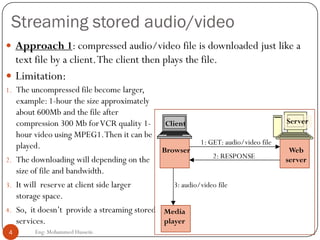
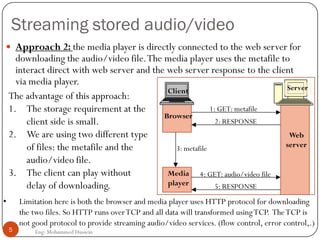
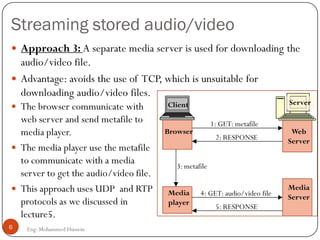
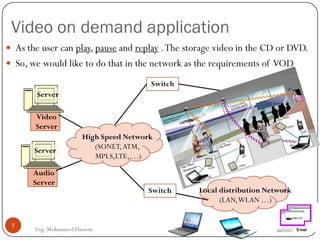
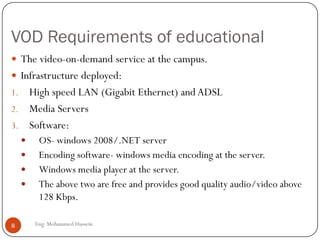
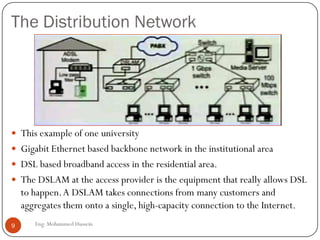
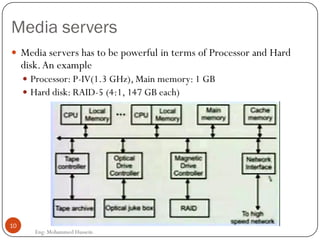
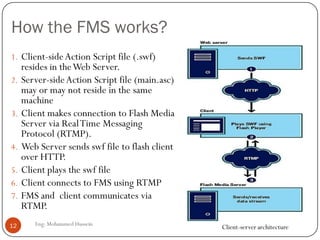
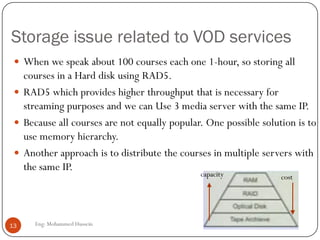
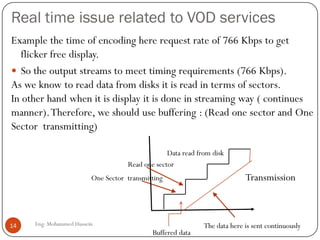
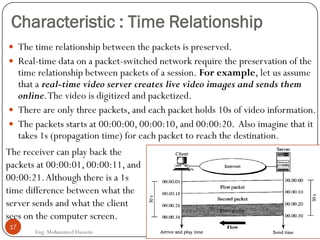
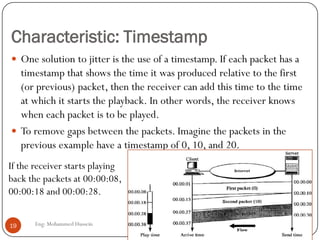
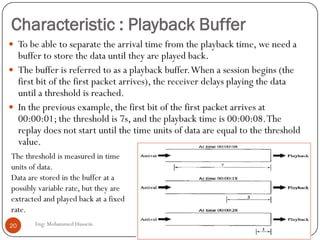
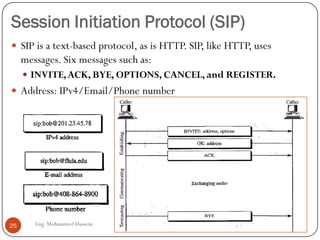
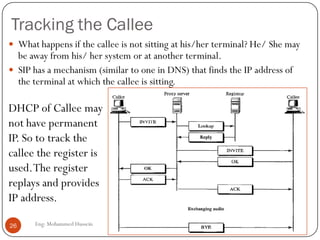
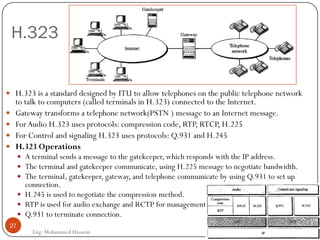
Mohammed Hussein's document discusses different types of multimedia services including streaming stored audio/video, streaming live audio/video, and interactive real-time audio/video. It provides approaches to streaming stored audio/video files and discusses applications like video on demand. Characteristics of real-time interactive services are described such as time relationship, jitter, timestamps, playback buffers, and ordering. Applications like video conferencing and voice over IP are also summarized along with protocols used.