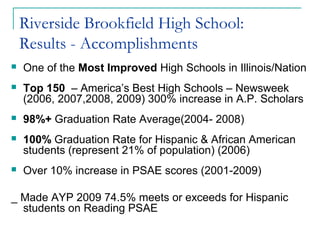
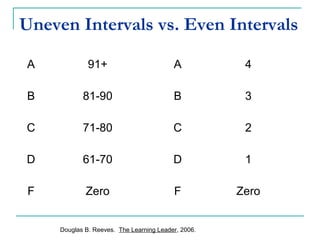
This document discusses strategies for motivating disengaged students. It begins by explaining common reasons students lack motivation, such as protecting their self-worth and not seeing relevance in their schoolwork. It then identifies practices that can help engage unmotivated students, such as building strong relationships through constructive feedback and focusing on their strengths, using formative assessment to promote a growth mindset, and making lessons more relevant by connecting them to real-world applications. The document advocates for collaborative practices like professional learning communities to help all students learn.