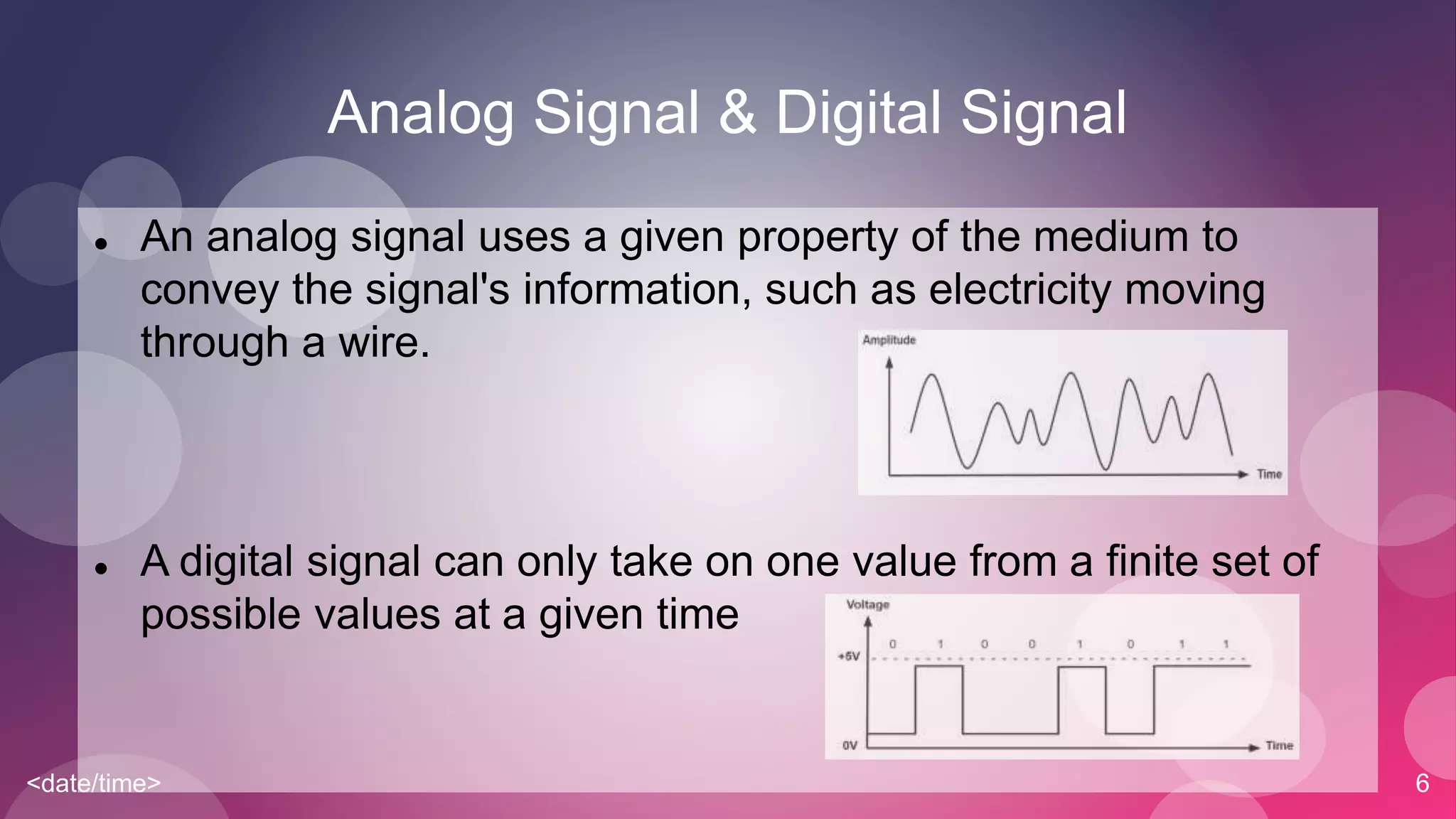
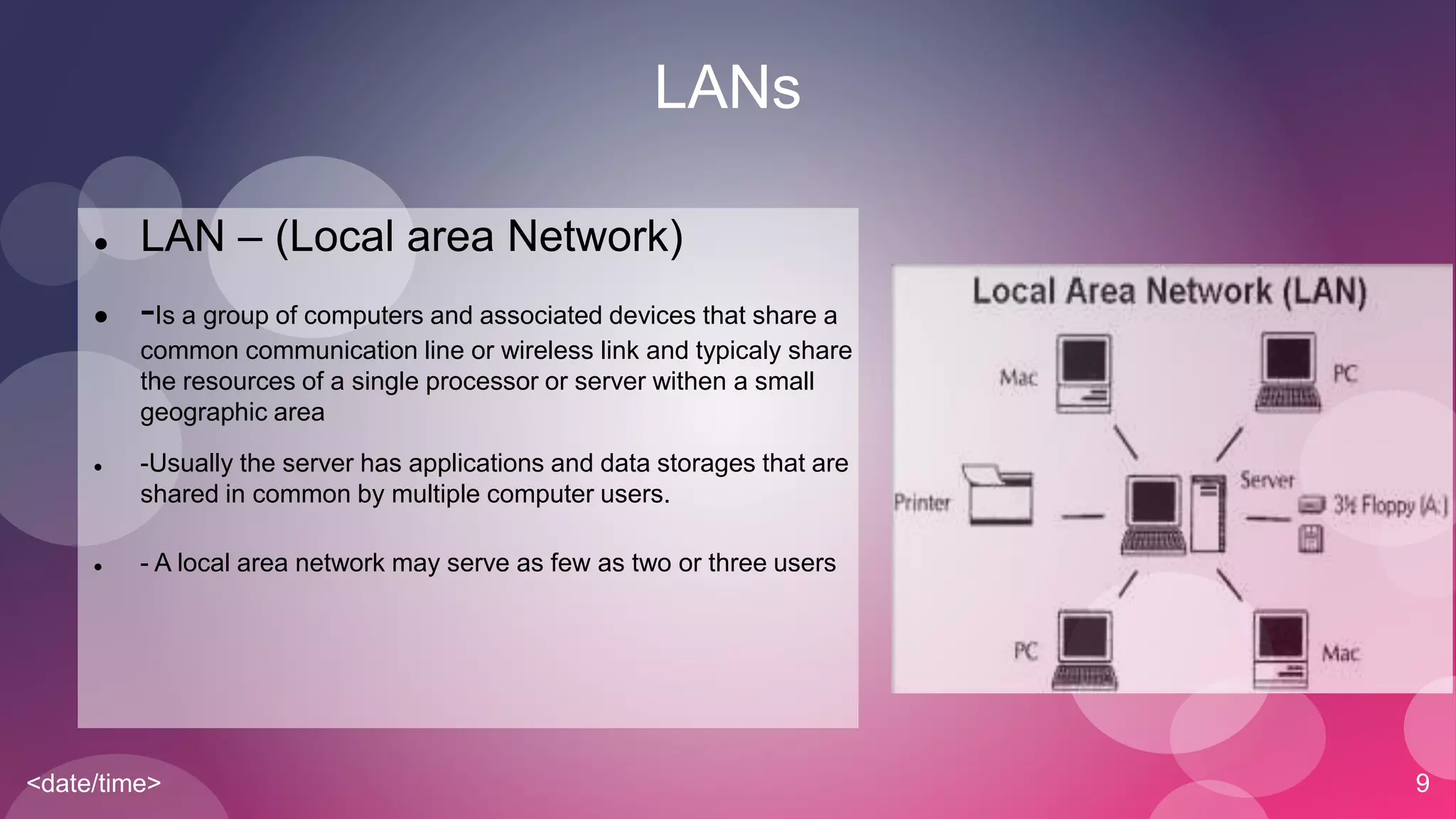
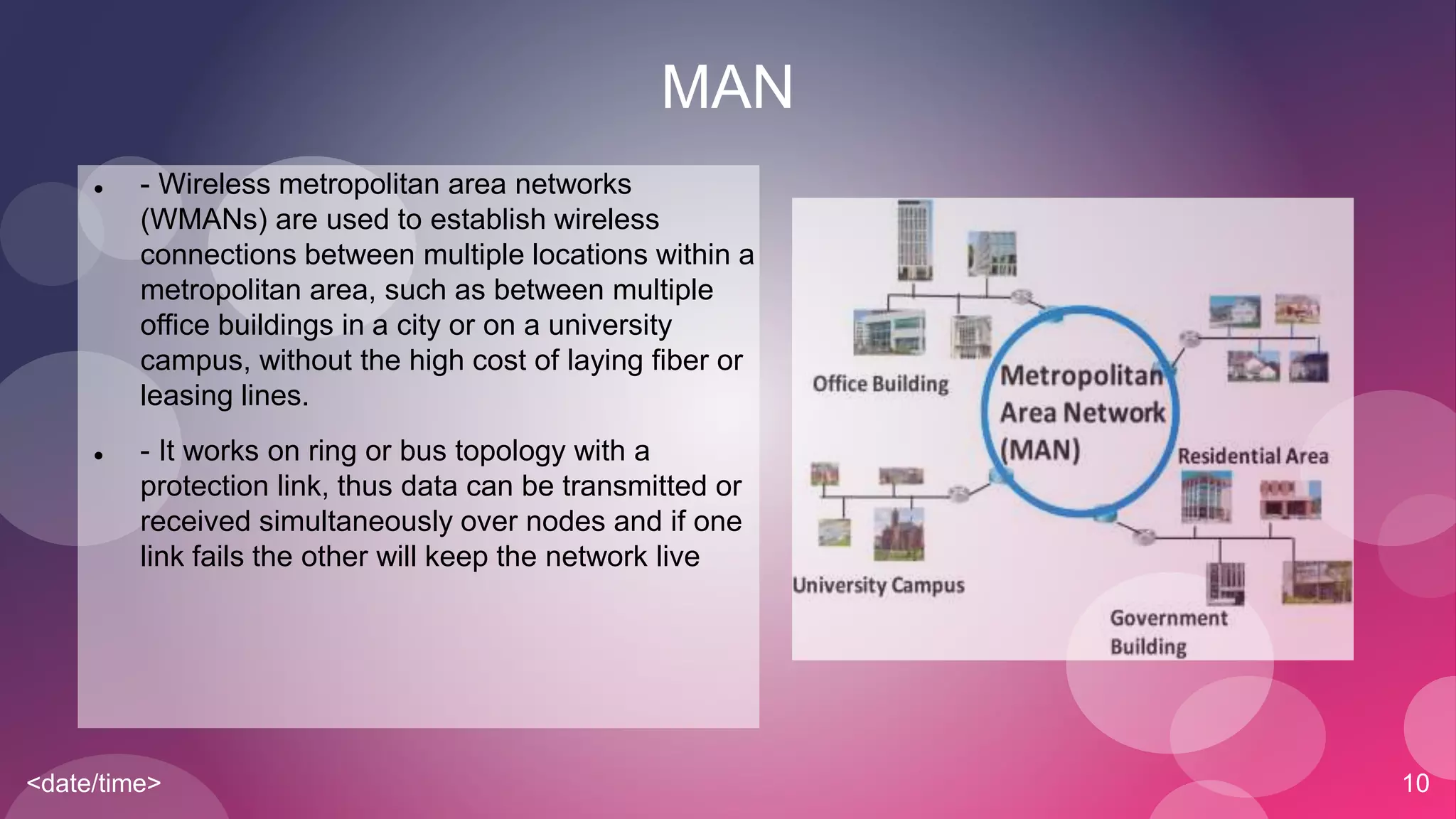
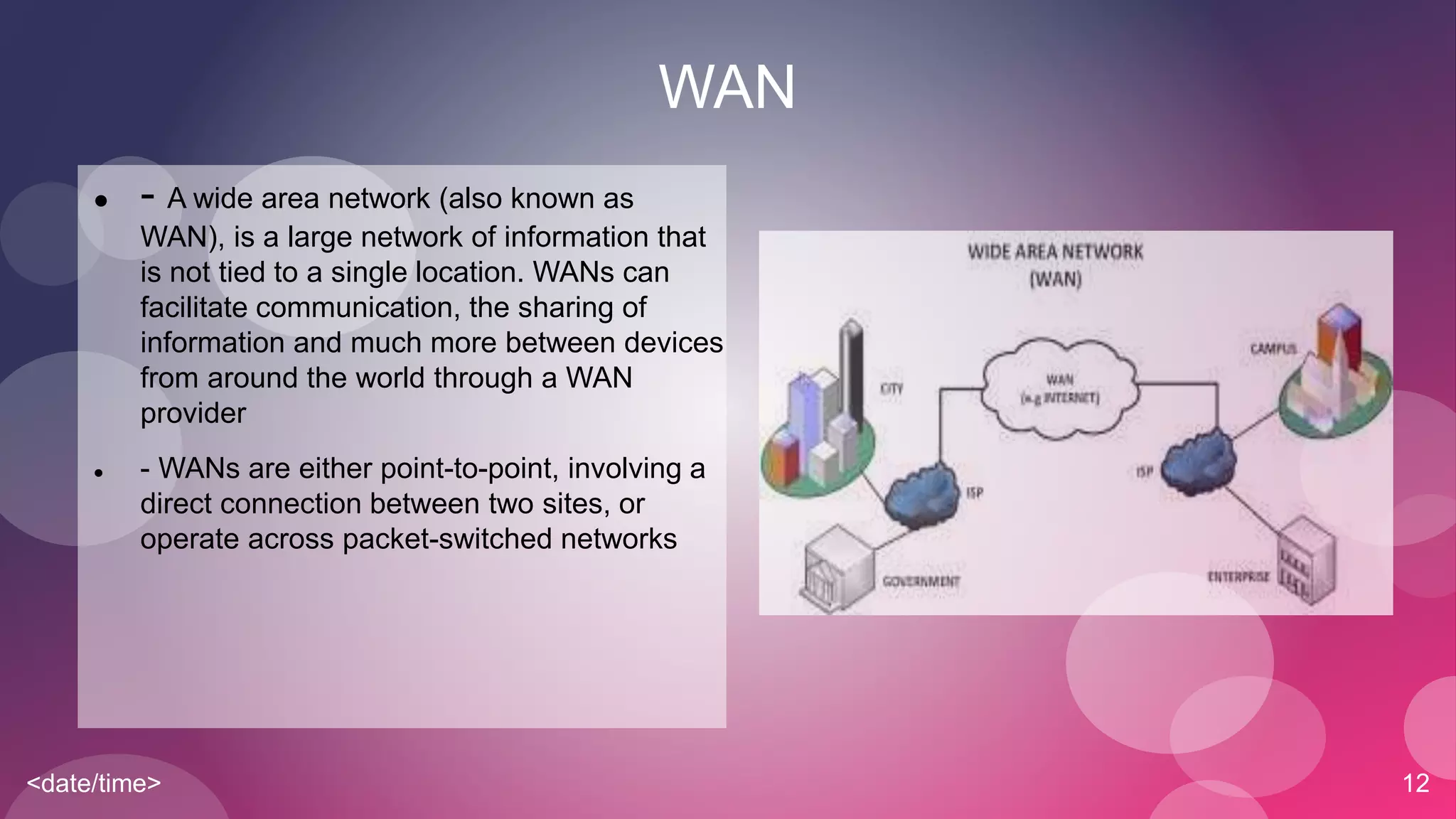
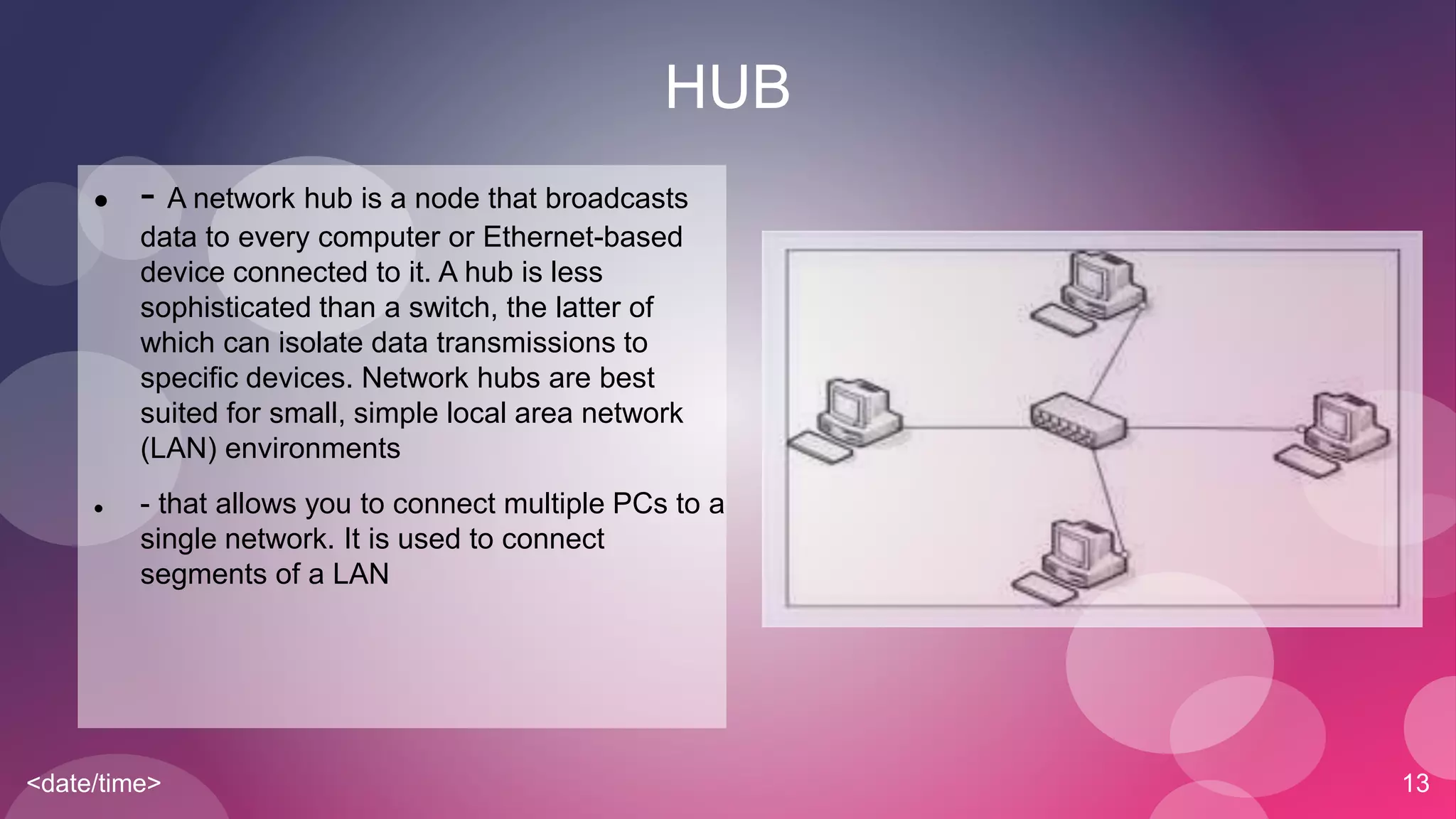
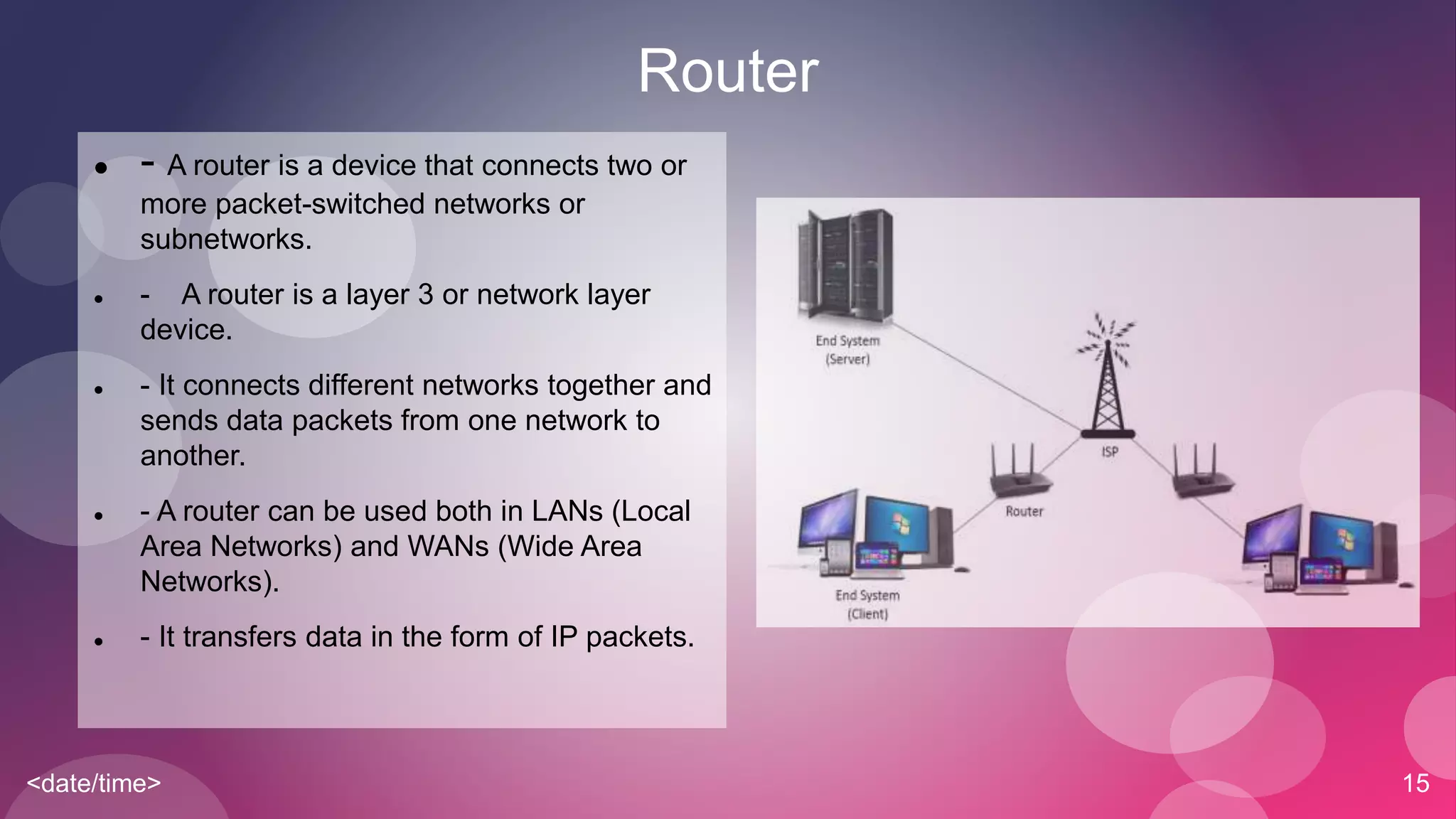
The document provides an overview of basic networking concepts including simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex communication modes, analog and digital signals, intranets and the internet, types of networks including LAN, MAN, WAN, and CAN, common networking devices like hubs, switches and routers, and IP addressing. Each concept is defined in 1-2 sentences with examples given for clarification.