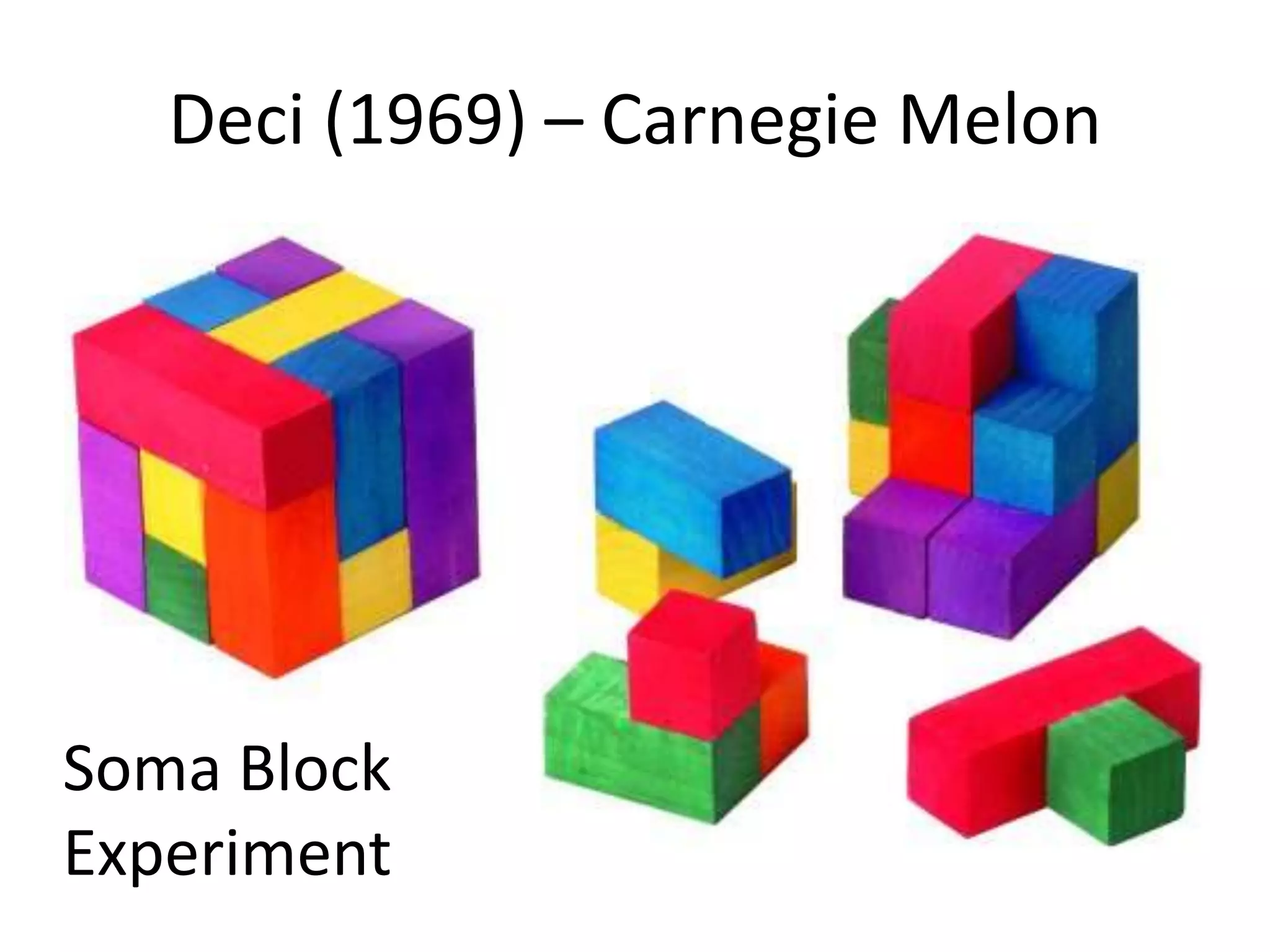
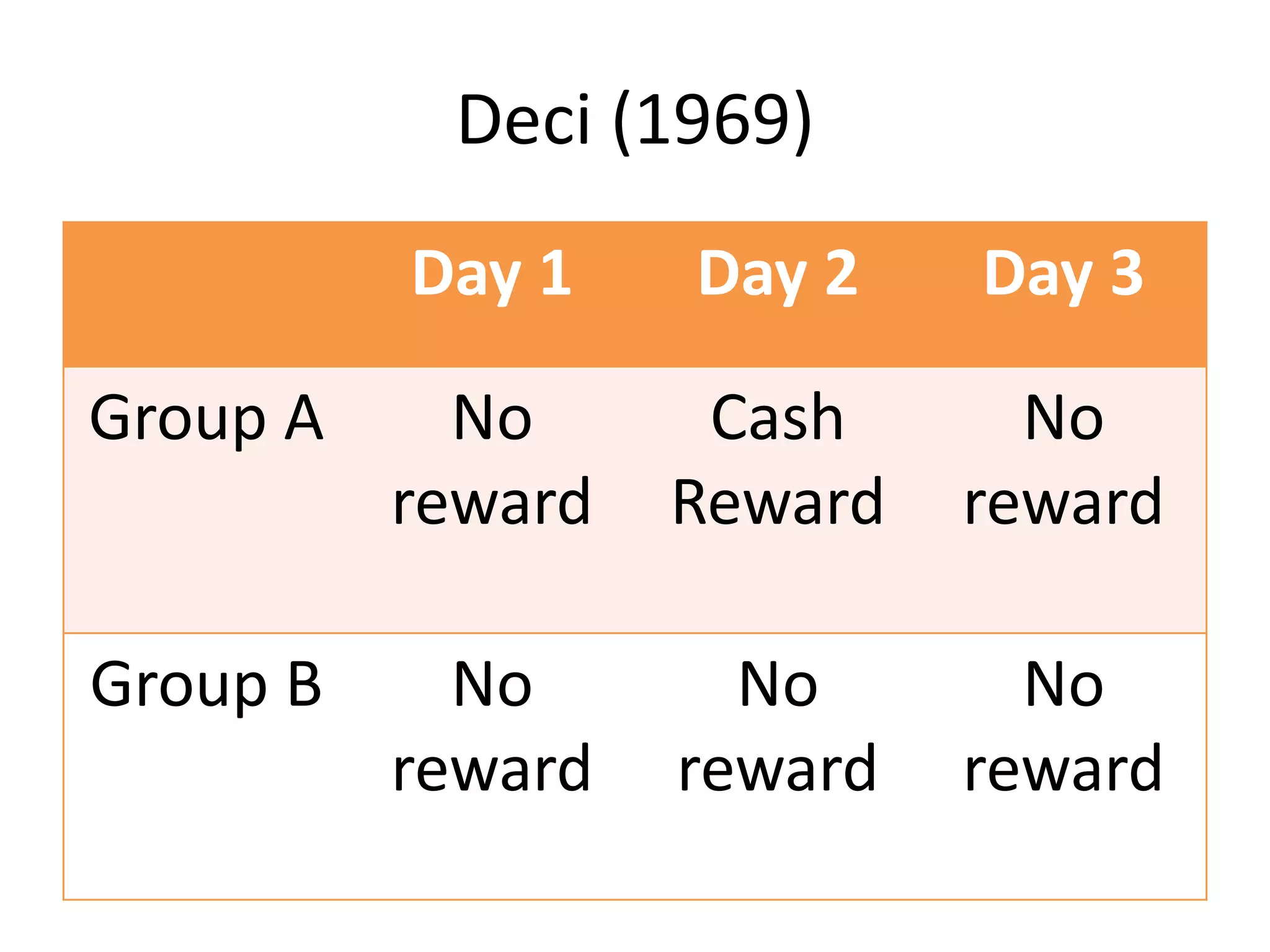
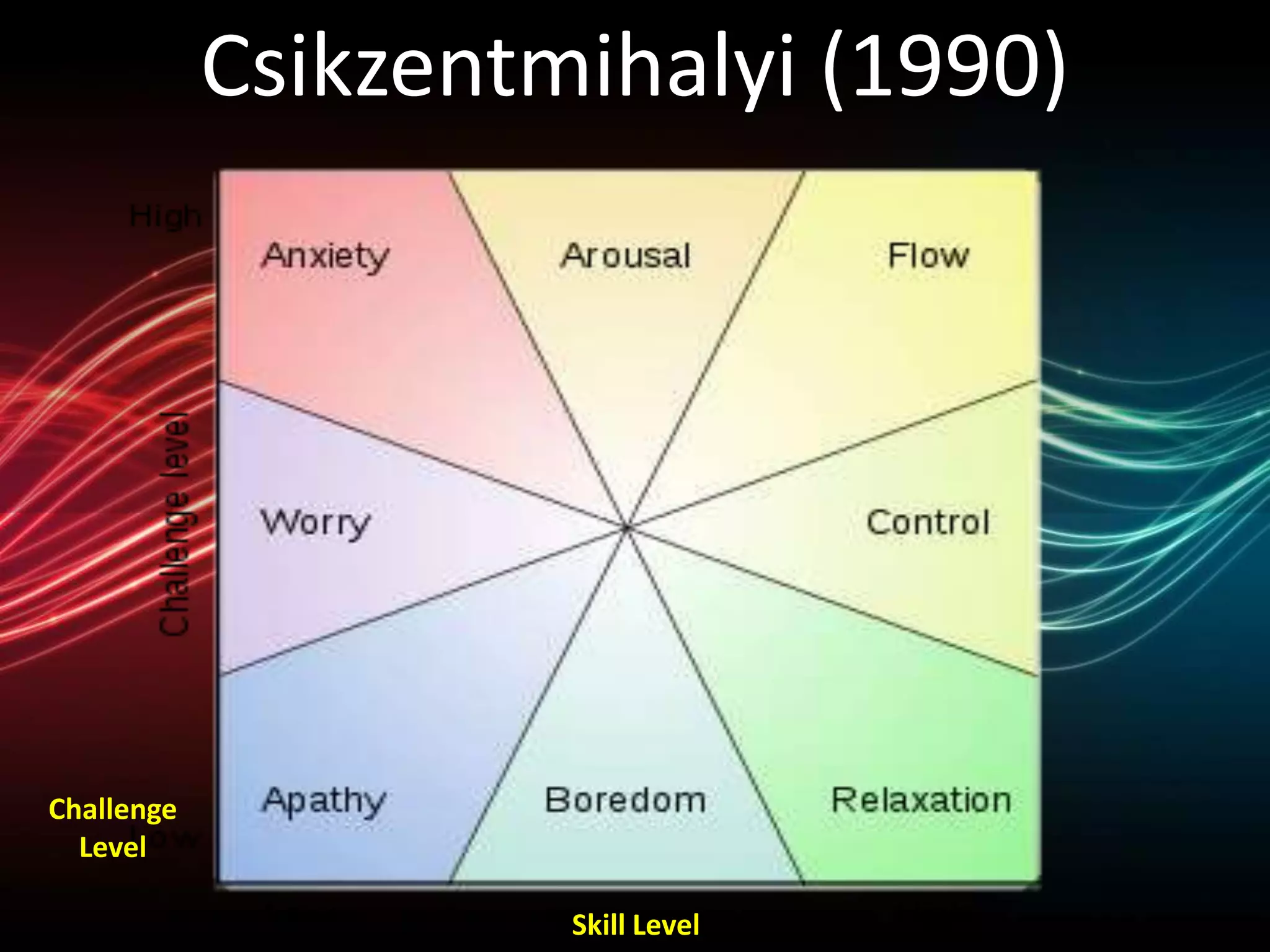
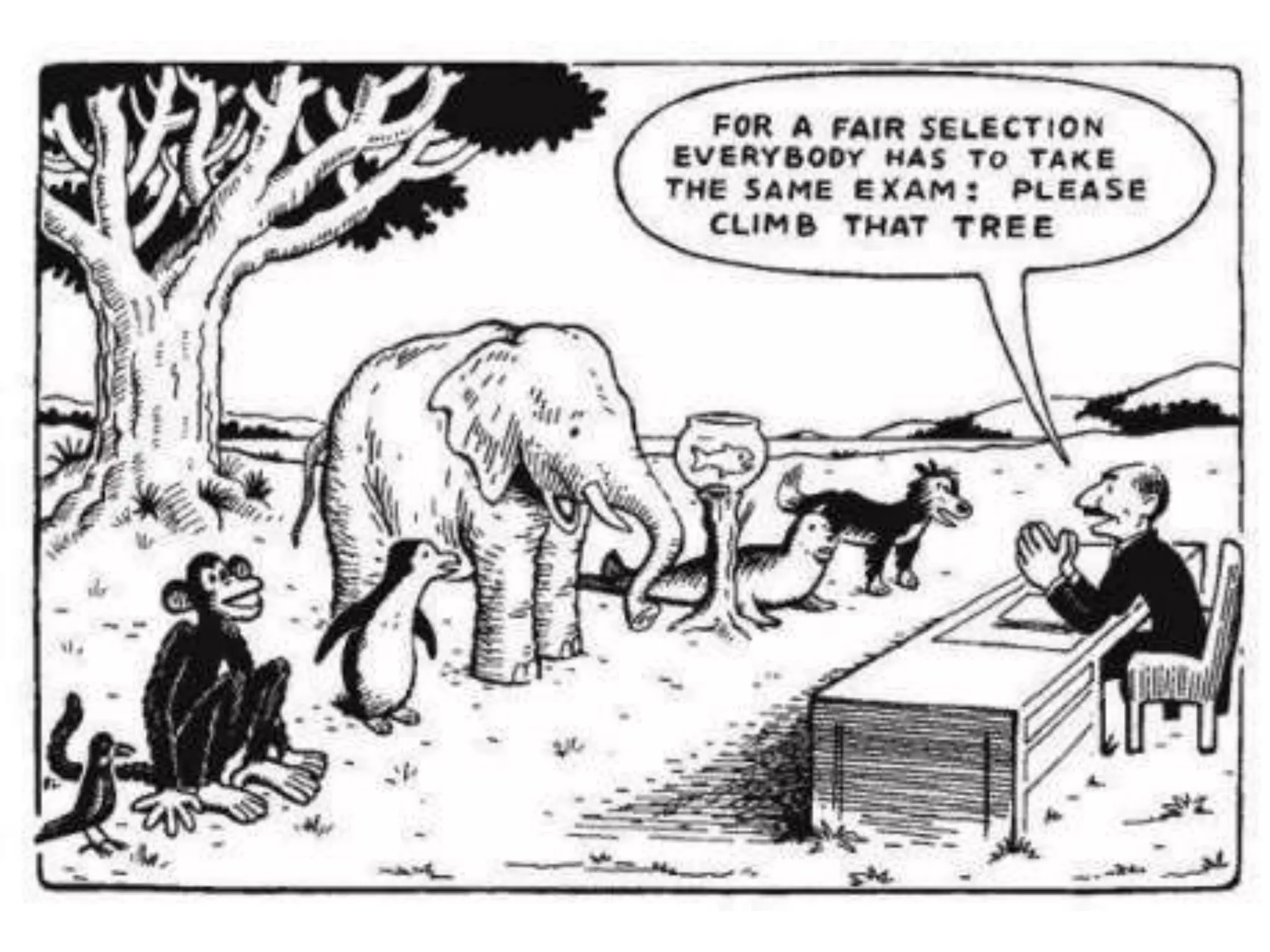
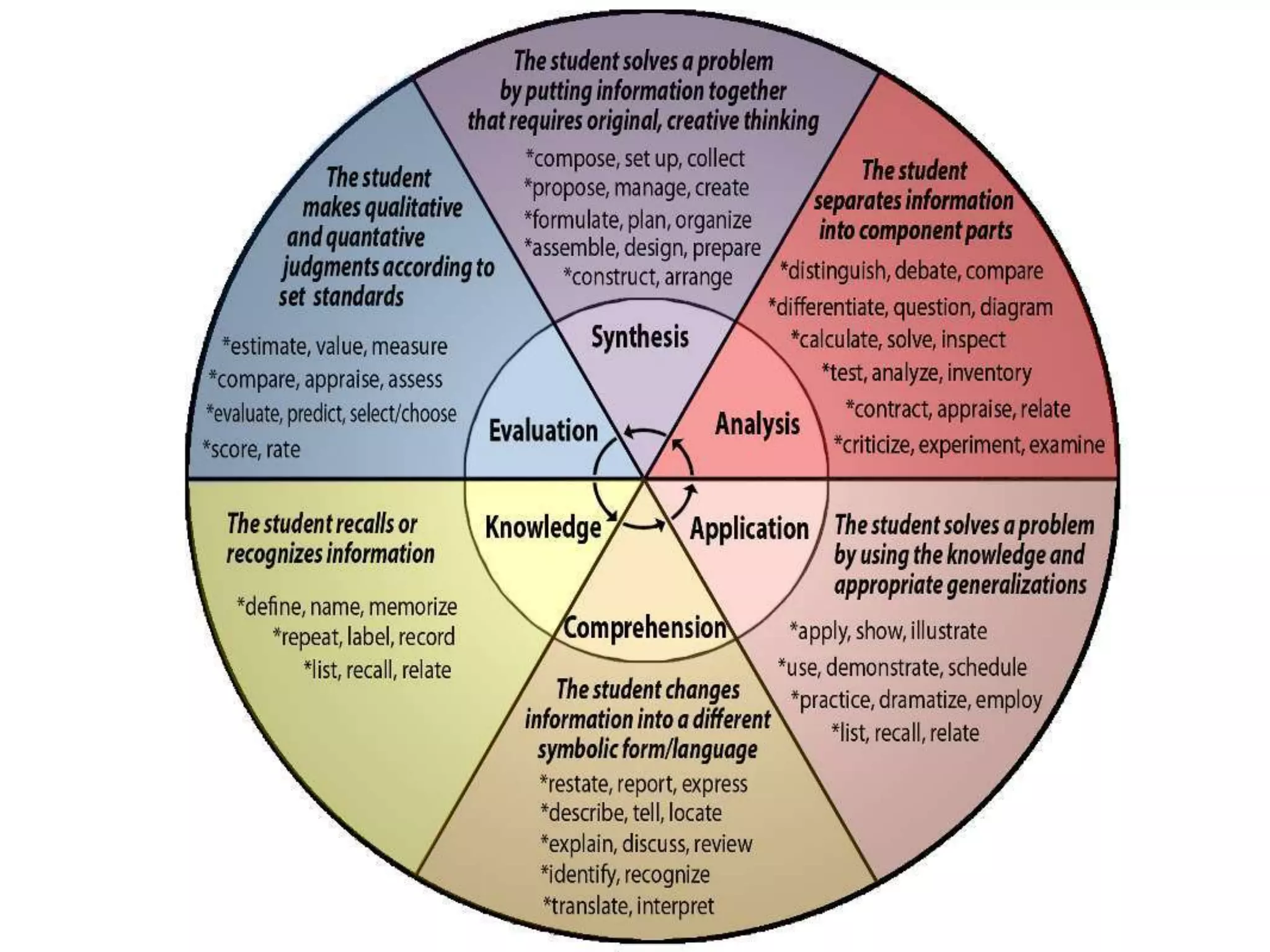
The document contains information about assessment and motivation from various researchers and experts. It discusses how intrinsic motivation can be undermined by extrinsic rewards, and that assessment should focus on helping students improve rather than just achieving goals. Formative assessment, when done effectively with feedback, can substantially improve student achievement according to researchers Black and William.