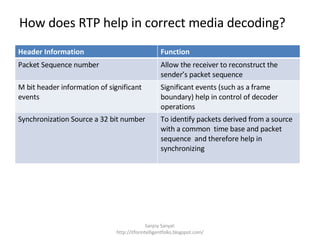
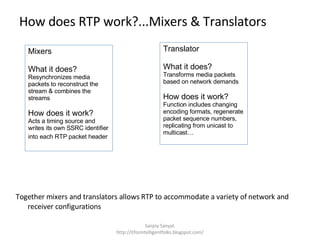
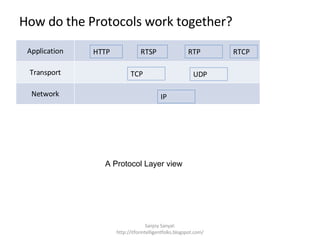
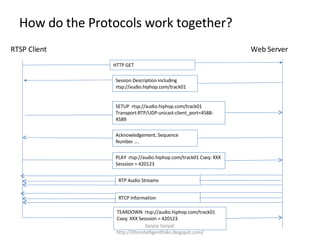
The document discusses several standard and proprietary streaming media protocols. It introduces Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP) which transport streaming media and provide quality of service reports. It also describes Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) which provides playback controls. Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language (SMIL) is mentioned as an XML language for multimedia content. Major companies like Real, Microsoft, and Apple are noted to use similar but proprietary protocols instead of the standards.