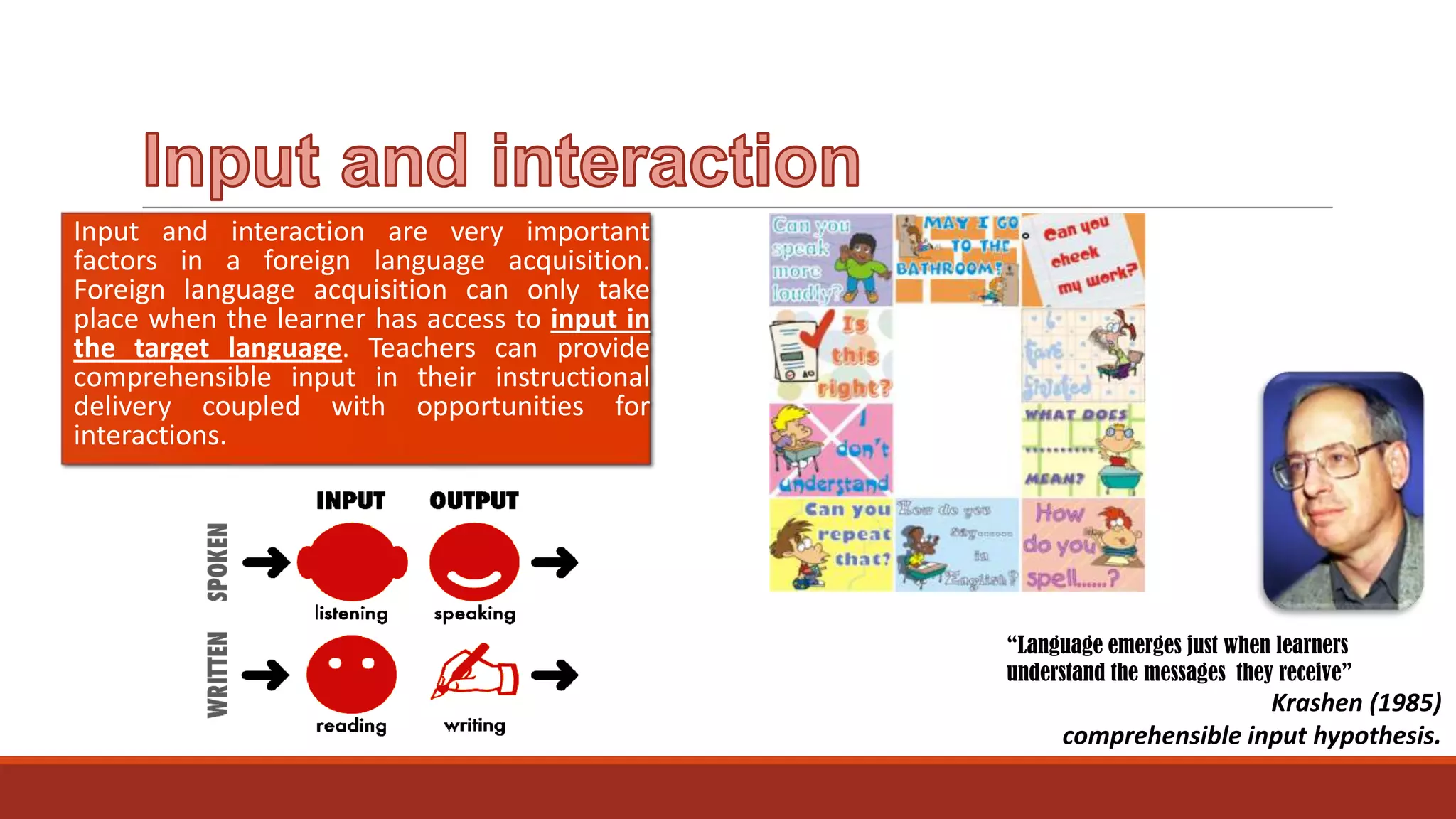
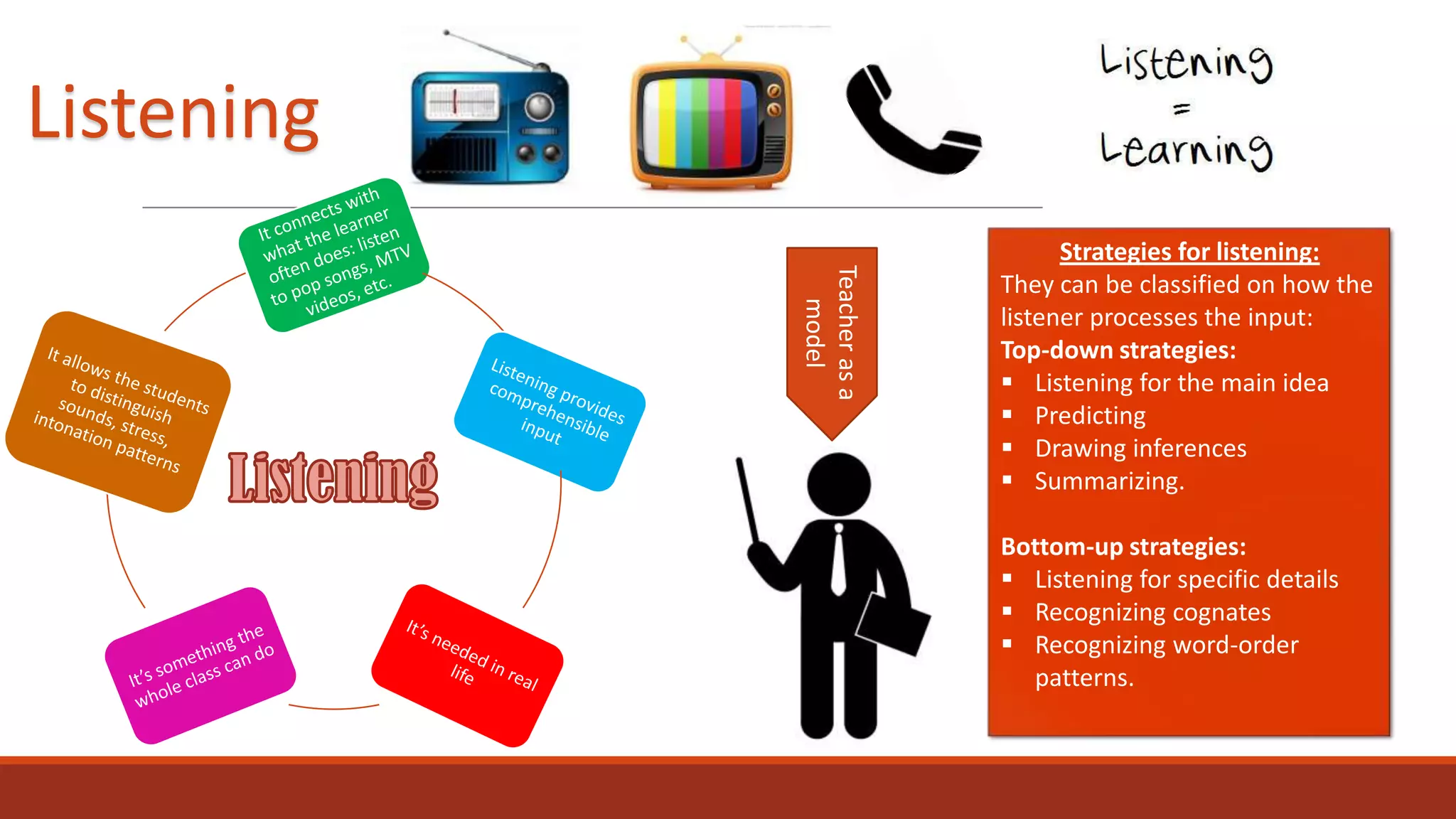
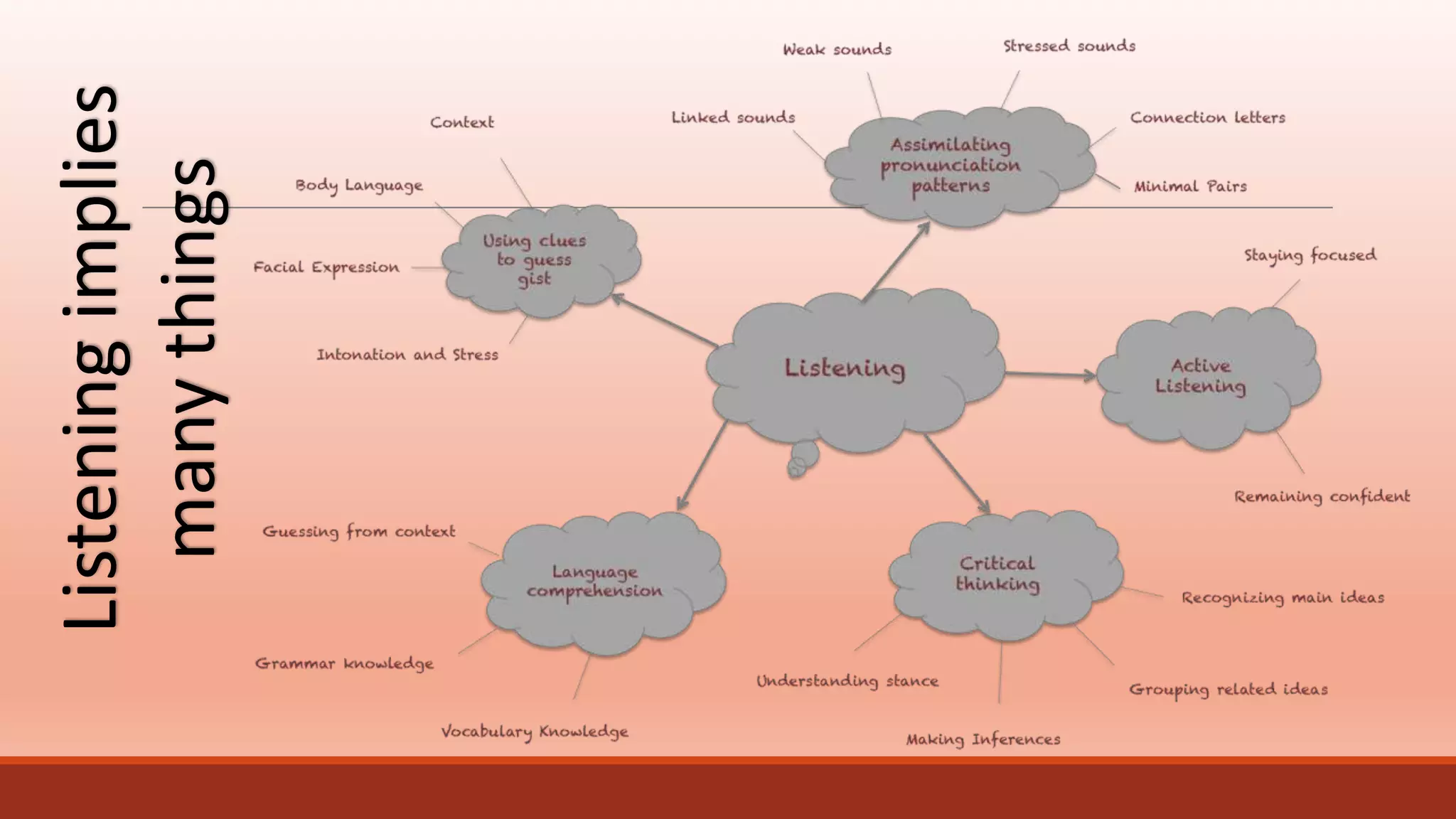
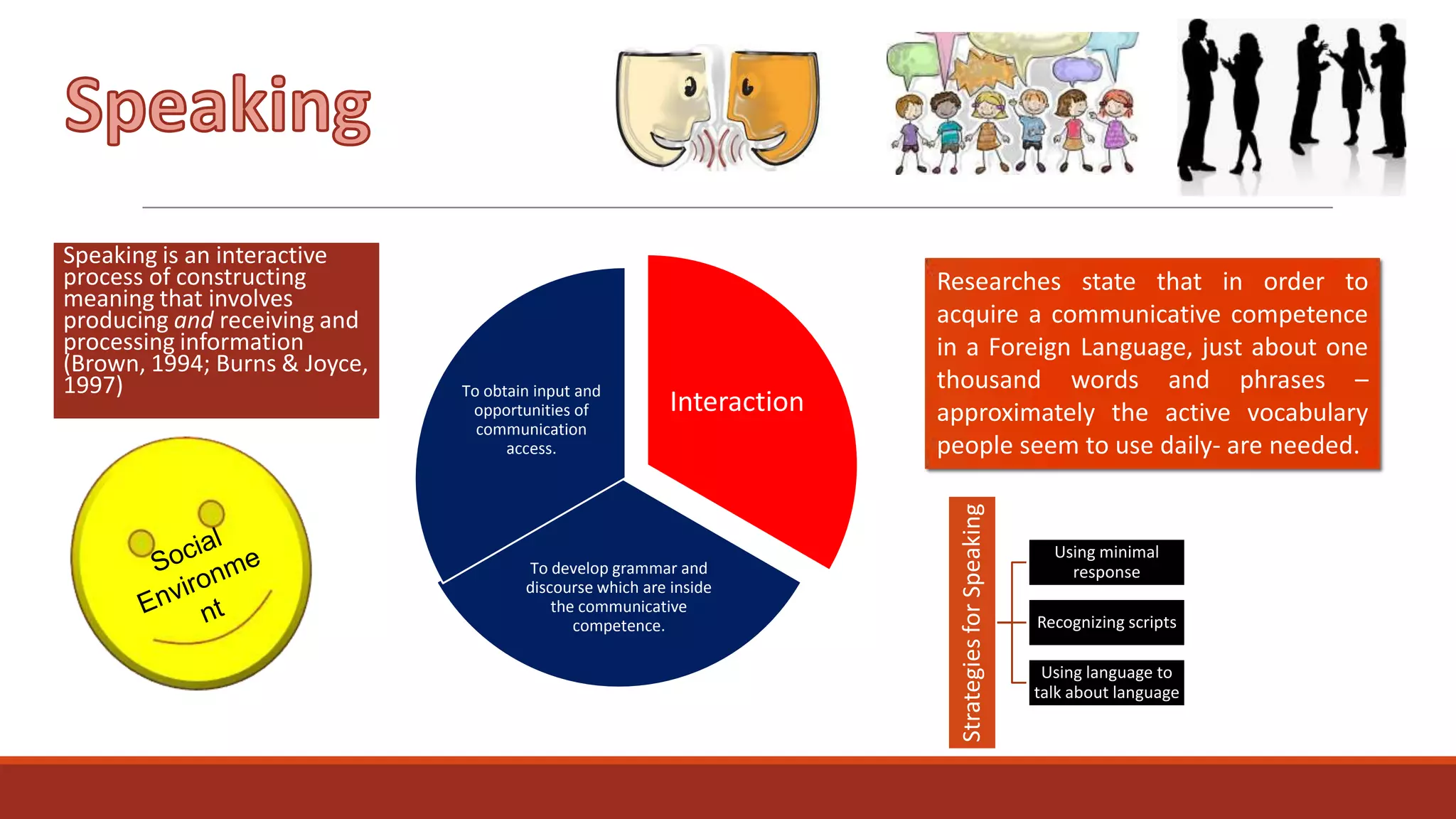
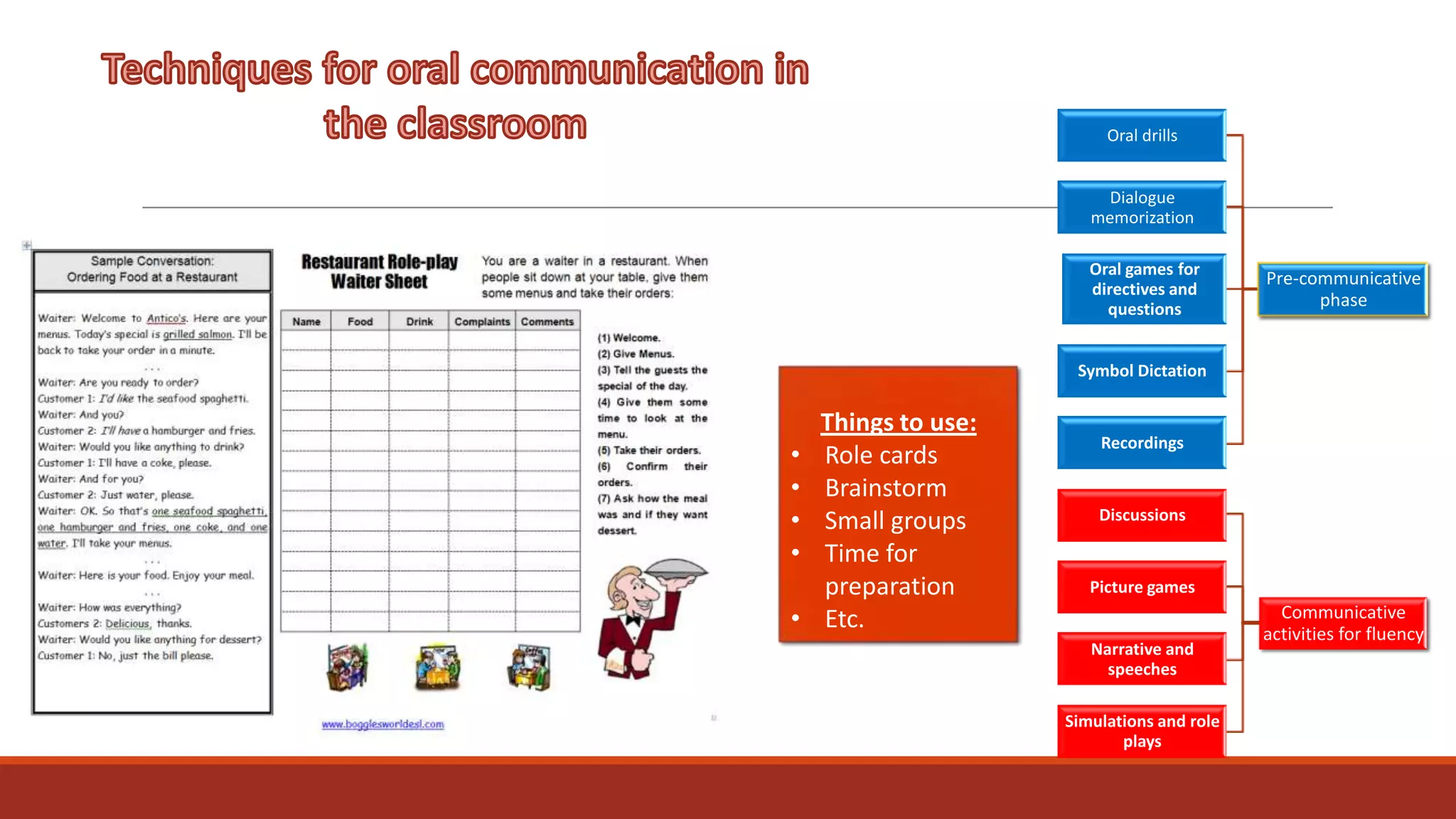
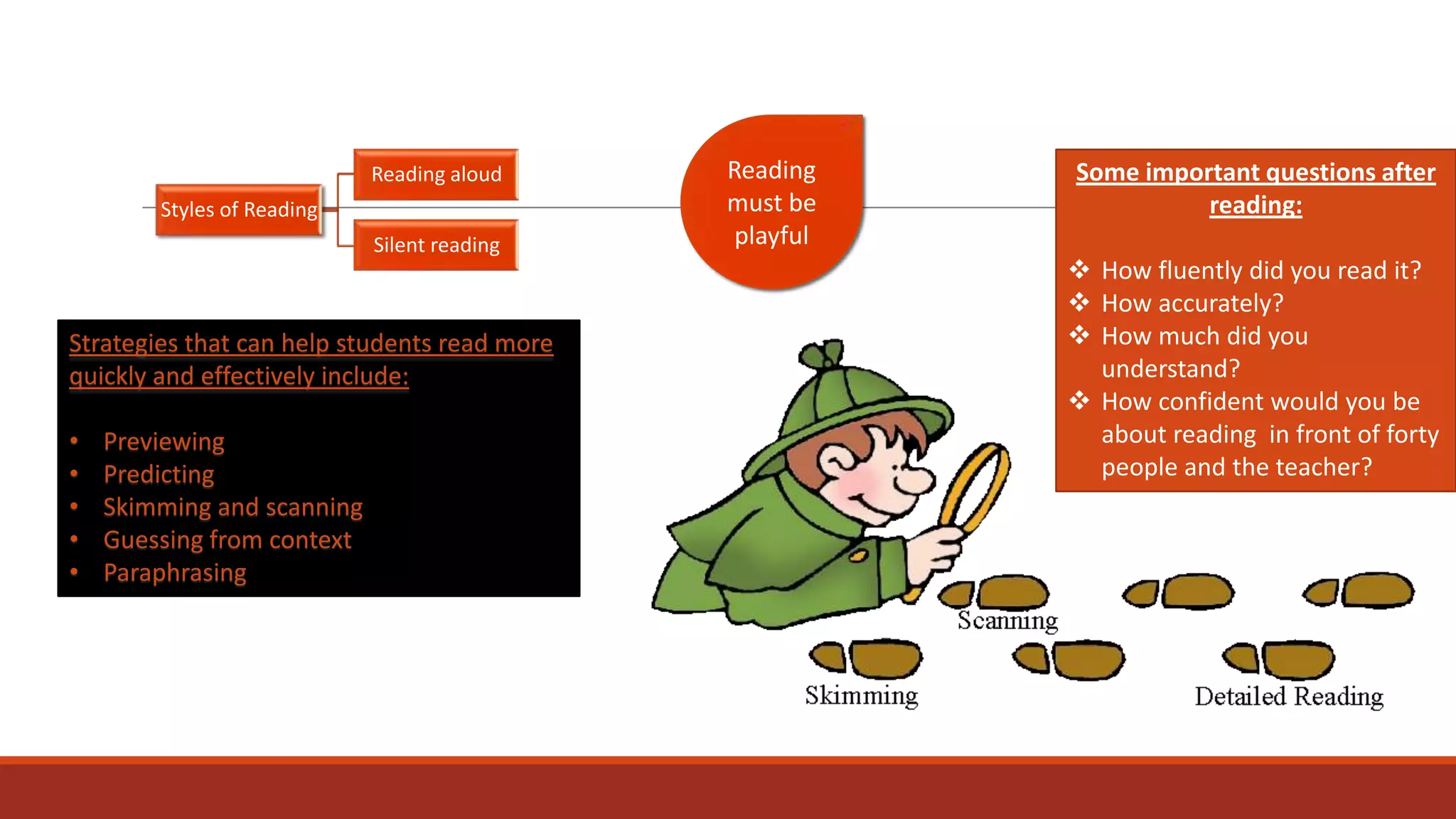
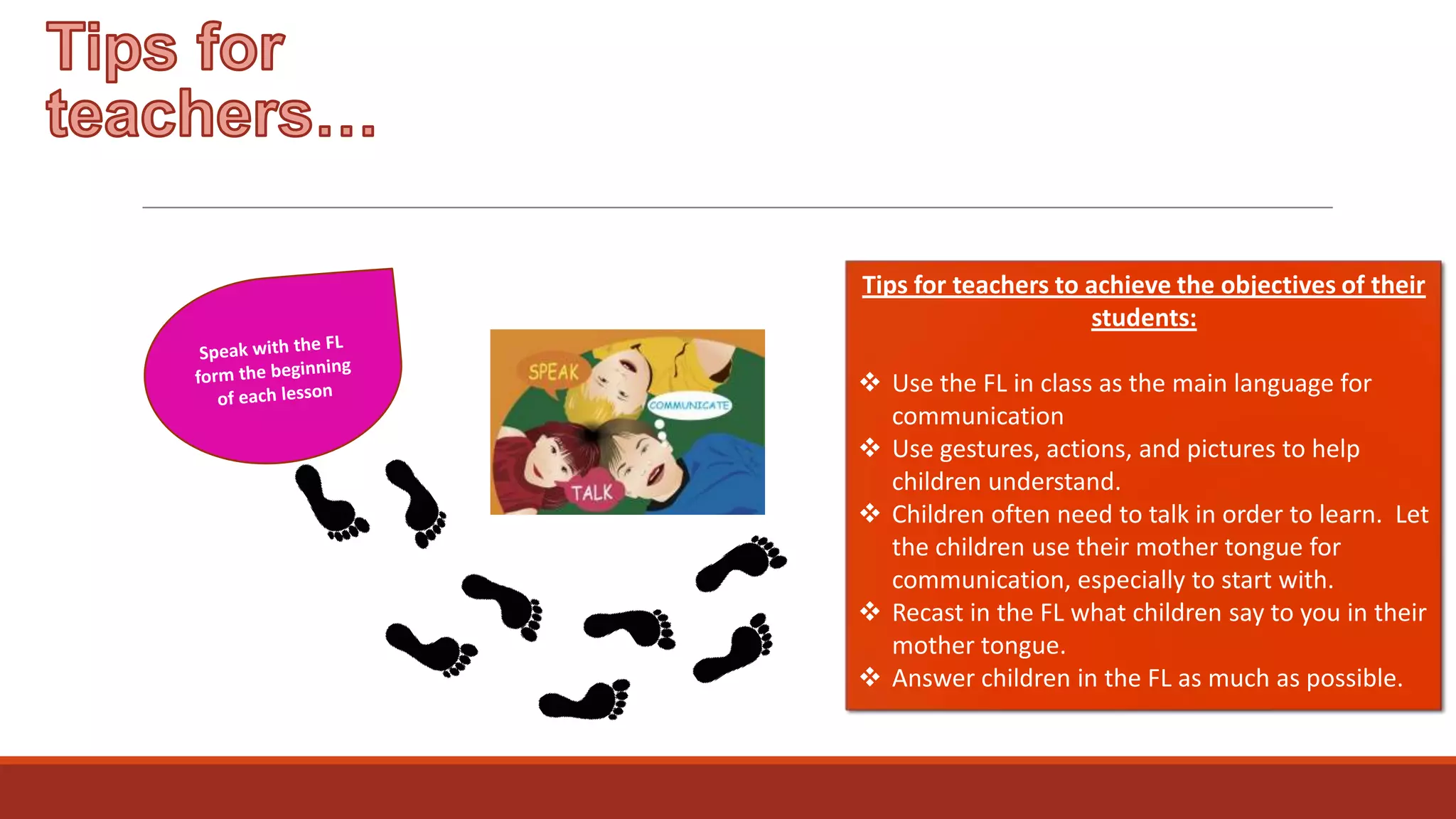
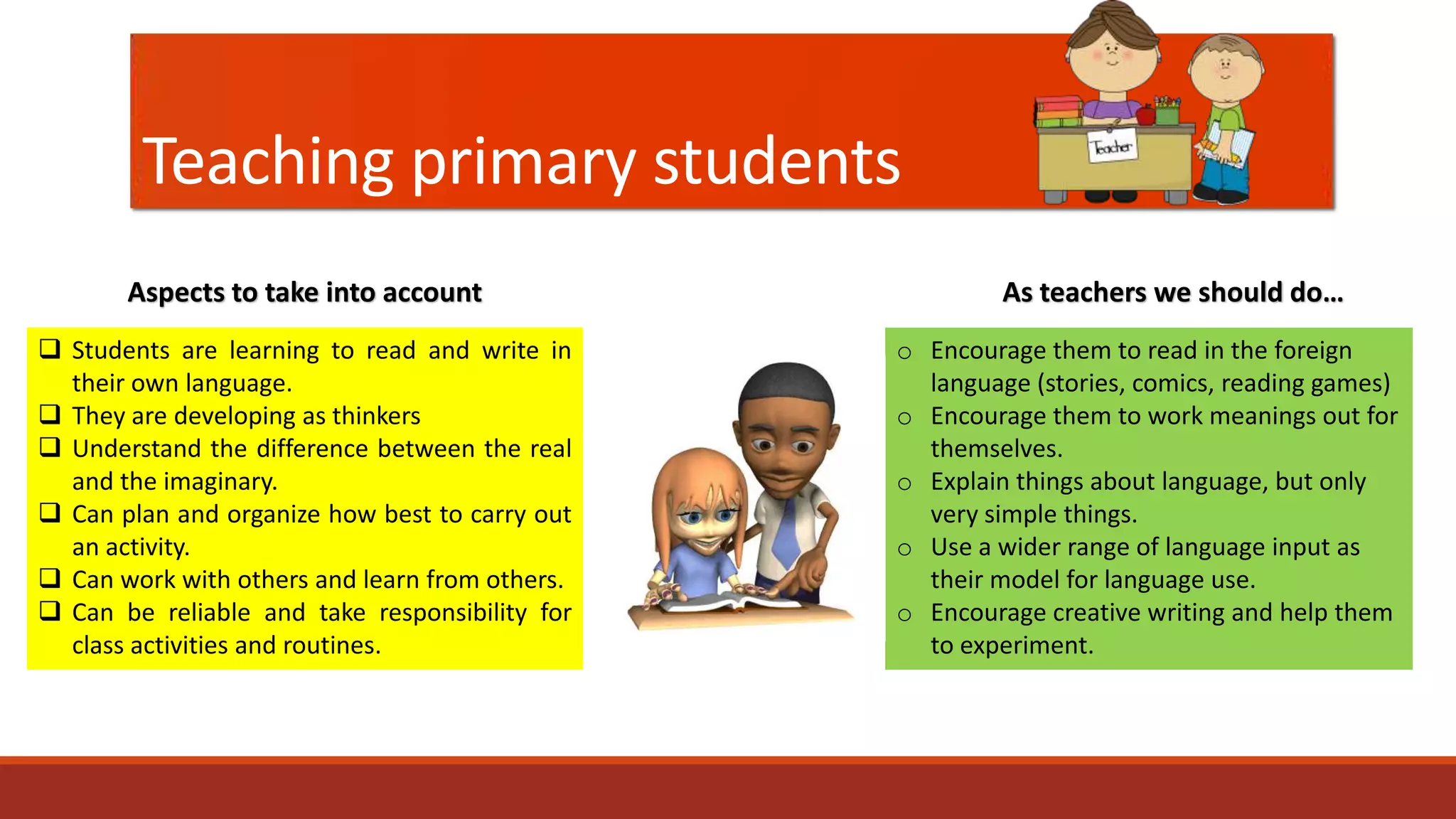
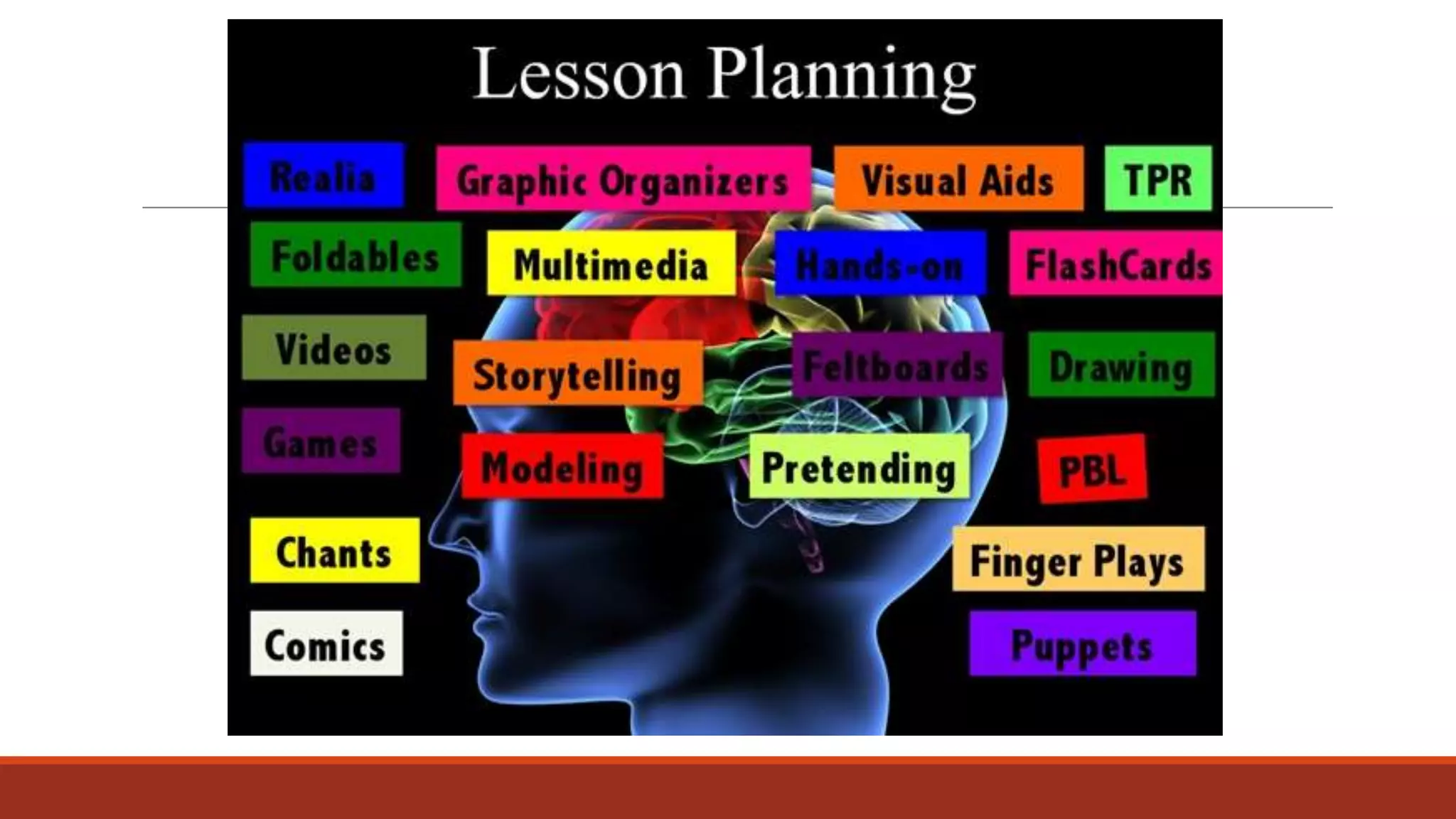
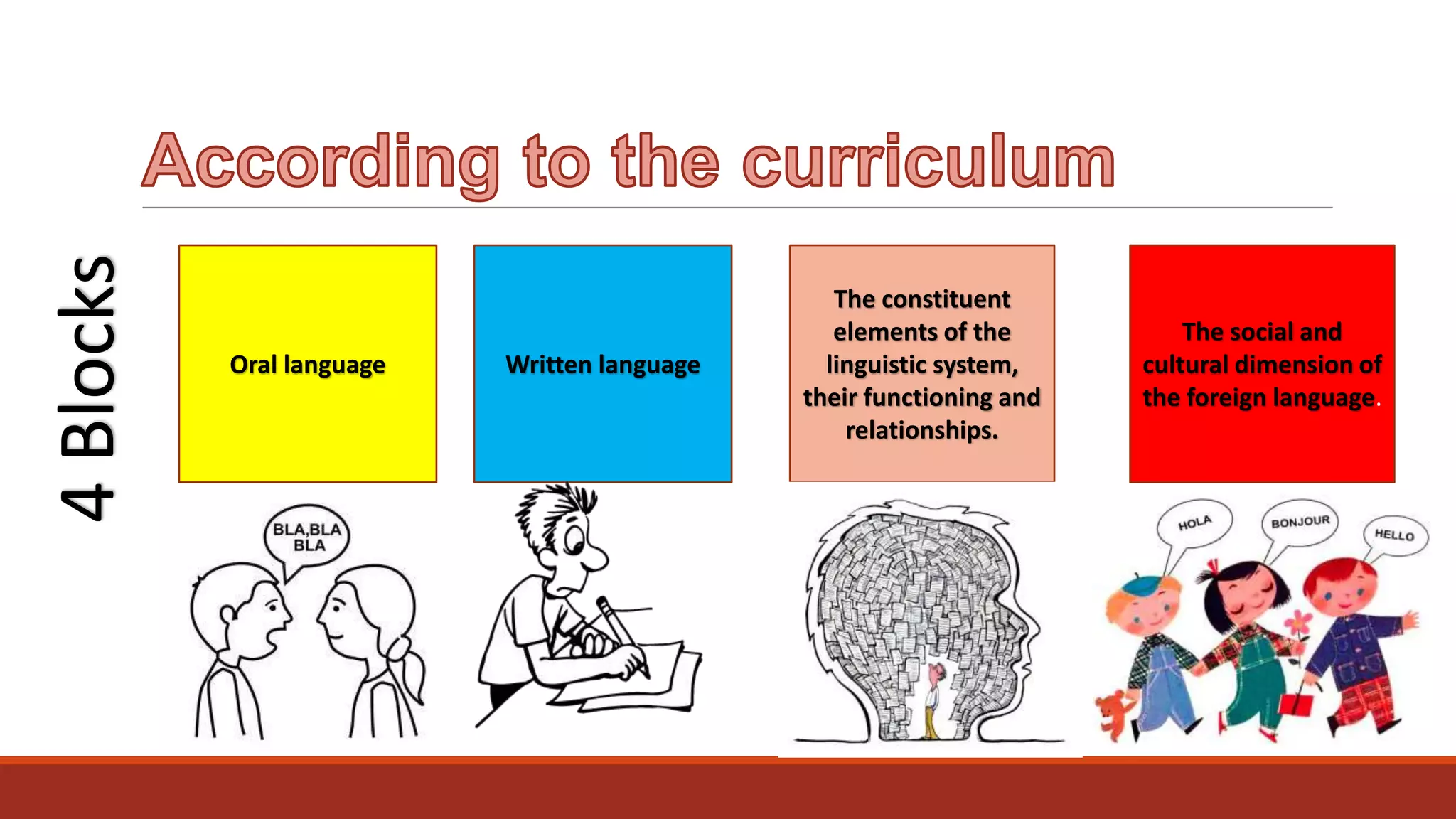
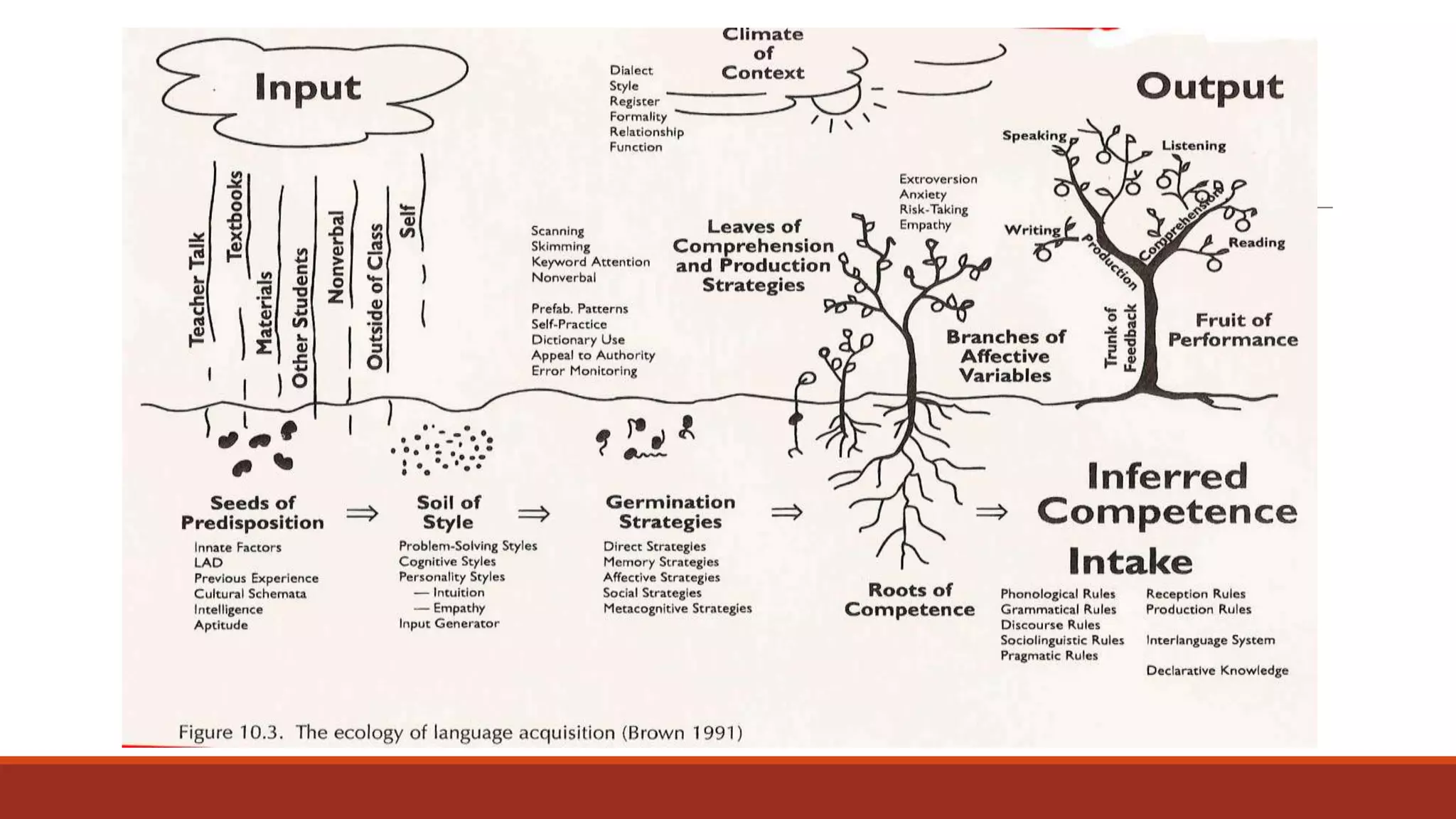
The document discusses the importance of preparing students for a multicultural and multilingual world through foreign language acquisition, emphasizing the development of positive attitudes towards different cultures. It highlights various teaching strategies and methodologies to facilitate language learning, including the significance of comprehension, interaction, and motivation in acquiring language skills. Additionally, it offers insights into effective pedagogical practices for listening, speaking, reading, and writing in a foreign language.