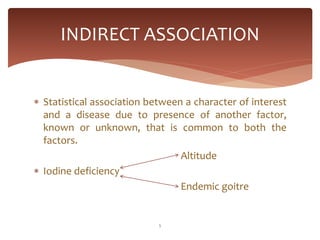
This document discusses the differences between association and causation. Association is when two variables occur together more often than chance, while causation means one variable directly causes the other. There are three types of associations - spurious associations which are not real, indirect associations where a third factor links two variables, and direct associations where one variable directly causes the other in either a one-to-one or multifactorial relationship. The Bradford Hill criteria are discussed as a way to judge causality, considering factors like temporal relationship, strength of association, specificity, consistency, and biological plausibility.