This document provides information about various topics related to computer networks:
- It defines hub, switch, router, bridge, and repeater components and their functions.
- It explains transmission modes like simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex.
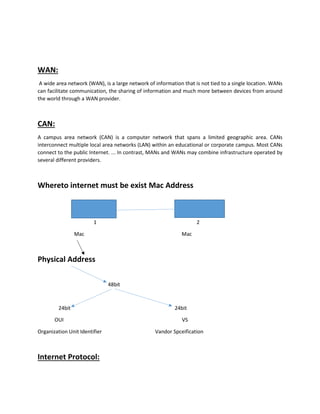
- It describes different types of computer networks including LAN, MAN, WAN, and CAN.
- It provides details about IP addressing and IP address classes.