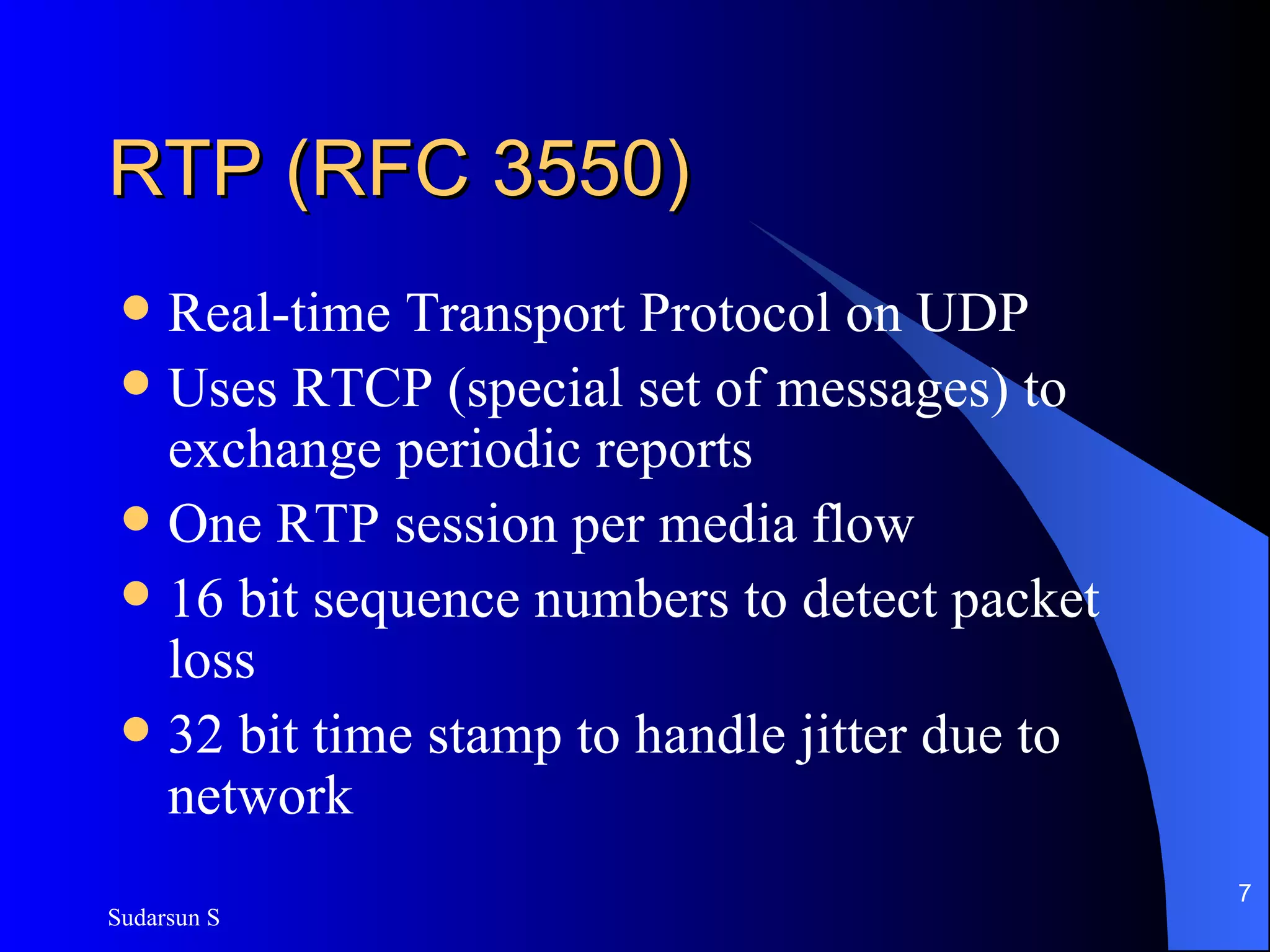
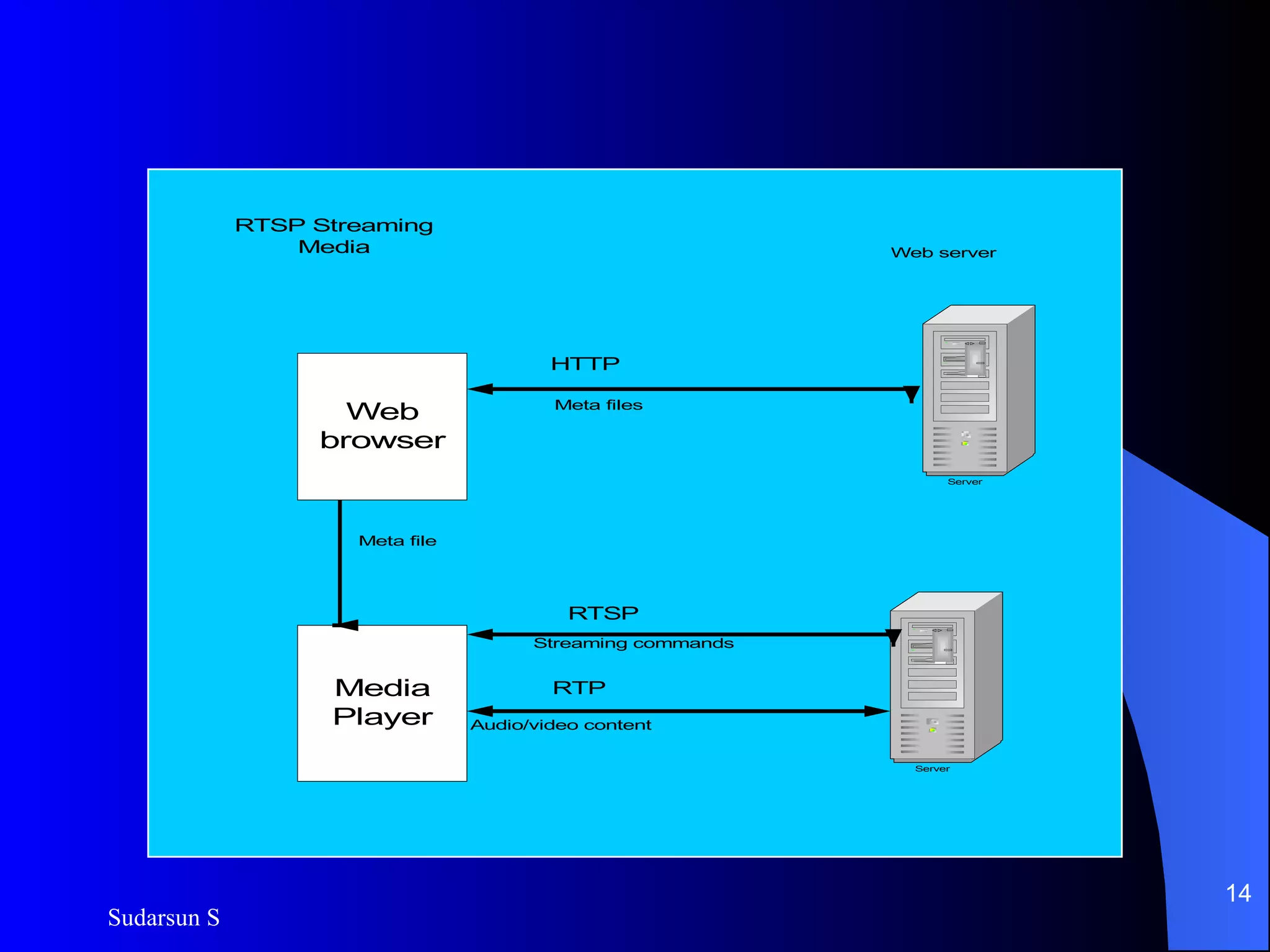
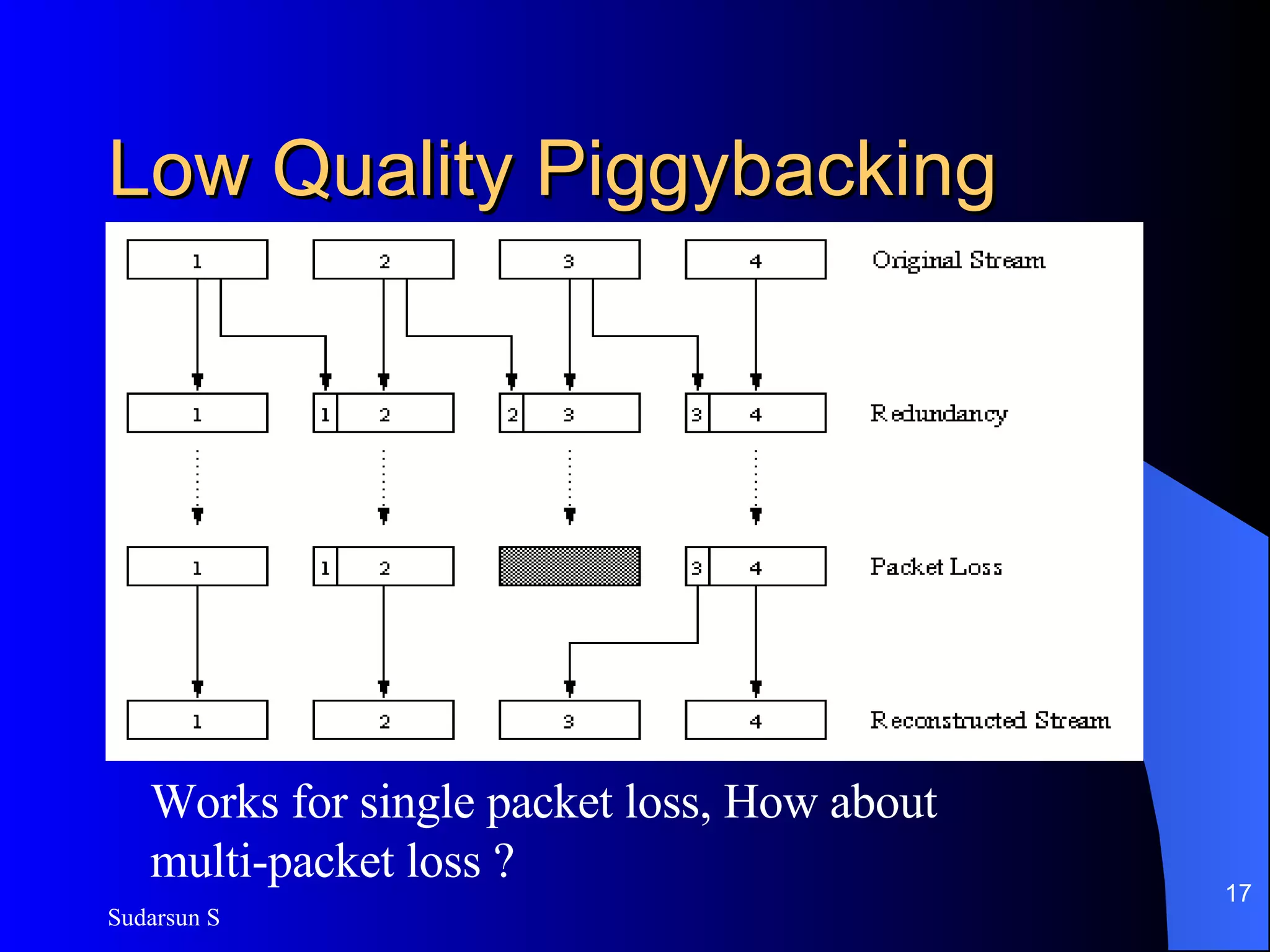
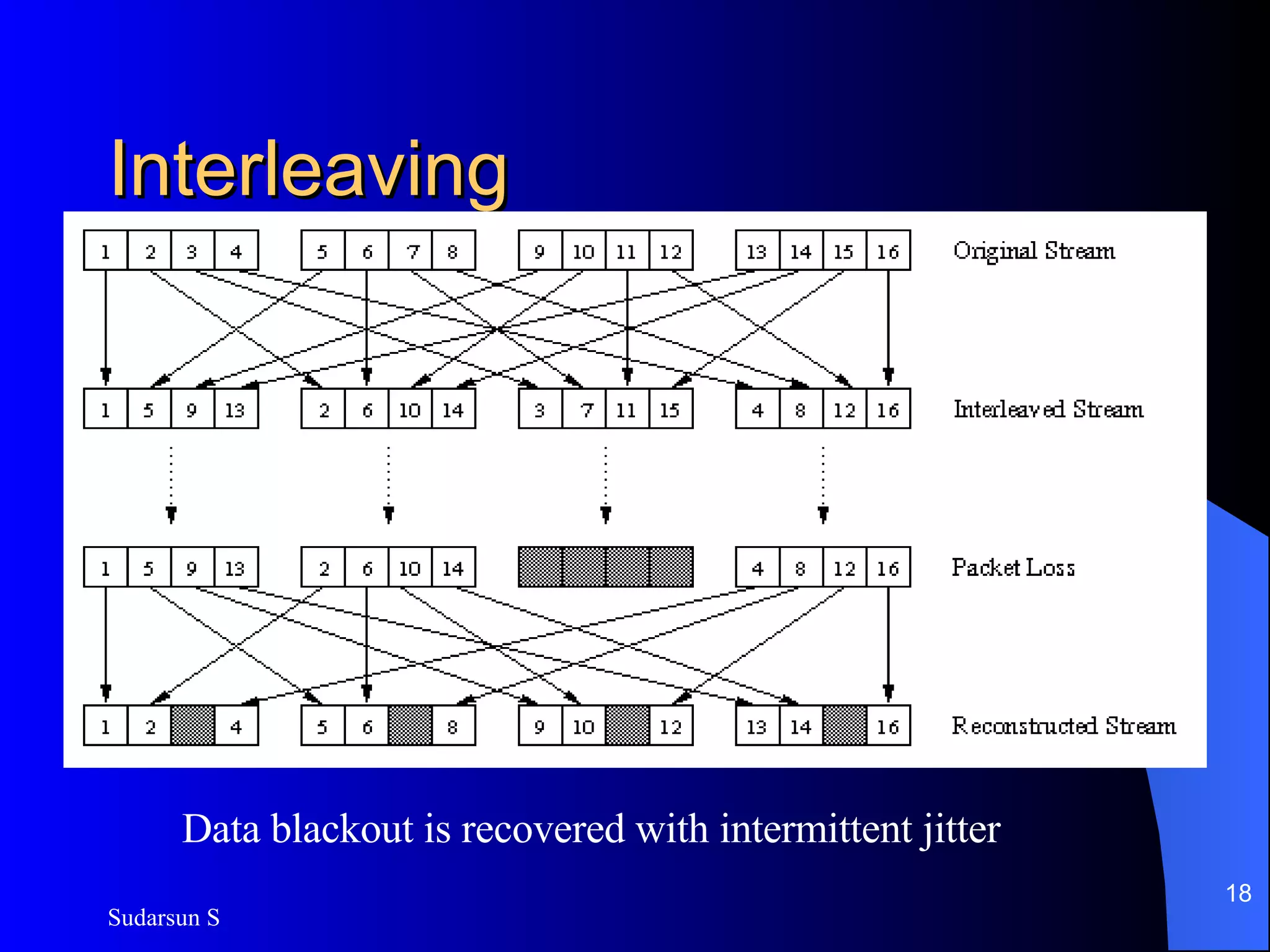
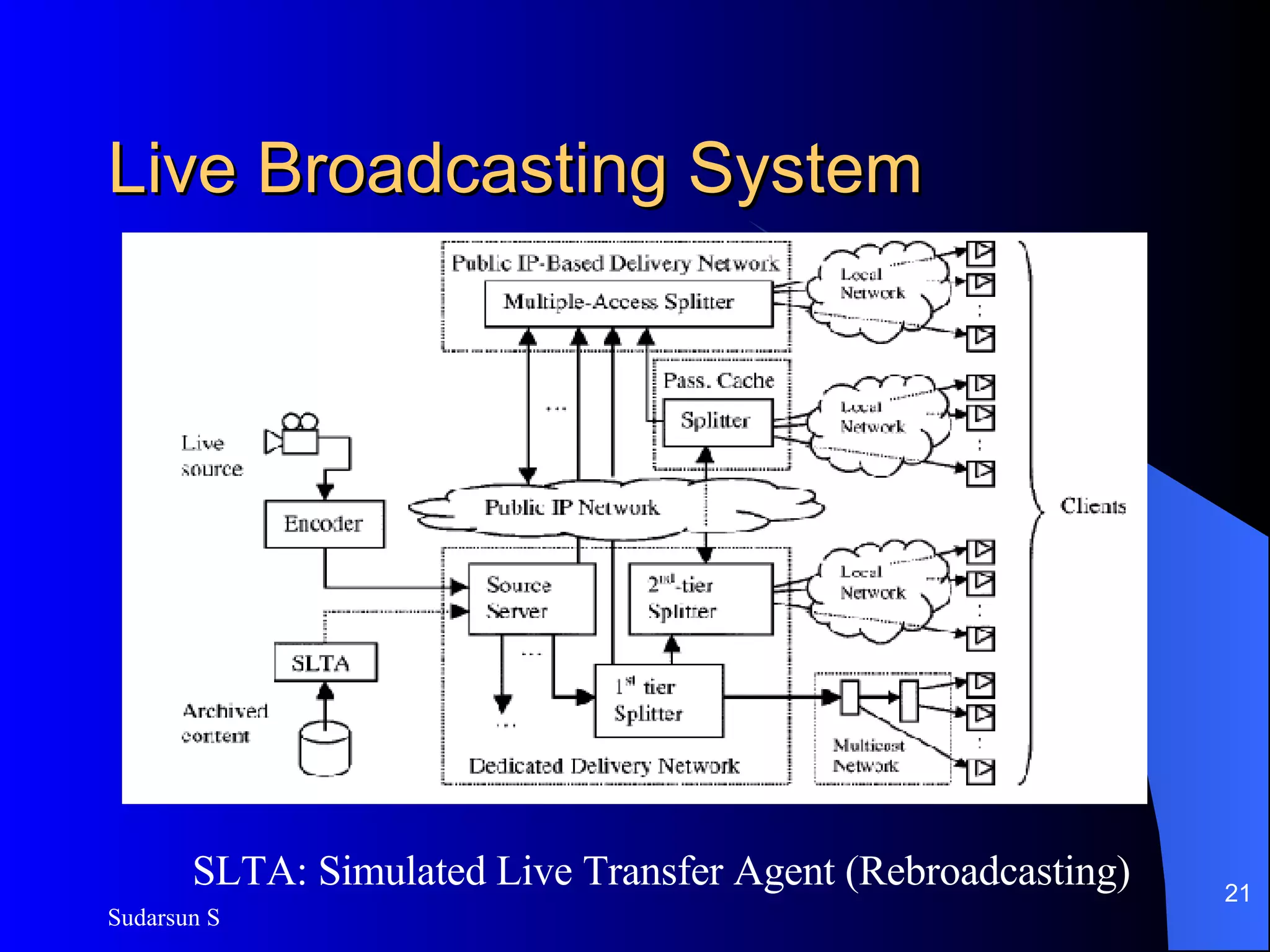
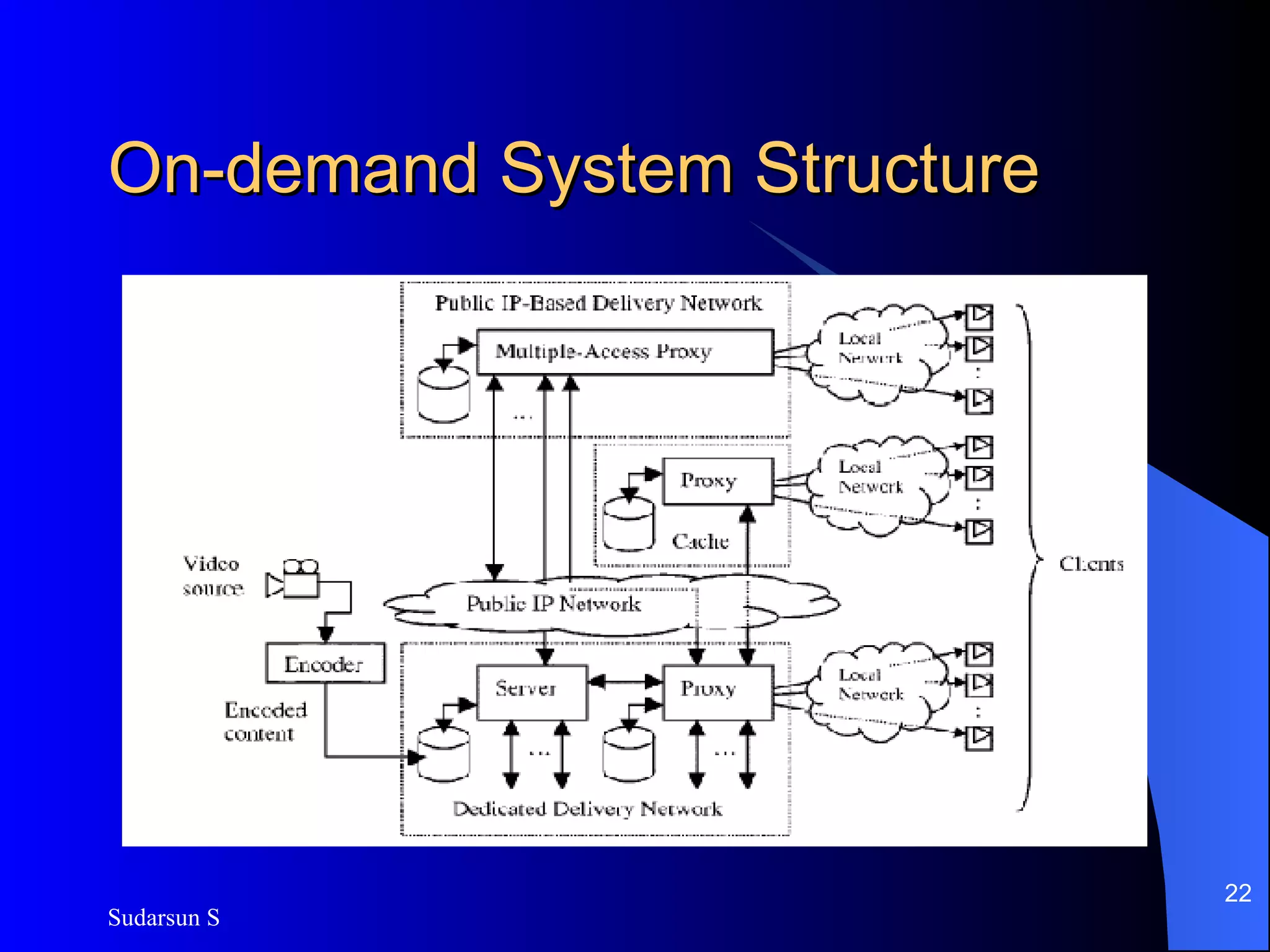
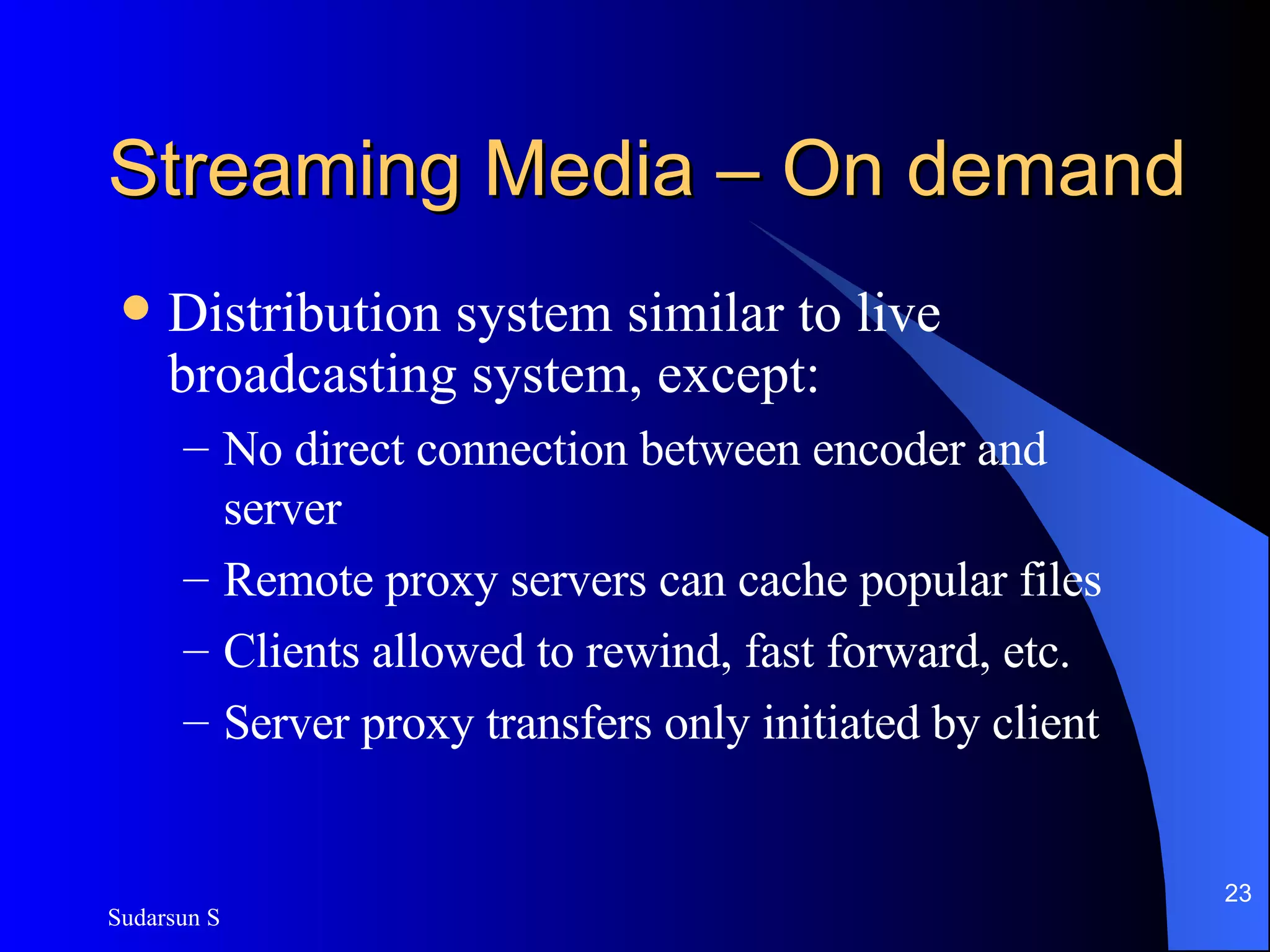
The document discusses audio and video streaming over the internet. It covers protocols like TCP, UDP, RTP and RTSP that are used for real-time media streaming. It also discusses error correction techniques like piggybacking and interleaving. Various streaming media delivery methods are described like live broadcasting, video on demand, and video conferencing. Limitations of streaming media and popular streaming servers are also summarized.
![Audio and Video over Internet Sudarsun S., M.Tech Checktronix India Pvt Ltd Chennai 600034 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/audio-and-video-over-internet-1193735644583180-2/75/Audio-And-Video-Over-Internet-1-2048.jpg)












![Thank You Sudarsun S., M.Tech Director – Research and Development Checktronix India Pvt Ltd [email_address] November 2005](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/audio-and-video-over-internet-1193735644583180-2/75/Audio-And-Video-Over-Internet-28-2048.jpg)