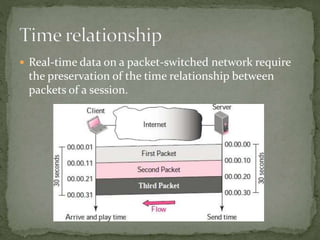
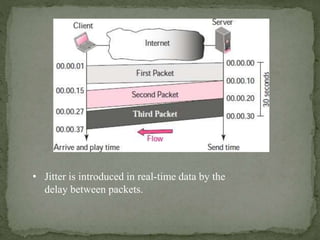
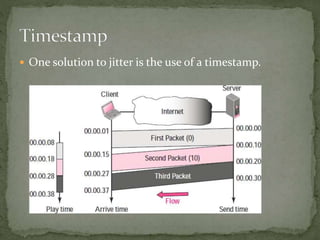
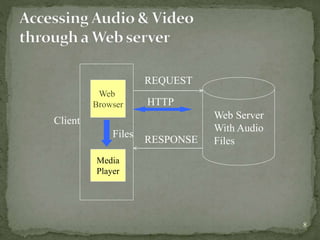
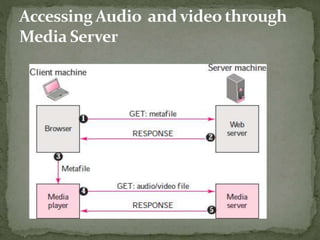
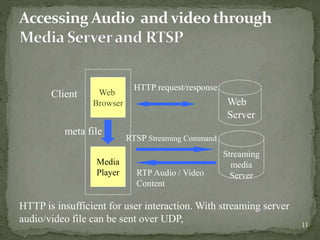
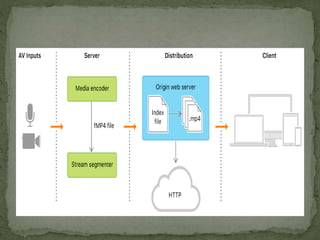
The document discusses streaming media technology which enables real-time distribution of audio, video, and multimedia over the Internet. Streamed data is transmitted by a server and received/displayed by client applications. There are advantages like steady service and on-demand access, but also disadvantages like difficulty maintaining steady service with low bandwidth and high maintenance costs for streaming servers. The document then describes different types of streaming including stored, live, and interactive audio/video. It also outlines four approaches to streaming using web servers and media servers with protocols like HTTP, RTSP, and RTP.










![18
Start Line
Message Header
……
Message Header
CRLF
[message body]
Method SP Request-URI SP RTSP-Version CRLF
RTSP-Version SP Status Code SP Reason Phrase CRLF
Request-Line
Status-Line
Field-name : field-value CRLF
Header](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamingmultimedia-210313154258/85/Streaming-multimedia-18-320.jpg)