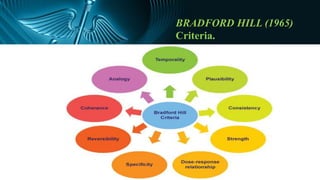
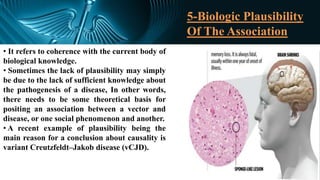
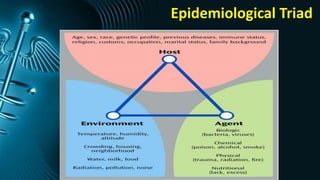
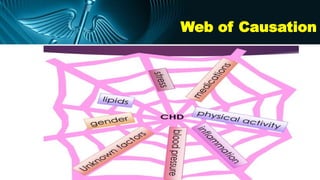
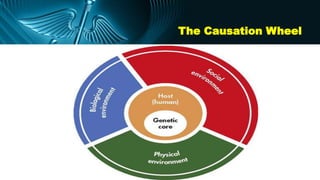
The document discusses various models of causation in epidemiology, including the epidemiological triad, the web, and component causes model. It elaborates on historical postulates for causation by Henle and Koch, as well as Hill's criteria for assessing causal relationships, emphasizing factors such as temporal association, strength of association, and biological plausibility. The text outlines the complexities of establishing causality and the considerations like bias, confounding, and interaction that influence causal inference.

![Evidence for causal Relationship
In 1840, Henle proposed postulates for causation that were expanded by Koch in the
1880s.The postulates for causation were as follows:
1. The organism is always found with the disease.
2. The organism is not found with any other disease.
3.The organism, isolated from one who has the disease, and cultured through several
generations, produces the disease (in experimental animals).
Koch added that “Even when an infectious disease cannot be transmitted to animals, the
‘regular’ and ‘exclusive’ presence of the organism [postulates 1 and 2] proves a causal
relationship.”
These postulates, though not perfect, proved very useful for infectious diseases. However,
as apparently non infectious diseases assumed increasing importance toward the middle of
the 20th century, the issue arose as to what would represent strong evidence of causation
in diseases that were generally not of infectious origin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/causationinepidemiology-200622082744/85/Causation-in-epidemiology-6-320.jpg)