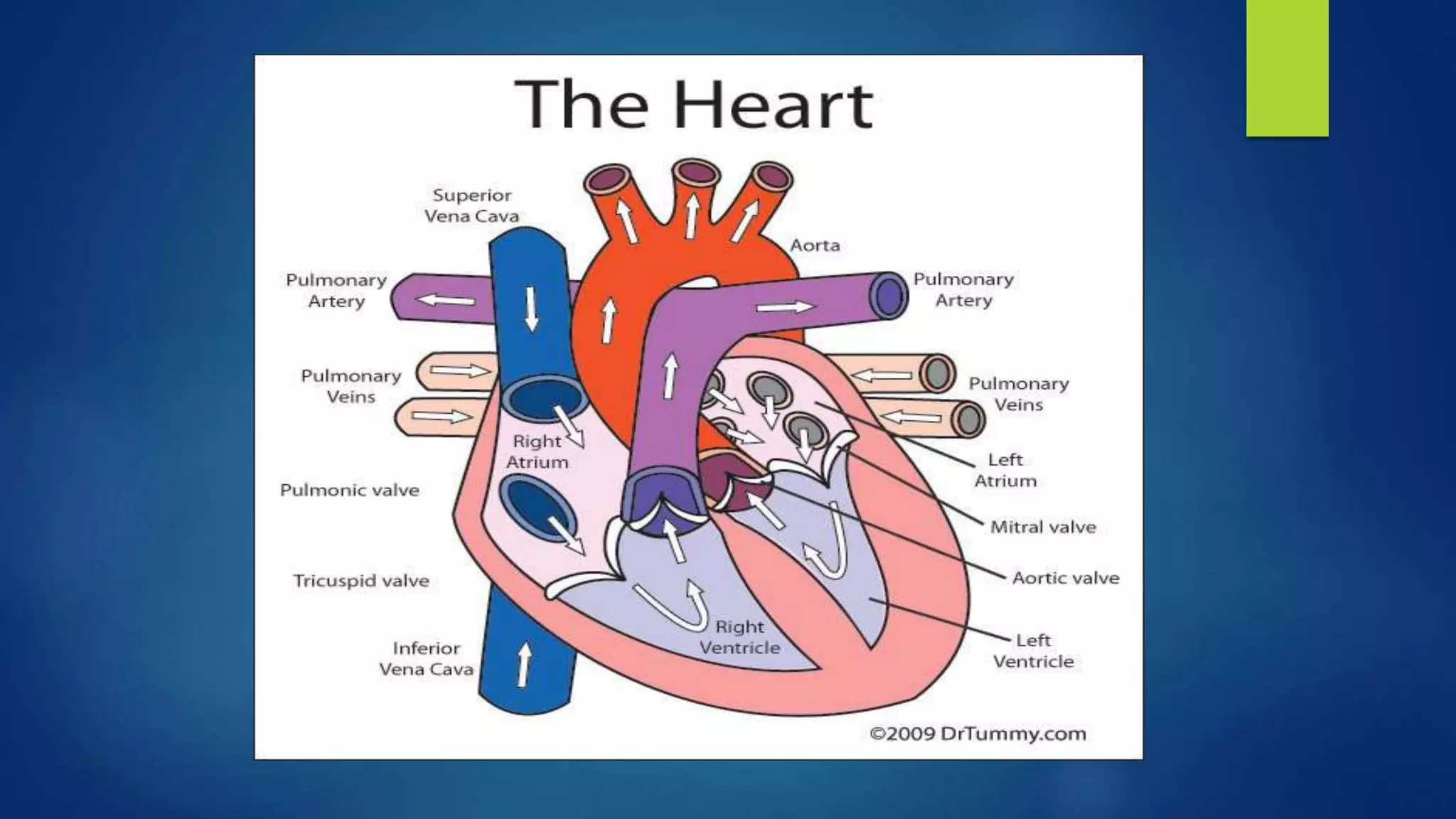
Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that leads to irregular heart rhythms, increasing the risk of heart failure, stroke, and death. There are three types: paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent, with various symptoms like dizziness and shortness of breath. Control methods include medications, cardioversion, ablation procedures, and the use of an atrial pacemaker to manage heart rhythms.